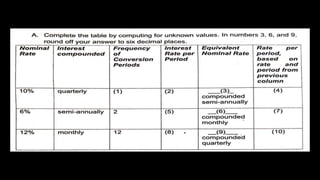
This document defines terms related to simple and compound interest such as principal, interest rate, time period, and discusses how to calculate simple interest, compound interest, maturity value, and present value. It provides examples of calculating simple interest, compound interest annually and for periods of less than 1 year. It also discusses how to find equivalent interest rates, effective rates, and the number of compounding periods or time required to reach a given future value.