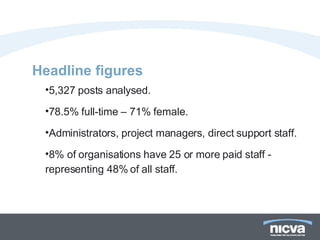
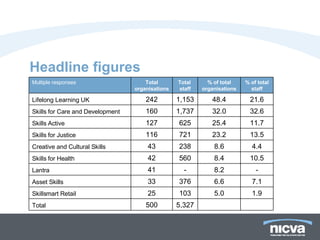
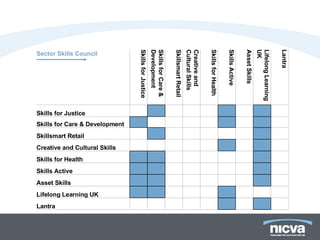
The document analyzes skills development in Northern Ireland's voluntary and community sector, highlighting key statistics and identified skills gaps. Major findings indicate that while most organizations report no skills gaps, significant needs exist in areas such as project management, finance, and essential skills like team working and IT. Additionally, barriers to training include funding limitations and time constraints, with many organizations relying on in-house training and volunteers to address these gaps.