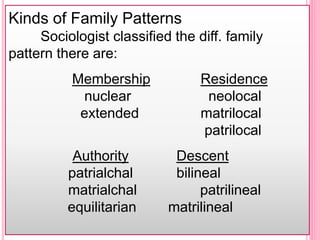
Social institutions are groups that perform social roles and socialize people. Key social institutions include families, governments, universities, and religious groups. Social institutions have several functions like simplifying social behavior, providing social roles, coordinating culture, and controlling behavior through shared expectations. The five major social institutions are family, education, religion, economics, and government. The family's functions include reproduction, socialization of children, and providing identity. Education's functions are transmitting culture, socializing children, and preparing them for social and economic roles. Religion's function is providing meaning and spiritual guidance.