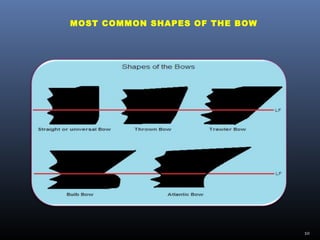
This document discusses the shapes of ship hulls and how they affect buoyancy and maneuverability. It describes several common hull shapes:
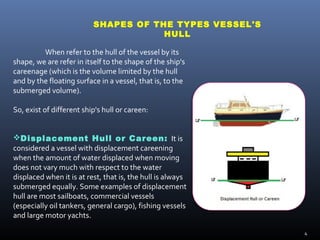
- Displacement hulls are always submerged equally and include commercial vessels like tankers and cargo ships.
- Flat hulls have a flat bottom and sail with most of the hull out of the water, used for boats and sports boats.
- Semi-displacement hulls move with part of the hull submerged and part above water, allowing for high speeds and good stability like many cruise ships.
- Round "U" hulls provide very smooth sailing with little power needed but also very slow speeds, used for large supertankers.
-