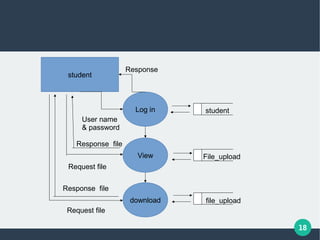
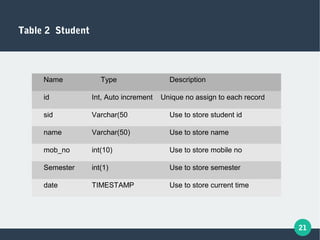
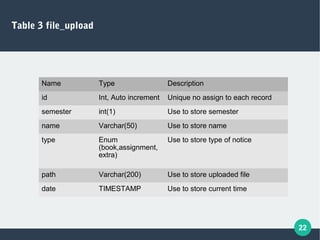
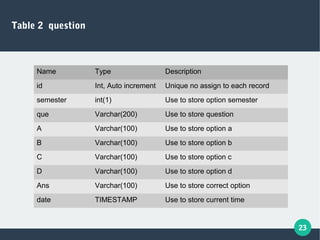
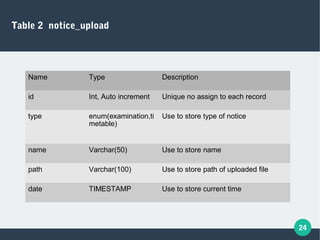
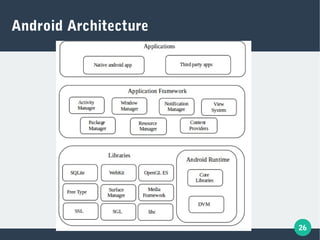
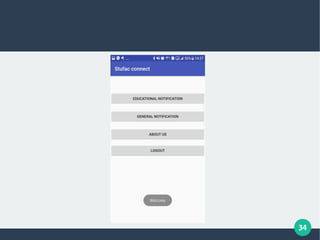
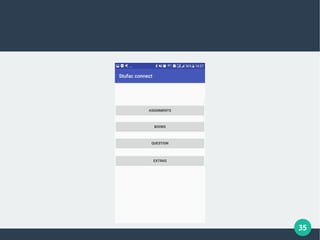
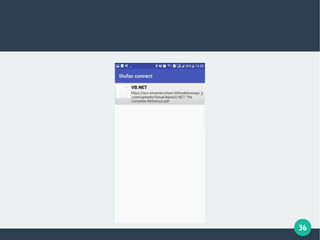
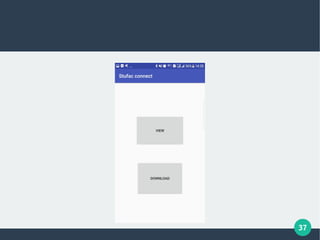
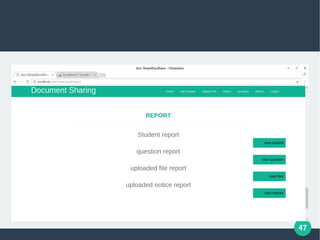
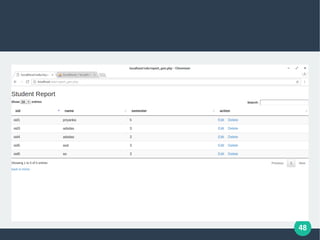
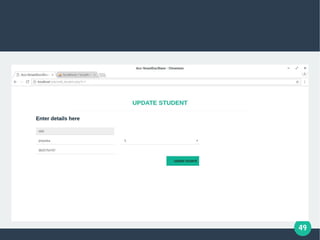
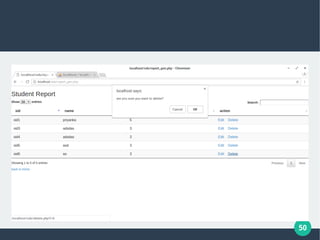
The document describes a student-faculty document sharing application called Stufac Connect. It was developed by Priyanka Thakker and guided by Bharat K Patel. The application allows faculty to upload documents like syllabi, timetables, notes etc. for students to view and download on their android devices. It discusses the project objectives, tools used, feasibility analysis, system design with modules for students and faculty, database tables, and testing conducted. Future enhancements planned include adding more features like password reset and improving the user interface.