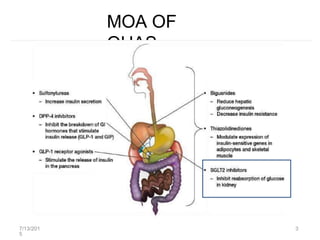
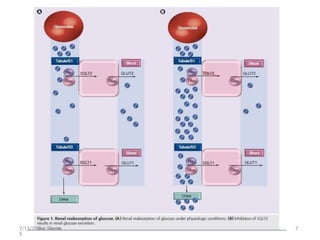
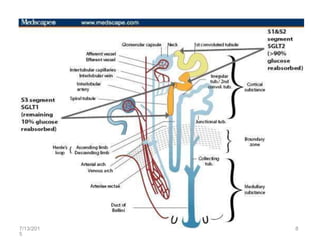
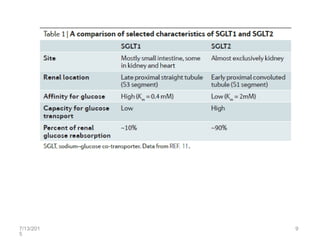
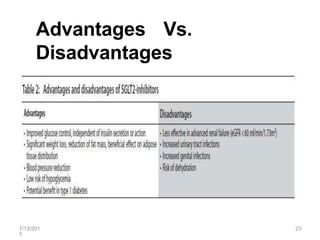
SGLT2 inhibitors are a new class of drugs for treating type 2 diabetes. They work by inhibiting sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) in the kidneys to reduce glucose reabsorption and increase glucose excretion in the urine. Three FDA approved SGLT2 inhibitors are canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin. They provide glycemic control and weight loss with a low risk of hypoglycemia when used alone or in combination with other antidiabetic agents. However, some concerns exist regarding an increased risk of bladder and breast cancer with dapagliflozin.