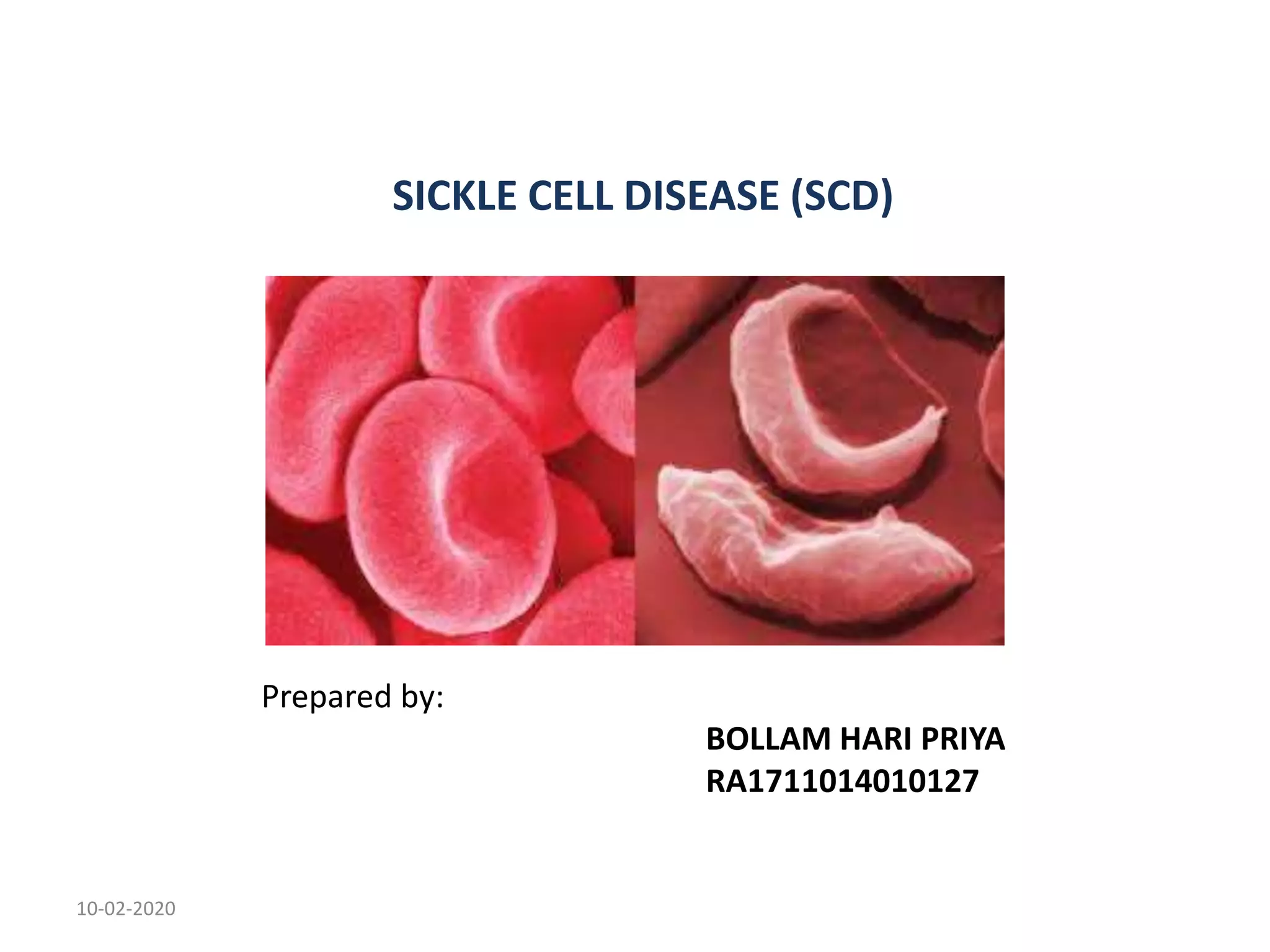
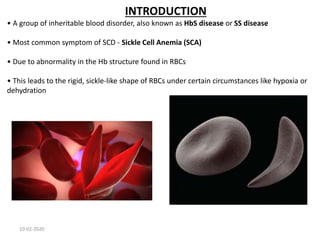
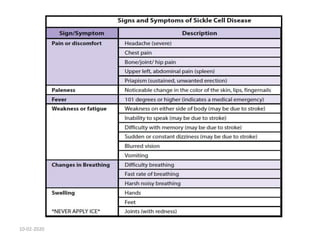
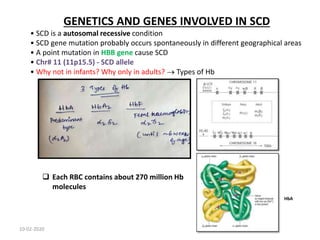
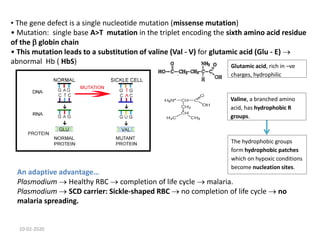
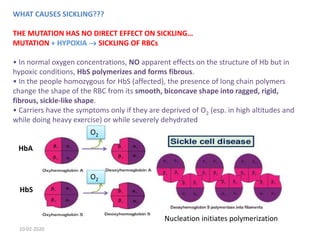
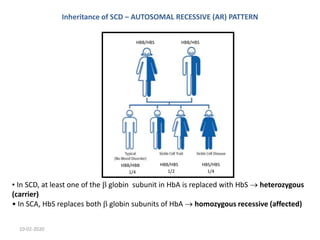
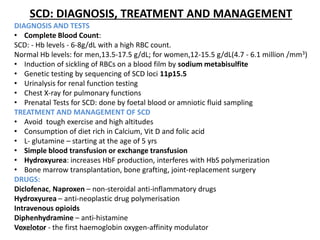
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene. This mutation causes red blood cells to become rigid and sickle-shaped under conditions of low oxygen. The disease predominates in people of African descent, with about 1 in 13 African American babies born with the sickle cell trait. Common symptoms include anemia, pain crises, infections, and organ damage over time. The disease was first described in the early 20th century and the genetic basis was identified in the 1950s. While there is no cure, treatment focuses on prevention of complications, pain management, antibiotics for infections, and hydroxyurea to reduce sickling.