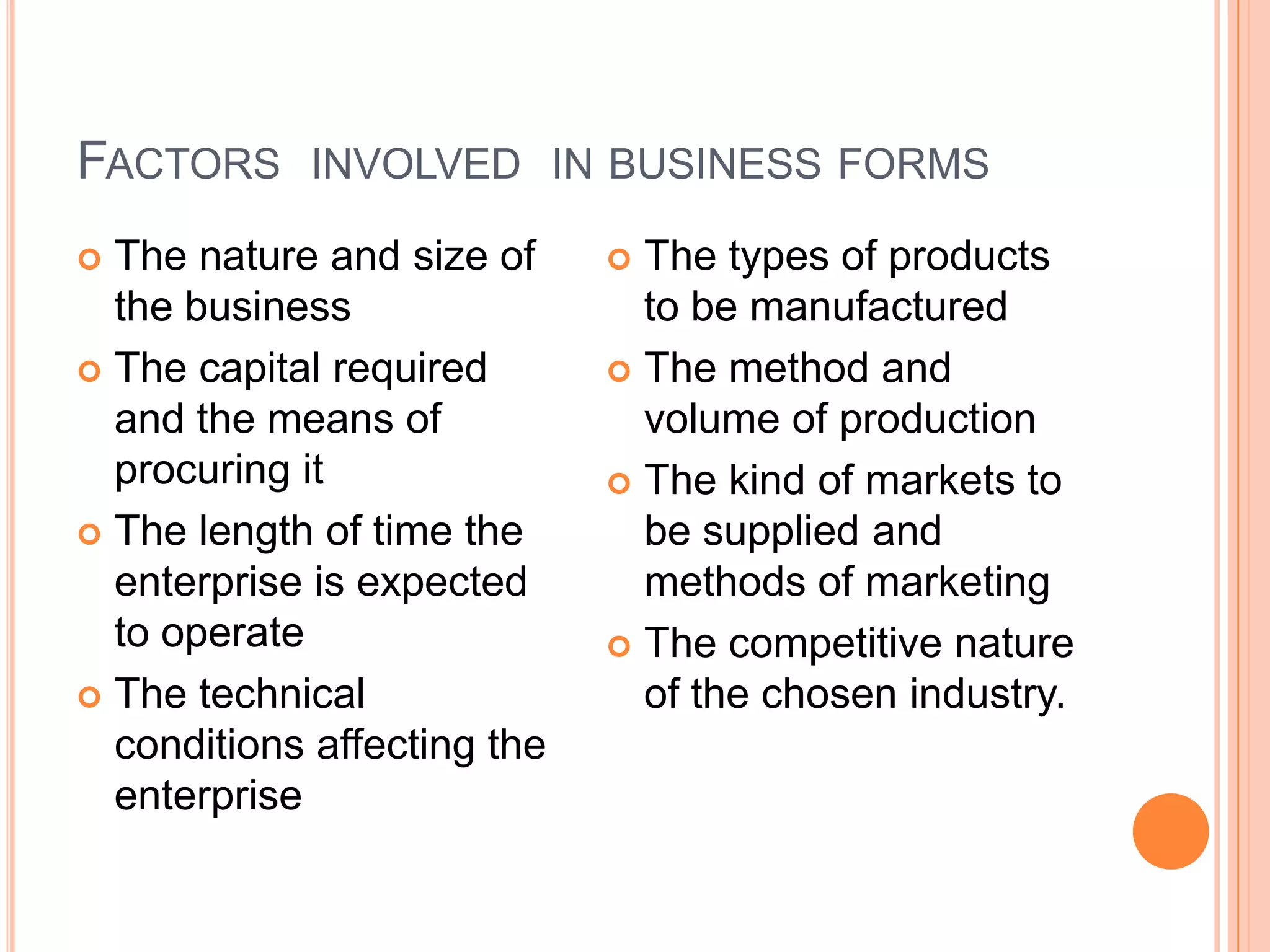
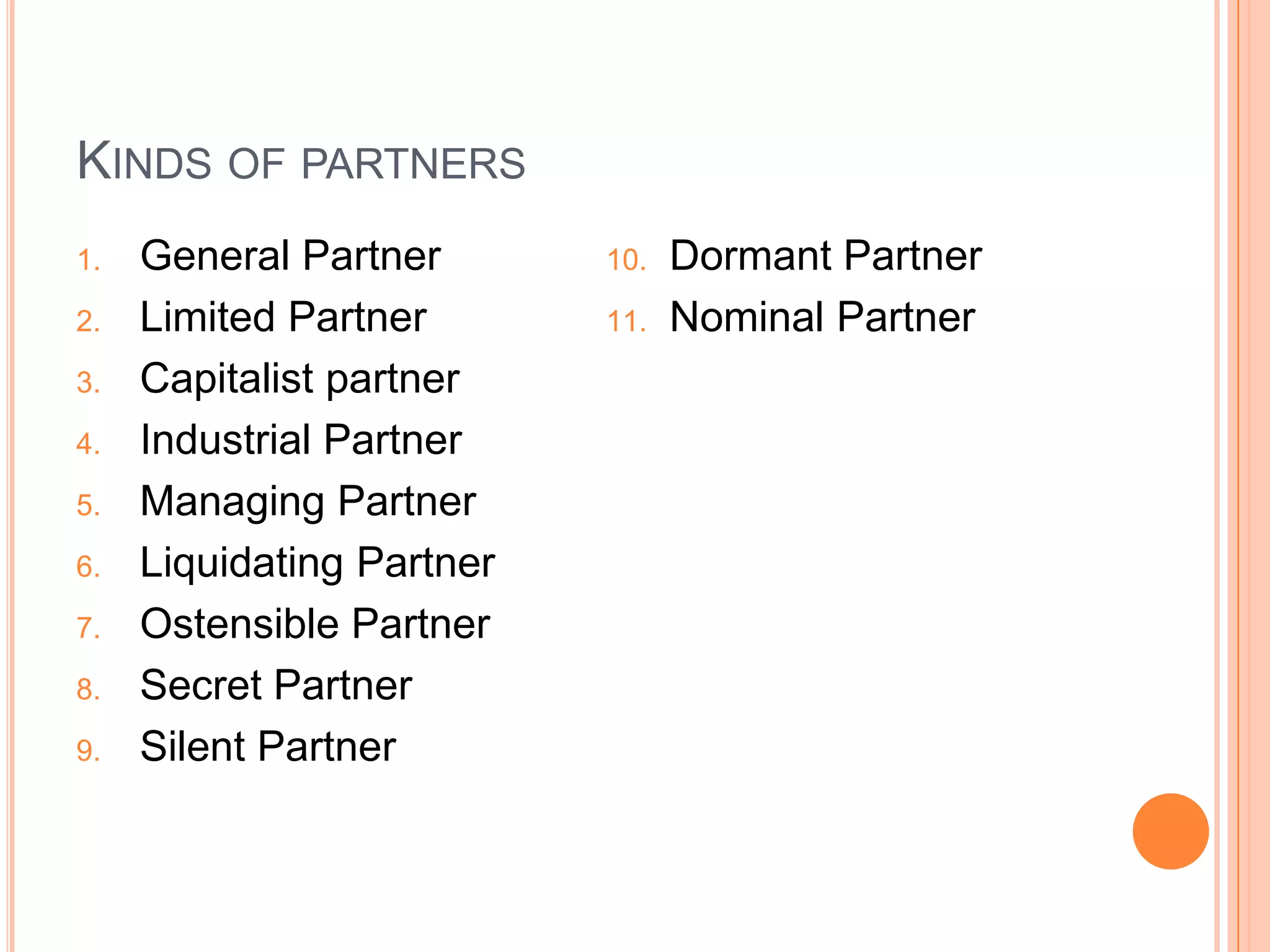
This document discusses different forms of business ownership and structure. It describes private, public, and mixed ownership. Under private ownership, it outlines sole proprietorships, partnerships, cooperatives, and corporations. It then discusses factors that influence business forms selection and provides details on sole proprietorships, partnerships, limited partnerships, and cooperatives - including their advantages and disadvantages.