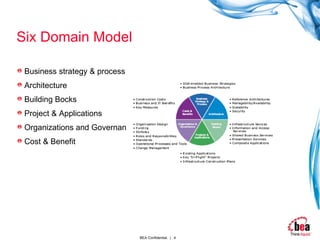
The document discusses the six domain model for SOA, which includes business strategy and process, architecture, building blocks, projects and applications, organization and governance, and cost and benefit. It provides details on each domain and how they are interrelated and important for a successful SOA implementation. Business strategy and process focuses on aligning IT with business goals through process optimization. Architecture discusses service-based and standard-based design. Cost and benefit outlines how benefits accumulate over time through reuse, standardization, and improved delivery capabilities.







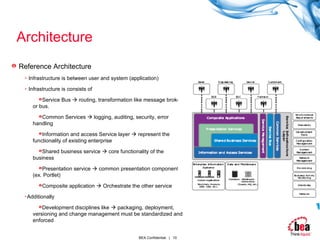
![Architecture Enterprise Focus In indivisual business project , it is hard to gain [ visibility and management ] of [ information or process ] was difficult. The organization group that not only focus on technology but also get governance, define, deploy , monitor and manage access to enterprise functionality is needed Business Focus In traditional IT, there were a lot of applications & interface from each different requirement . training overhead , over-reliance on specialist skills, duplicate data entry and lack of visibility and lack of control of overall business process. SOA aimed at providing functionality to the business at the level where business users conceive of the business , making easier for the user to understand, specify,test and operate on a daily basis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/soasixdomainmodelparti-123923937797-phpapp01/85/Soa-Six-Domain-Model-Part-I-9-320.jpg)