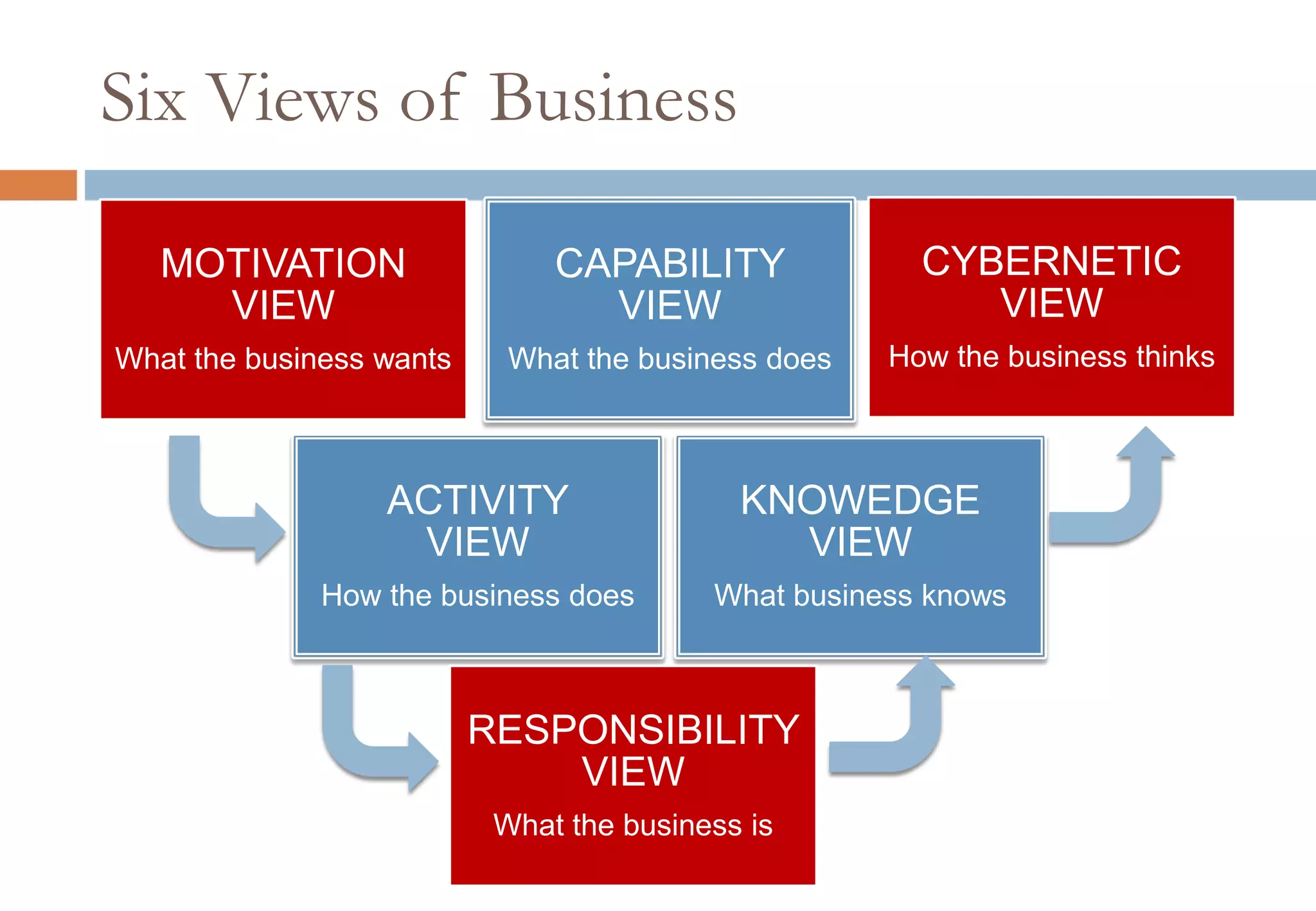
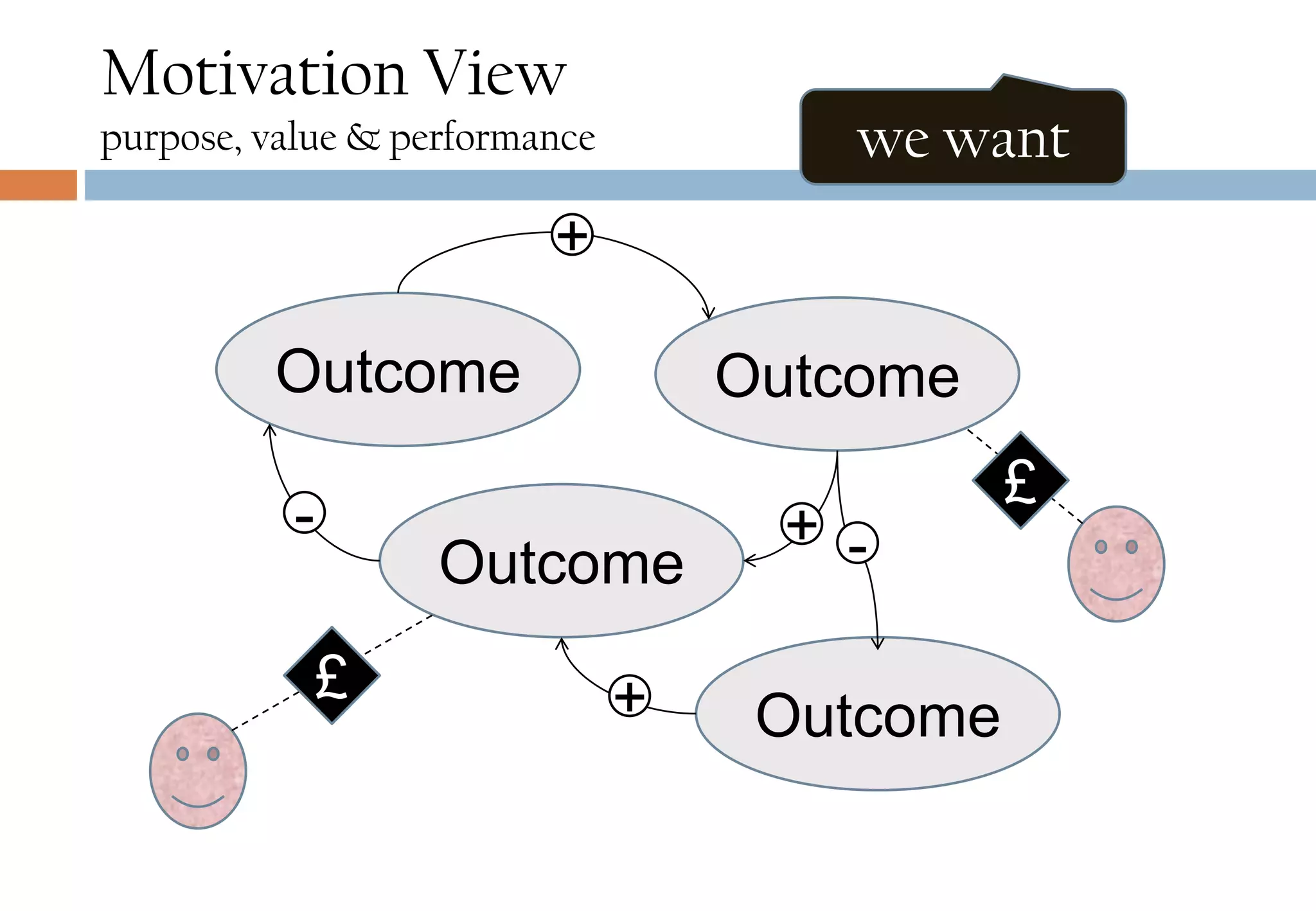
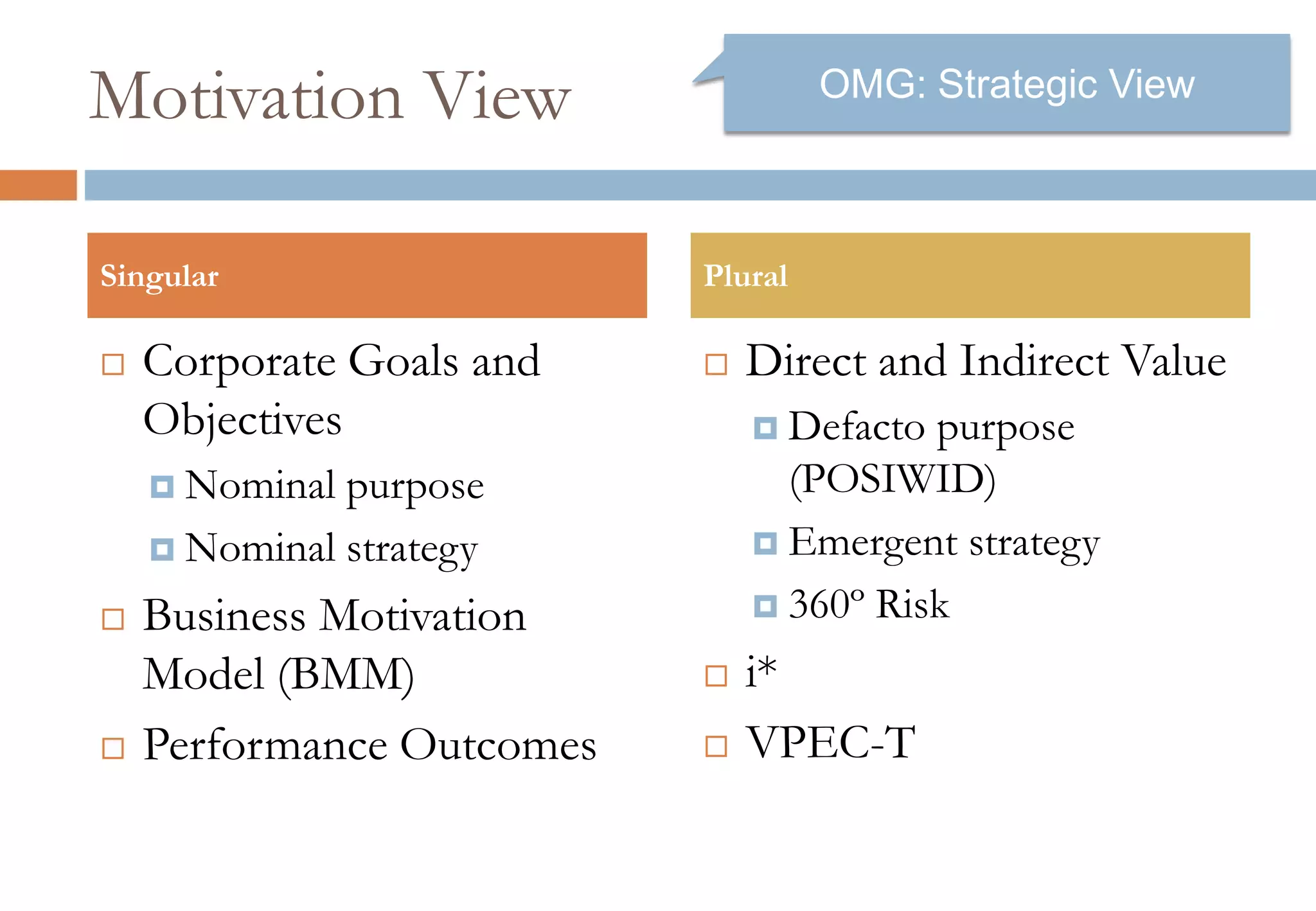
