- Social exchange theory proposes that social behavior results from a cost-benefit analysis where people aim to maximize rewards and minimize costs in relationships. Costs involve things like time and effort while rewards include friendship and support.
- The theory was introduced by George Homans in 1958 and views human relationships as formed through subjective evaluations of alternatives based on costs and benefits. It has been expanded on by other sociologists like Frazer, Malinowski, and Homans himself.
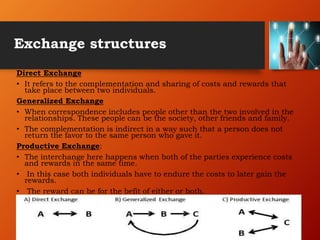
- Key concepts include direct and generalized exchange, rewards and costs, and rules of reciprocity and negotiation that govern exchanges between parties in relationships. The theory provides a framework for understanding relationship development and outcomes based on subjective worth calculations.