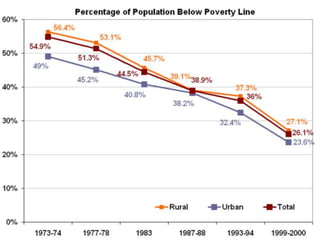
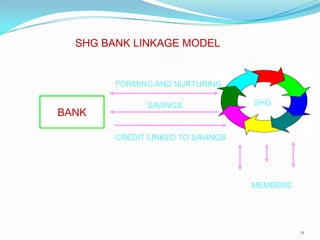
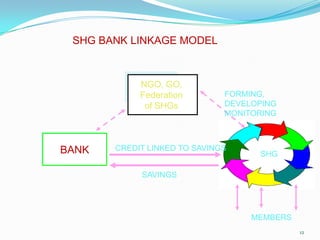
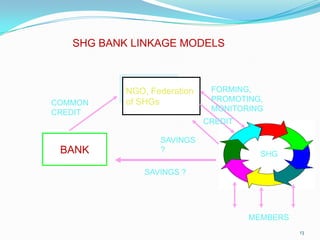
This document discusses the history and development of self-help groups (SHGs) in India. It notes that SHGs first emerged in the 1970s to provide microfinance and empower women. Major organizations like NABARD, MYRADA, and SEWA promoted SHG models. By the 1990s, NABARD began large-scale promotion of SHGs and banks started allowing SHG savings accounts. SHGs are now widespread across India, with millions of members, providing financial services and livelihood support to rural communities while empowering women. The most common model involves NGOs forming SHGs that are then linked to banks for credit.