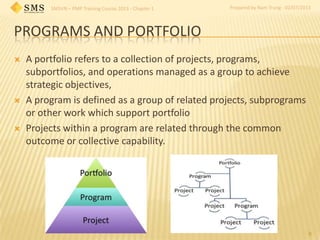
The document provides an introduction to an SMSVN PMP training course in 2013. It discusses the purposes of the course, which are to provide basic PMP knowledge and improve project management skills. The course consists of 15 sessions over 13 chapters and 2 exams held every Tuesday and Friday from 4-5pm. It also establishes ground rules for the class, including penalties for lateness and absence. Chapter 1 introduces key project management concepts like the project lifecycle, triple constraint of cost, time and scope, roles of project managers and stakeholders, and how enterprise environmental factors can influence projects.