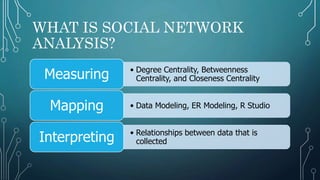
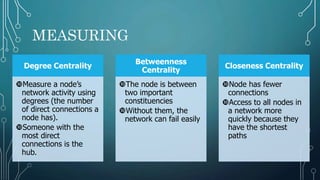
This document discusses social network analysis. It describes social network analysis as evaluating the location and grouping of actors in networks to understand the networks and participants. It explains that degree centrality, betweenness centrality, and closeness centrality are used to measure nodes' positions in a network. Entity relationship modeling and R Studio are mapping and analysis tools used to import, observe relationships, and analyze network data.