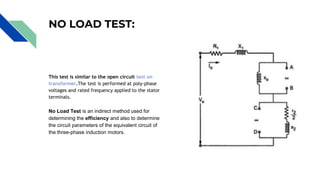
This document provides an overview of single phase induction motors. It discusses the construction of single phase induction motors including the stator and squirrel cage rotor. It explains the working principle, describing how a single phase AC supply to the stator produces a rotating magnetic field that induces current in the rotor. It also introduces the double field revolving theory to explain why single phase motors are not self-starting. The document discusses the equivalent circuit of induction motors and describes no load and blocked rotor tests that are used to determine the circuit parameters.


![BLOCKED ROTOR TEST:
A blocked rotor test is conducted on an induction motor. It is
also known as short circuit test, locked rotor test or stalled
torque test.[1] From this test, short circuit current at normal
voltage, power factor on short circuit, total leakage reactance,
and starting torque of the motor can be found.[2][3] The test is
conducted at low voltage because if the applied voltage was
normal voltage then the current through the stator windings
would be high enough to overheat the windings and damage
them.[4] The blocked rotor torque test is not performed on
wound-rotor motors because the starting torque can be varied
as desired. However, a blocked rotor current test is conducted
on squirrel cage rotor motors.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1phaseim-181126093319/85/SINGLE-PHASE-INDUCTION-MOTOR-9-320.jpg)
