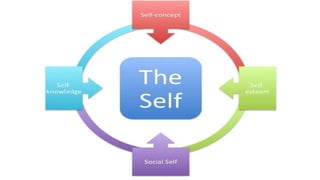
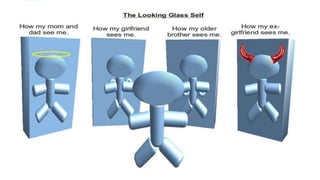
The document discusses the concept of self, including definitions and examples of self-concept, self-knowledge, self-esteem, and social self. It highlights the contributions of Charles Cooley, particularly his 'looking glass self' theory, which explains how self-perception is shaped by societal interactions and others' perceptions. The theory involves three steps: imagining one's appearance to others, their judgment, and the emotional impact of that judgment.