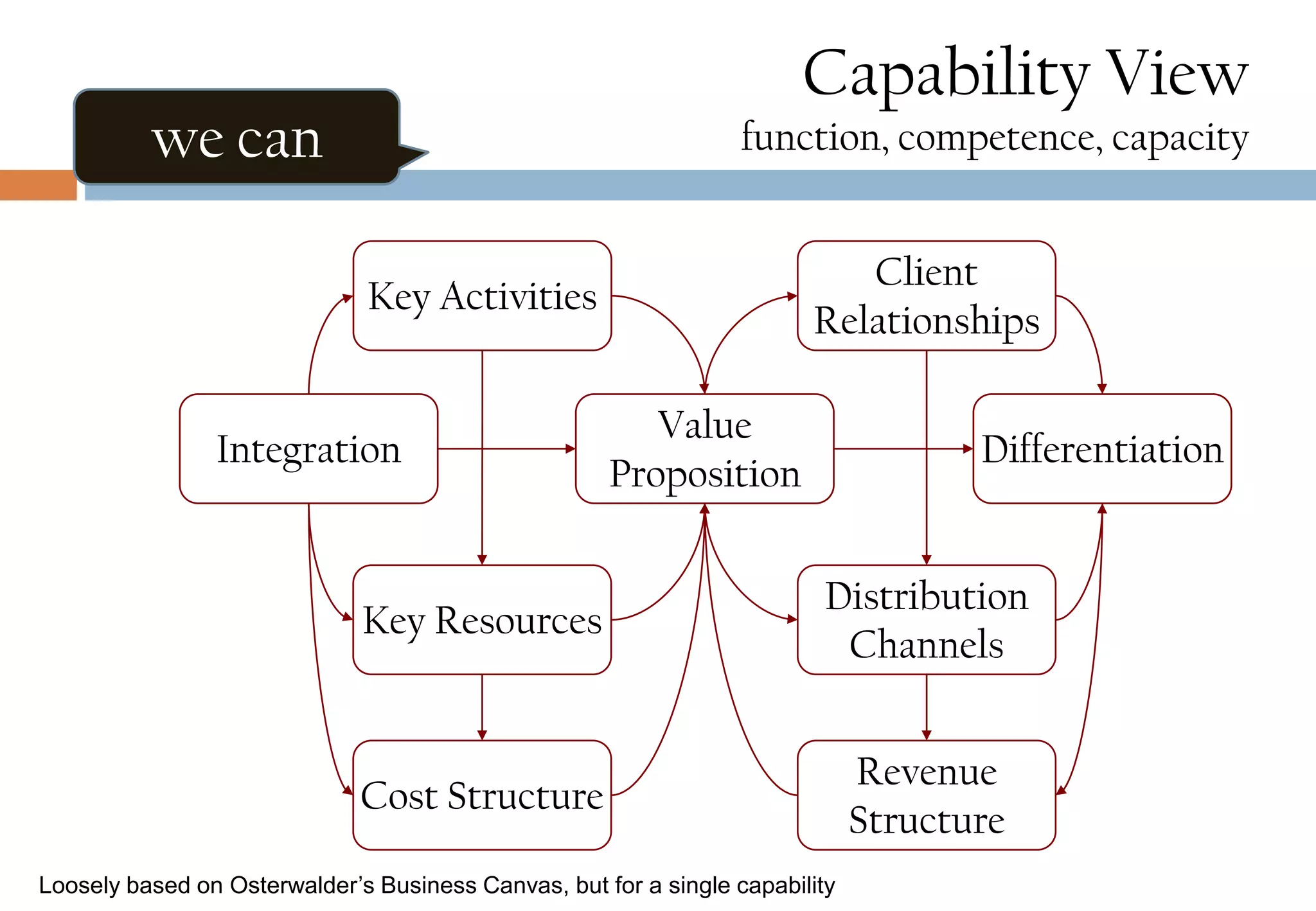
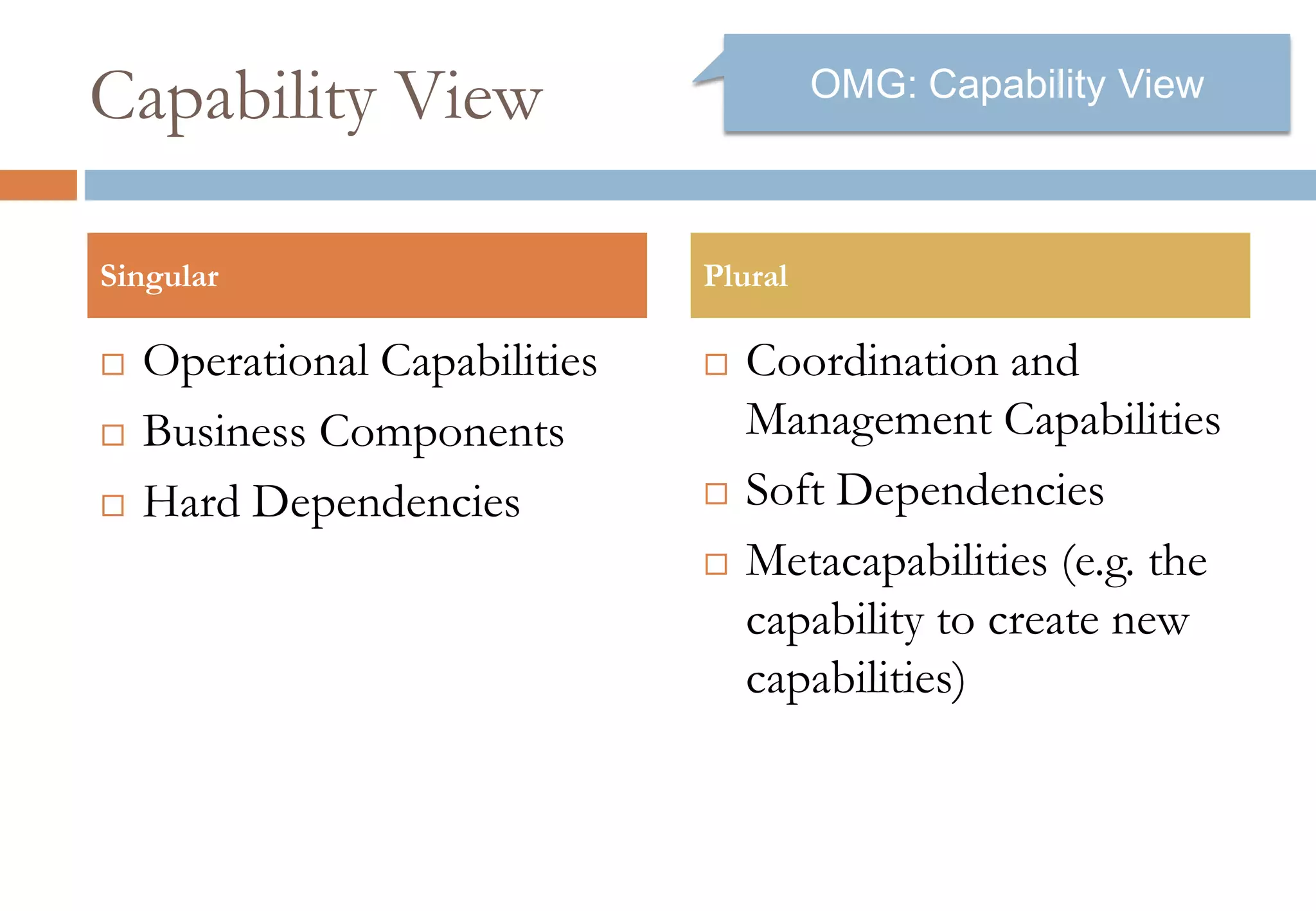
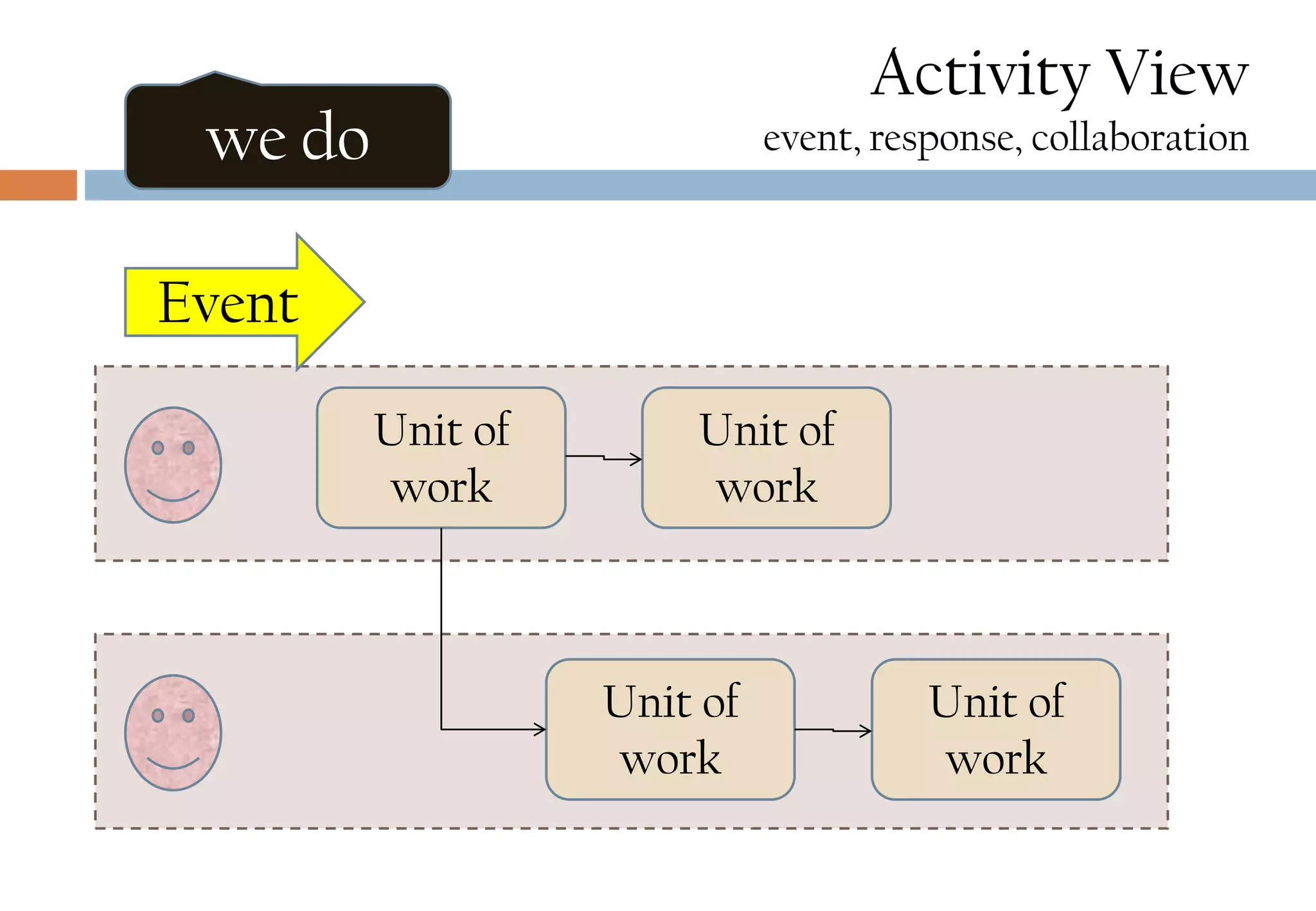
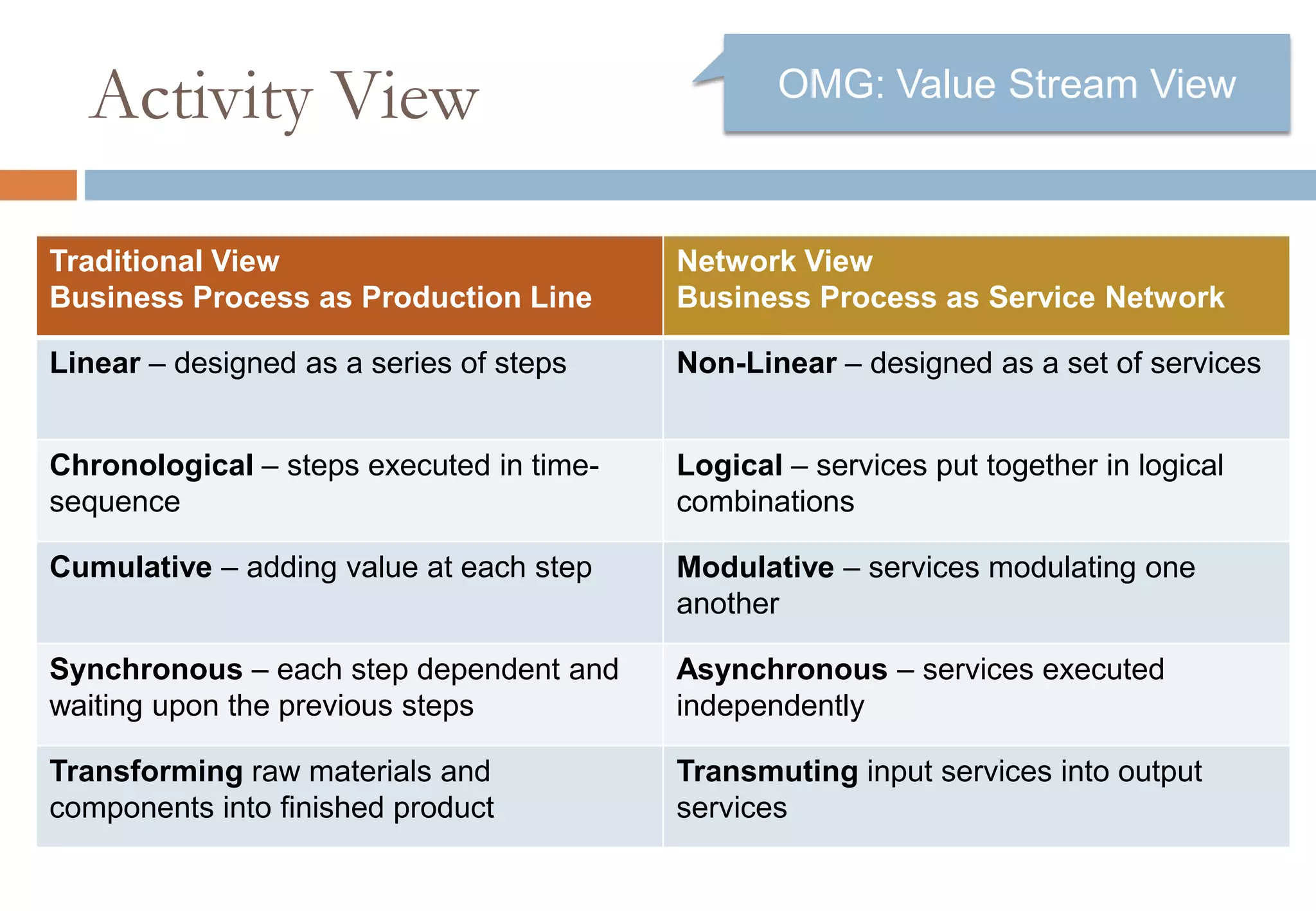
