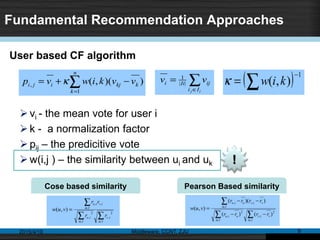
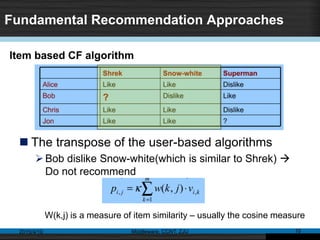
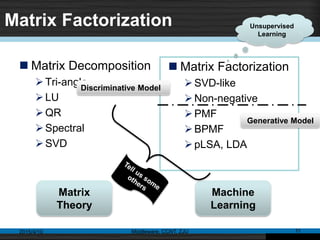
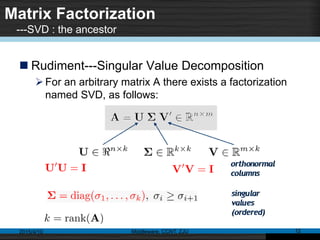
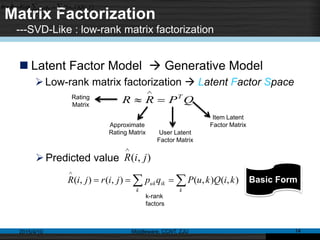
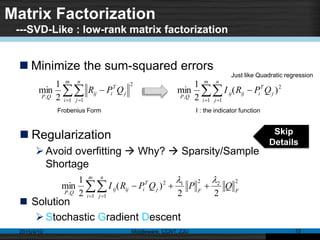
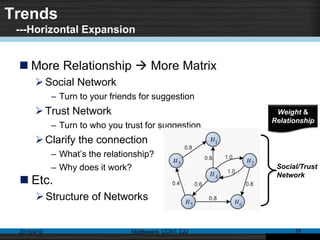
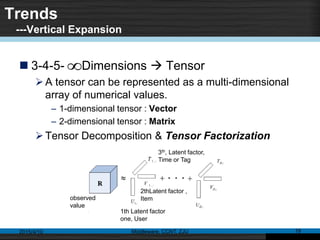
This document discusses social recommender systems. It begins by noting the large size of major social media sites and how recommender systems can help with information overload on these sites. It then discusses how recommender systems are based on principles of word-of-mouth recommendations and collaborate filtering. Several fundamental recommendation approaches are described, including collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, and hybrid methods. Matrix factorization techniques like singular value decomposition (SVD) are also covered. The document concludes by discussing trends in expanding recommender systems to incorporate more relationship data and higher-dimensional tensor models.