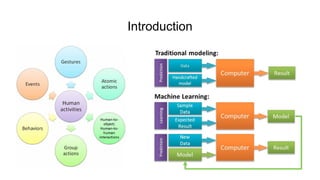
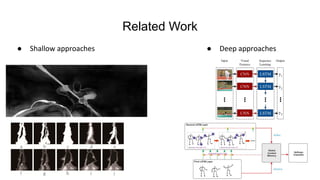
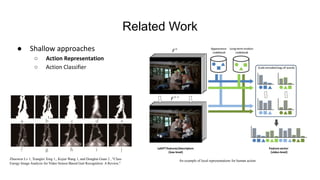
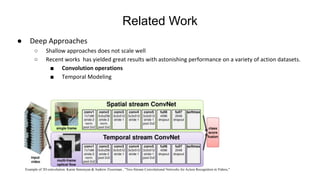
This document presents a thesis on using recurrent neural networks for skeleton-based human action recognition. The proposed method uses two RNNs - a temporal RNN to model the temporal dynamics of joints over time, and a spatial RNN to model the dependencies between joints spatially. The RNNs are trained on skeleton data extracted from video datasets like NTU RGB+D and Kinetics. Experimental results show the method achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on the NTU datasets and can recognize actions in real-time from new video inputs. Future work involves exploring more advanced temporal modeling and evaluating on larger datasets.