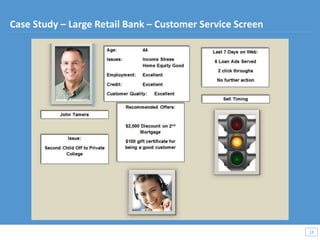
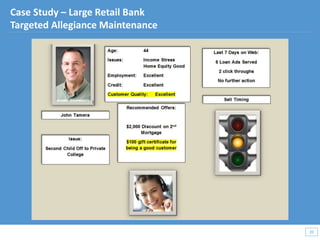
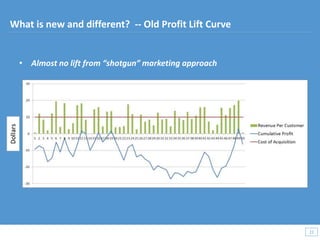
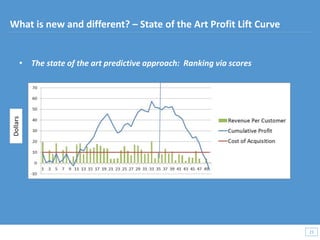
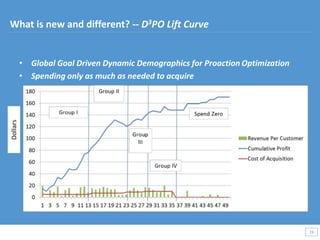
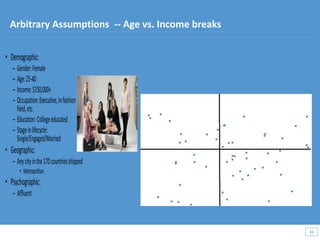
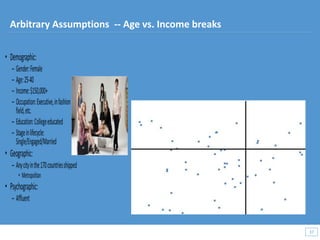
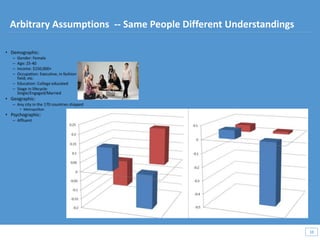
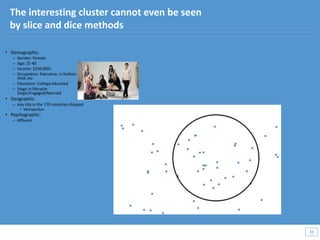
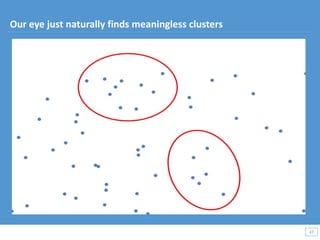
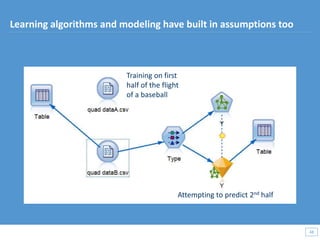
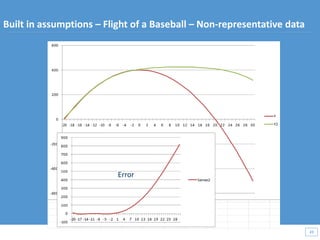
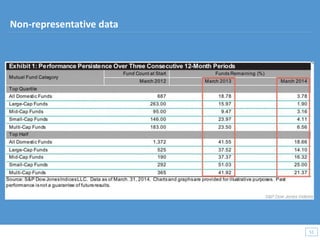
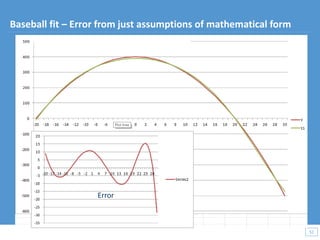
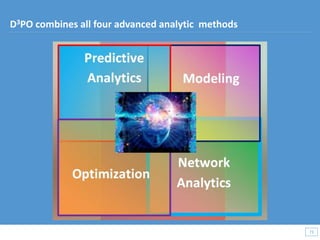
This document discusses how big data and data science can help businesses and healthcare. It provides examples of how analyzing large amounts of data can help optimize customer groups and actions to maximize results. Specifically, one case study shows how a bank increased new product conversions by 100x and profits by $1 billion by using big data to better target customer groups and proposals. The document also discusses how data science involves descriptive, predictive, prescriptive and proactive analytics and how global goal driven dynamic demographics for proaction optimization (D3PO) can combine these approaches.