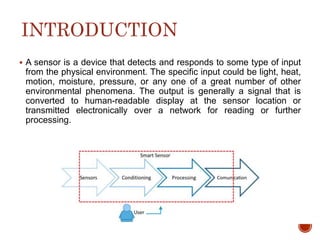
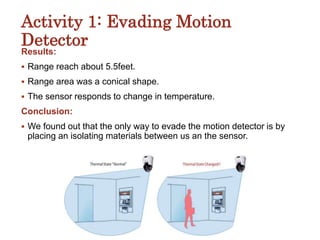
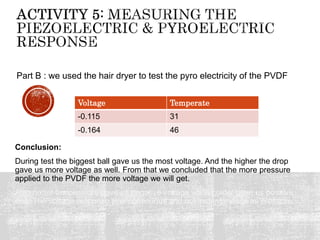
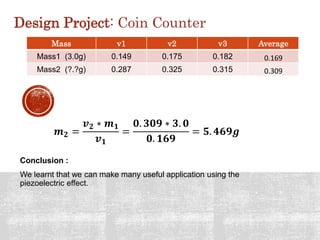
The document details a project exploring various sensor technologies, including activities like evading motion detection and building microphones using PVDF film. It emphasizes learning through practical experiments and results, highlighting the piezoelectric effect and discussing a design project for a coin counter and innovative smart street lights. The project culminated in gaining technical skills and insights into sensor applications, with gratitude expressed towards supporting teams and sponsors.