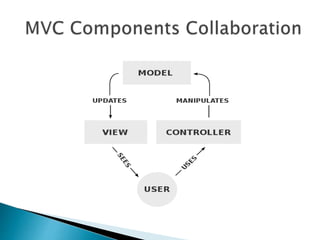
The document discusses different types of file sharing, including peer-to-peer file sharing where users can search for and download files from other connected users, and file sync and sharing services that allow users to access and share files across devices. It also describes the authors' selection of the Ruby on Rails framework for their project and some of Rails' features like MVC architecture and convention over configuration. Finally, it outlines some initial requirements and considerations around security and portability.