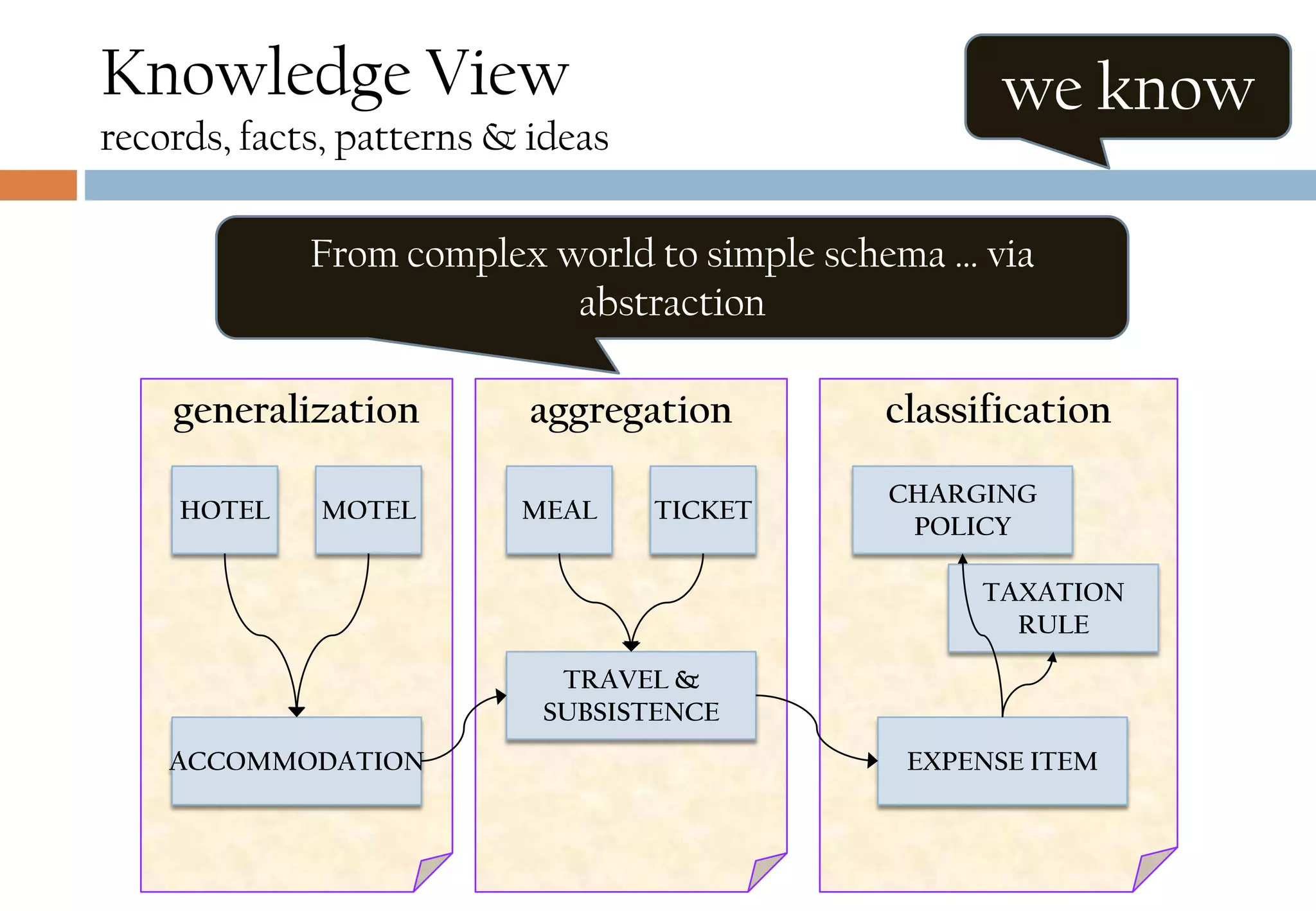
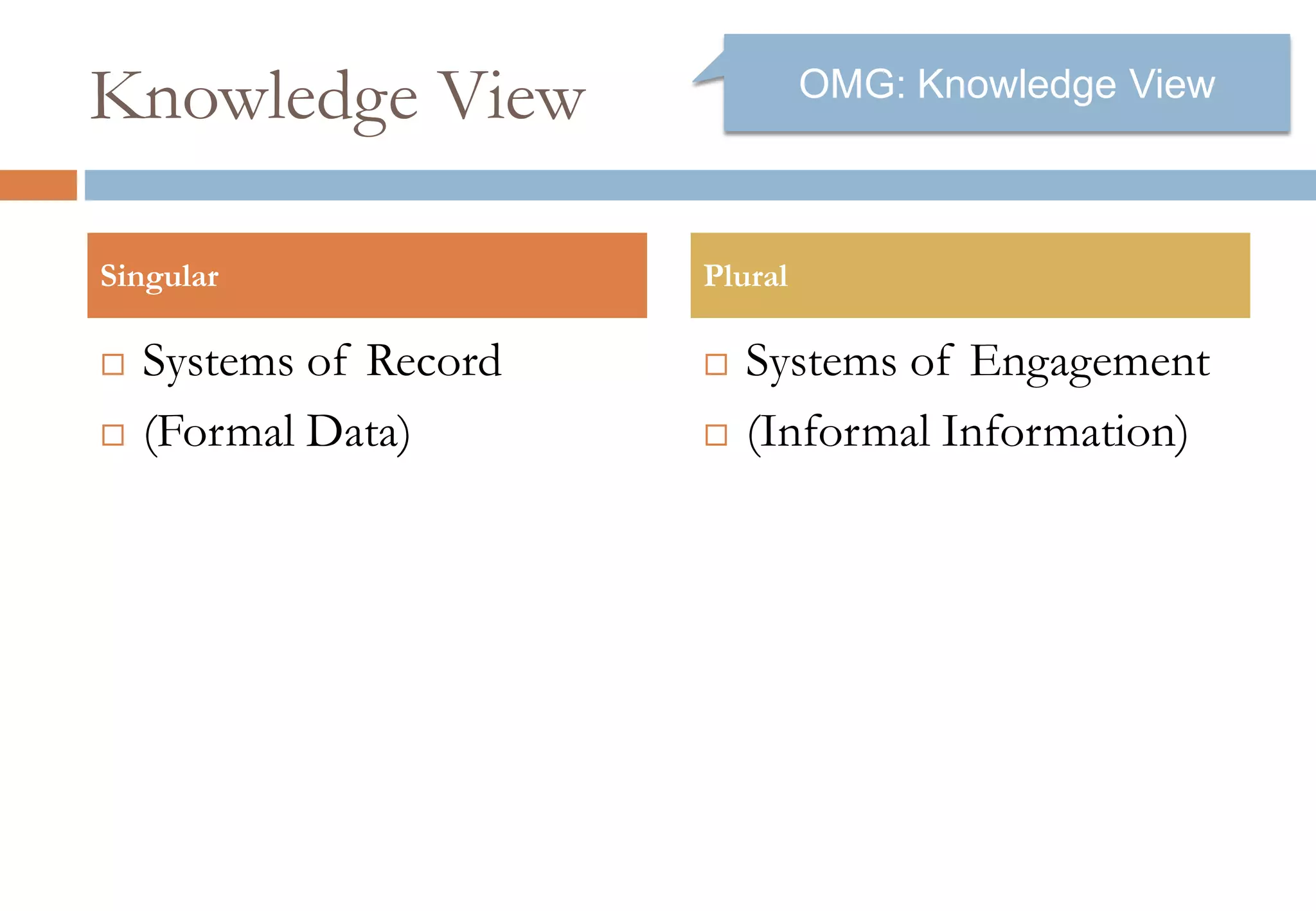
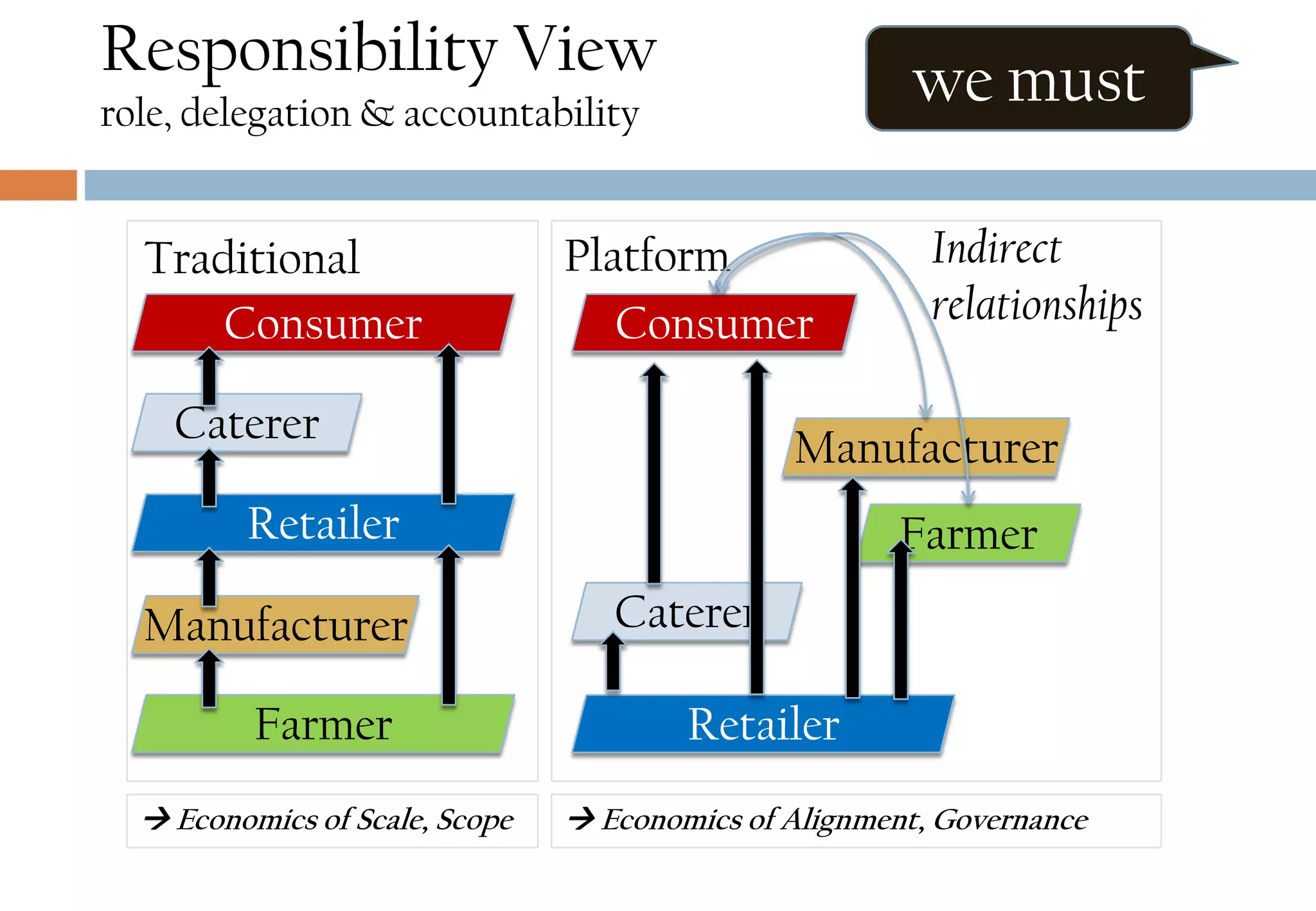
