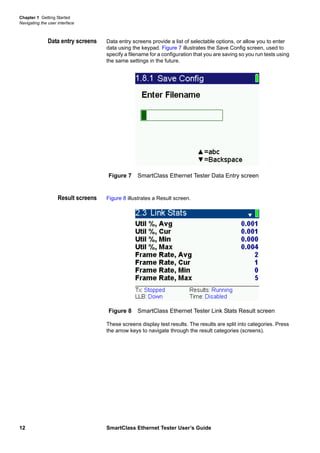
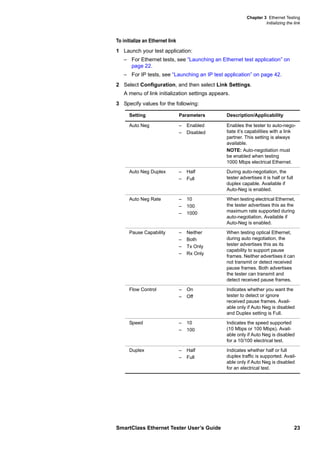
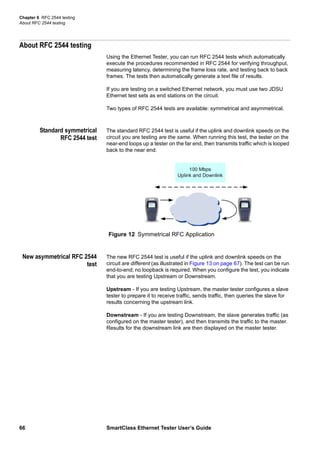
This document is the user's guide for the SmartClass Ethernet Tester. It contains information about features and capabilities, preparation for use, navigating the user interface, instrument settings, and Ethernet testing functions. The guide includes sections on exploring the front panel, powering the tester on and off, menu screens, data entry, test results, and specific tests for cable diagnostics and Ethernet.