The document provides an overview of simplified TRIZ (the theory of inventive problem solving). It discusses the background and basics of TRIZ, which was developed by Genrich Altshuller to analyze and resolve contradictions in complex systems. The document notes that TRIZ complements other innovation methods and can help understand why good ideas sometimes take time to achieve success. It also outlines some of TRIZ's key concepts, including resolving contradictions, reaching ideality, and using idle resources.

![Background - points
• Complement tool to many other methods
– Theory of Constraints (TOC), Six Sigma, Quality Function Deployment, Taguchi
method, DFM-A
• Biography of Altshuller / TRIZ
– Resident of Baku | tormented by Stalin until 1954 |
• Basic Principles
– Ideality | Contradiction | Resources | Patterns of Evolution|Innovative
Principles
– Motivation | Orientation | Internalization | Application | Evaluation |
Implementation [Learning cycle]
• How does this compare with the Kaplan learning model?
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-2-320.jpg)
![Why do good ideas take time to
fruition?
• Xerox – lithography • Is it sales? – May be no
– Richard Foster’s book Innovation
• Penicillin – Alex Fleming • National Cash Register continued to
• Molok – dust bins advertise electromechanical cash
registers in the 1970s
• Mcdonalds – Ray kroc • Is it Prejudice?
• Horizontal Petro Drilling – We don’t know whats good or Bad?
• T – Drill [without T joint]
• Appa – jute wire for
opening furnace ladles
• Flash smelting
• Linz donovitz process ….
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-3-320.jpg)
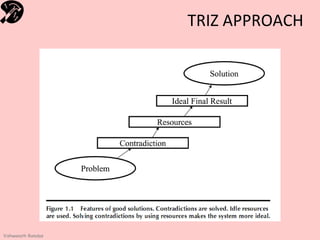
![How to know? – 3 features?
• Resolves a contradiction [ 2 – dim TOC ]
– Tradeoffs / Inherent
• Reaches Ideality
– All features / No costs * No harmful effects * less complexity
• Uses idle resources [no waste – Lean]
– Energy / Materials / Information / objects
• 2 Views
– Mcgregor :: Cristopher Freeman :: Engestrom :: De Bono
– Theory Y :: Demand Pull :: Humanized :: Lateral
– Theory X :: Science Push :: Rationlized :: Straight
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-4-320.jpg)



![Getting to the ideal final result –
completing the model
• Features • ARIZ
– Whole gamut of components and – Method guide for solving TRIZ
functionality
• Standards [76 standards]
• Patterns – List of system transformations
– Soft formulae [ not rigid algorithms!]
• Effects
• Laws / Innovative Principles – Database of phenomena
– Electro, mechanical, chemical, physical
• Software
– Automated above!
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-10-320.jpg)
![Some training standards
• Maintain the good / best practices
– Some elements like 40 principles that reflects evolution of thinking for
innovation should be maintained
• General Concepts >> short procedures
– Less than 1 page the better [ capability vs usability]
• Social network – provide overall concepts
– People will internailze and adapt [ don’t regidify!]
– Peter Senge and Engestorm.
“Leave the beaten track occasionally and dive into the woods. You
will be certain to find something that you have never seen before.”
Alexander Graham Bell in the foyer of Bell Labs as observed by Shockley
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-11-320.jpg)
![Trade-Offs [Multi]
Inherent Contradictions [
single]
Understanding Contradictions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-12-320.jpg)

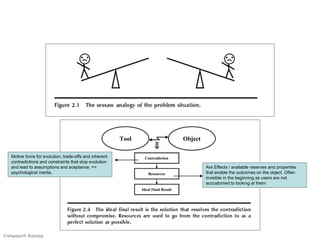
![Draft the problem to expose the
tradeoffs.
• Problems are sirens OR scylla & Charybdis
– Homers illyiad
• Understand the problem – 50% solution!
– Problem Finding * Problem Solving
– The tool – Action / Effect – Object
– Defining what is the end outcome / effect on the object / user
• A system by its existence creates trade-offs
– Its continuous iterative method [TOC]
• Define systems not by deficiencies but by trade-offs
– Safety reduces X | Safety reduces as speed increases
• Describe the systems as Actions & Features
– Typically it is easier to describe features [nouns] than actions [verbs]
• Trade-offs happen at different system levels
– Needs systems thinking e.g. Lawnmover – muffler noise
– Study at muffler system | lawnmover system | Garden system
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-14-320.jpg)

![Screens of talented thinking [9
screens]
• System @ Present
• enhance understanding of a
problem
– expand the areas in which you can
look for solutions.
• Simplify by asking what is
good or bad in a part [de
bono forced removal]
– what happens if left out?
– Alex Osborn
• “What can we eliminate?… Suppose
we leave this out.…Why not fewer
parts?”
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-17-320.jpg)

![System operator –between the boxes
SLP
• Step in & view from each
room
• Small little people – get into
the problem
• Become the problem
[synectics]
• E.g.s
– Helicopter blades & dust
– Airports & People [beyond airport]
– Future modeling
Vishwanath Ramdas Darell Manns description of the system operator model from triz journal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-19-320.jpg)

![System operator- integrations
• Using System operator with
other models like
– SWOT
– Co-optition [M]
– Association / Dissociation
– VAKOG
• Kinesthetics / Olfactory / Gustative /
Visual / Auditory /
Vishwanath Ramdas Darell Manns description of the system operator model from triz journal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-21-320.jpg)

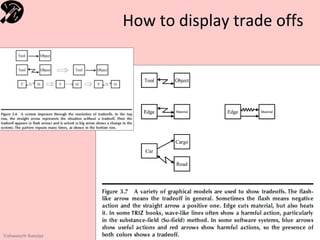
![Selecting the right trade-off
• Iterative Definition of the problem based on state of
solution
• Available resources & time
• Select Effected Components
• From the problem to the tradeoff
– Describe pairs of tools and objects and the action that links them. [Chain]
• Select one pair. Explain why you picked this tool and object.
– Describe features and conflicts between them.
• Select one tradeoff.
– Explain why you identified this tradeoff.
– Describe the tradeoff graphically and in words.
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-23-320.jpg)


![Inherent contradiction – The root
cause?
• Solution of this solves many • Much ↔ little : water
– Atomized water spray
• Focus on one provides
– Extinguishers [www.hi-fog.com]
better answers
• Long ↔ short : training
• Presenting & influencing
with one is better than • Present ↔ Absent : Object
cluttered many.
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-26-320.jpg)






![• What are the invisible resources?
– Boundary conditions [ proximal / gray zones] of development
• Benefits from resources analysis
– Understand customer needs
– Foresee the evolution of development
• What are the resource types and classes?
• The seven most important resources in detail
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-33-320.jpg)


![Resource Types & Classes
• System levels [ref fig]
• Type of Resource
– Substances and things | Modified
substances and things| Voids |
Interactions | energy | Form |
Features or properties | Space |
Time
• Additional resources
– Information | Harm – Side FX| skills
& abilities
Vishwanath Ramdas](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasrchivsimplifiedtriz-120103220756-phpapp01/85/simplified-triz-notes-36-320.jpg)