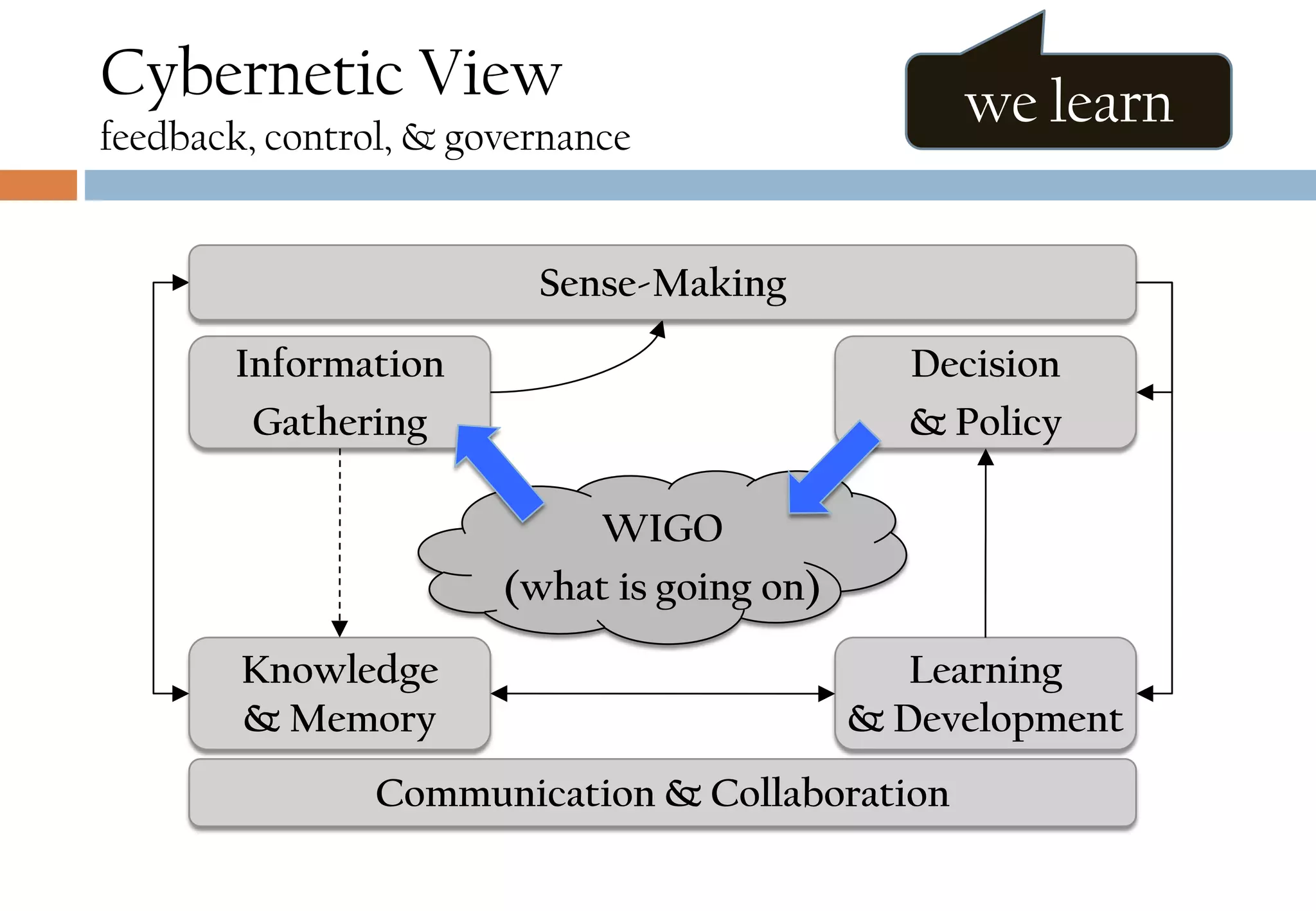
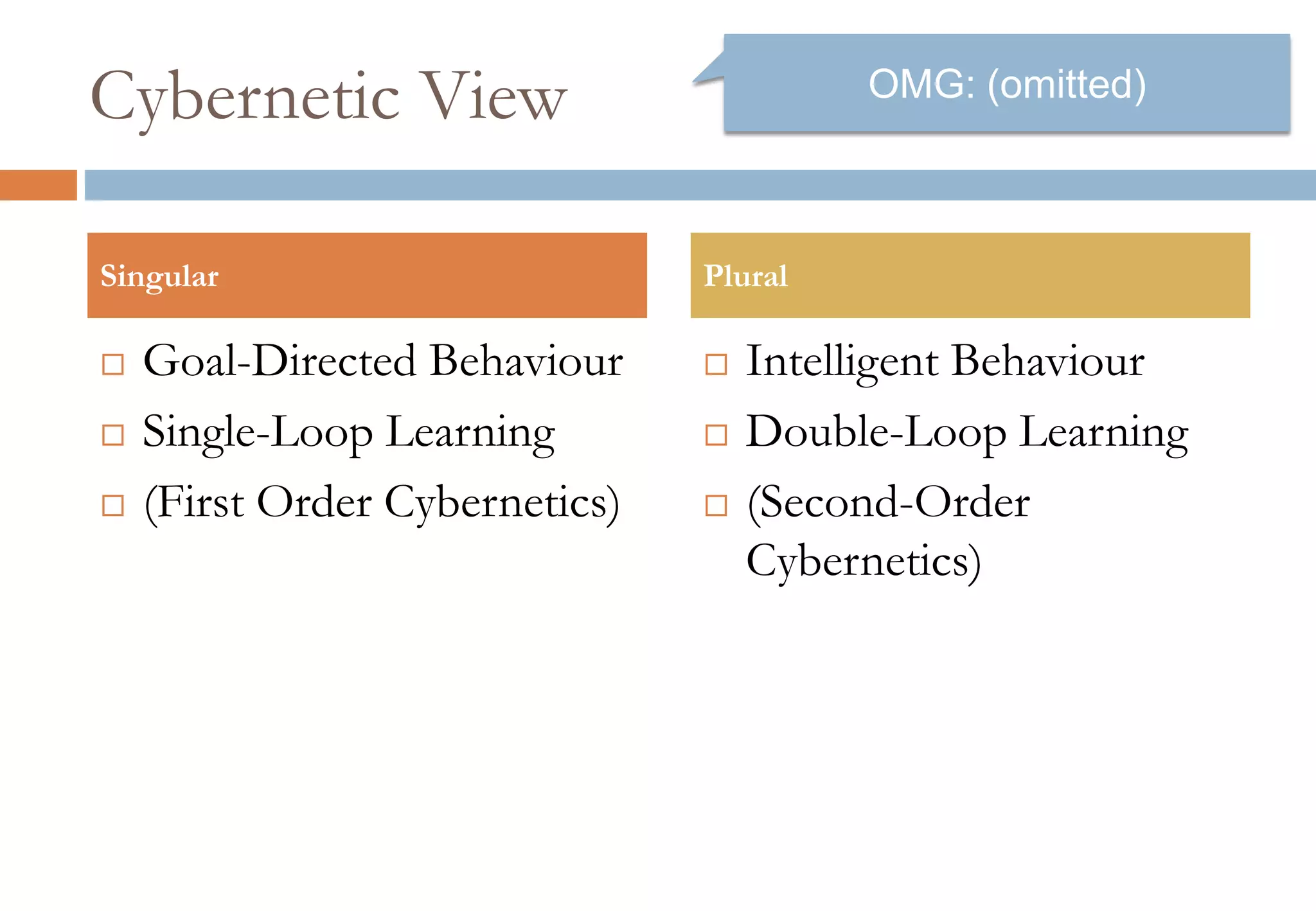
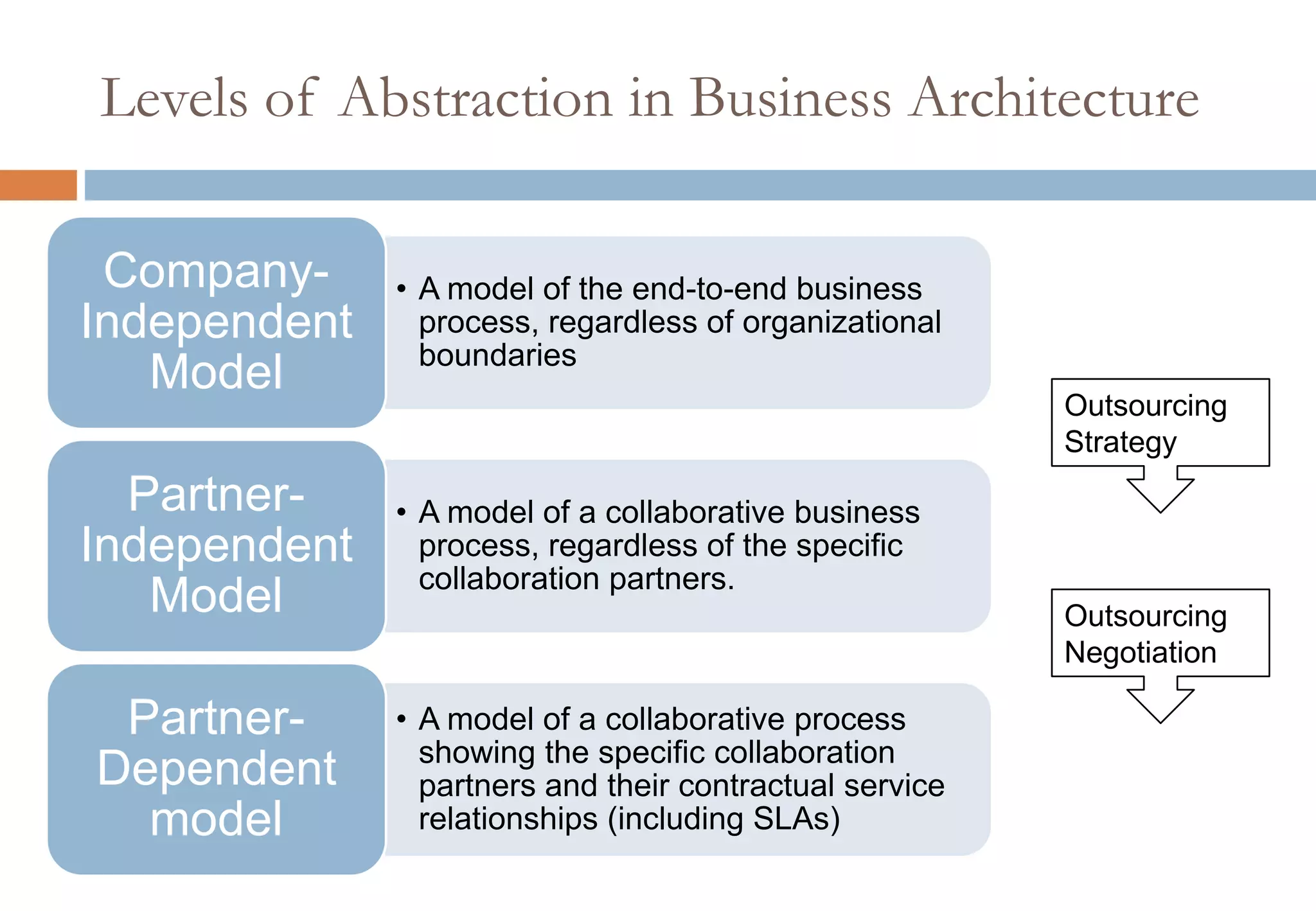
