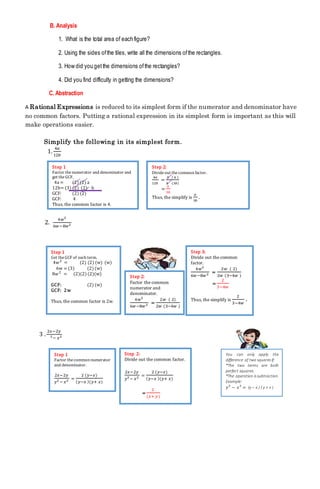
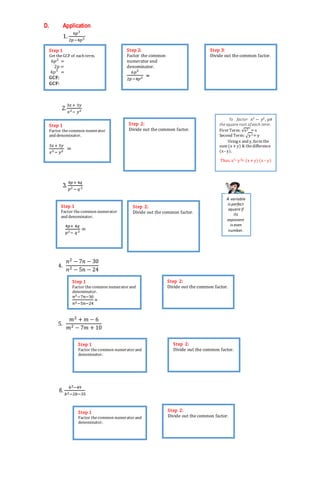
This document contains a lesson plan for teaching simplifying rational expressions in Math 8 at Quiot National High School. The lesson plan outlines the intended learning outcomes, learning content including reference materials, learning activities and experiences, and an evaluation section containing practice problems for students. The lesson aims to teach students how to define, simplify, and apply rational expressions in real-life contexts. Learning activities include defining rational expressions, simplifying examples by factoring and cancelling common factors, and applying the process to additional practice problems. The evaluation section contains 4 practice problems for students to simplify rational expressions.