This document discusses smart home systems. It defines a smart home as a house that incorporates a communications network connecting electrical systems and services to allow remote control, monitoring and access both inside and outside the home. The document outlines key elements of smart home systems including communication networks, intelligent control and home automation components. It also discusses current and future applications of smart home technologies in areas like home functions, healthcare, security and entertainment. Finally, it examines research challenges around privacy, system complexity, cost effectiveness and the social impacts of smart homes.







![Smart Home System
9
Typical example of a smart home environment [2, 3].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smarthome-130513093838-phpapp01/85/Smart-home-9-320.jpg)
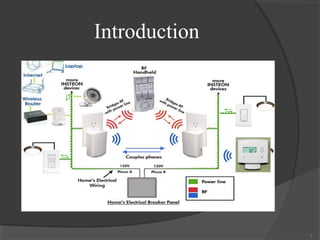
![Smart Home System
10
Typical architecture for smart home system [4].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/smarthome-130513093838-phpapp01/85/Smart-home-10-320.jpg)