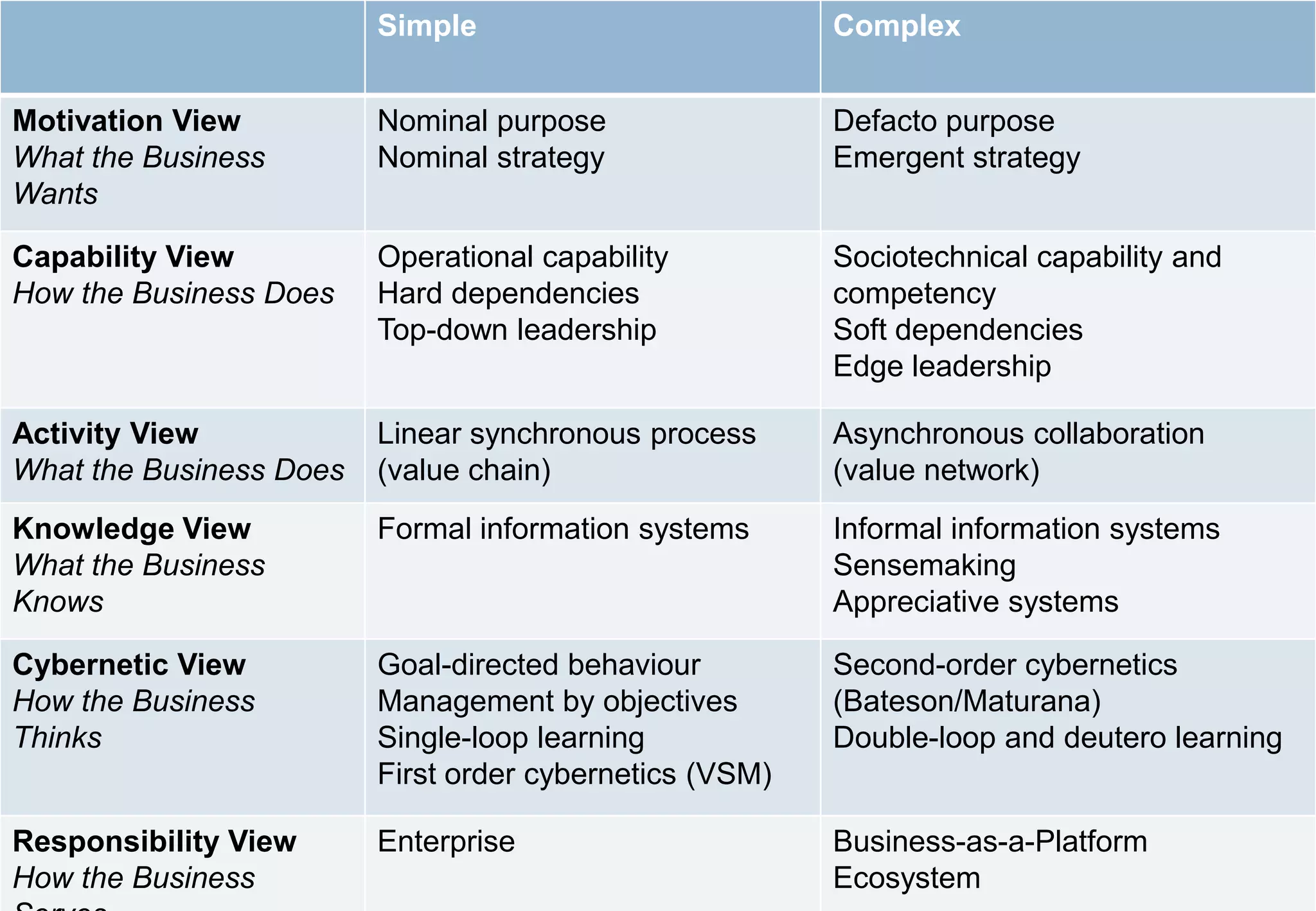
The document presents six viewpoints of business architecture: motivation, capability, activity, knowledge, responsibility, and cybernetic, each illustrating different aspects of a business's functioning and structure. It discusses how these viewpoints can help in understanding business processes, strategies, and relationships within various companies. Additionally, it highlights the importance of abstraction levels in modeling business processes and the roles of leadership and learning in organizational dynamics.