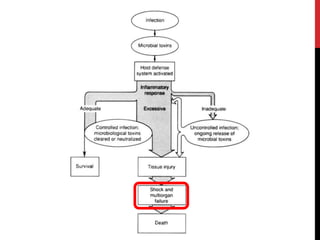
This document defines and describes the different types of shock, including anaphylactic, cardiogenic, hypovolaemic, neurogenic, and septic shock. It provides details on the causes, signs, and emergency management for anaphylactic shock. Management of cardiogenic shock includes oxygen, pain relief, investigations, and close monitoring. Hypovolaemic shock requires rapid fluid resuscitation and treating the underlying cause of blood or fluid loss. Neurogenic and septic shock involve disruption of autonomic pathways and endotoxin-induced vasodilation respectively, and both require ABC support and fluids or antibiotics.