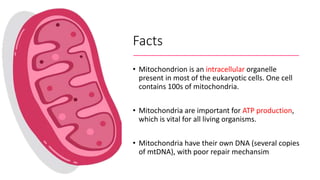
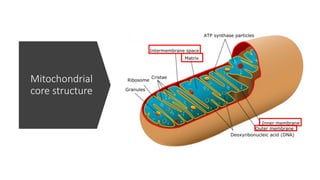
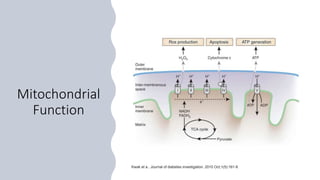
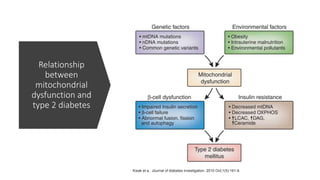
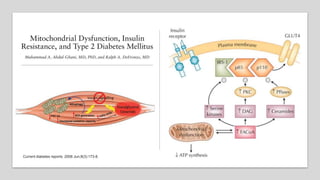
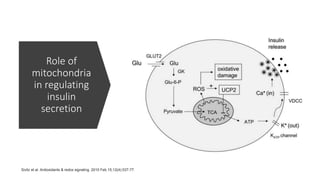
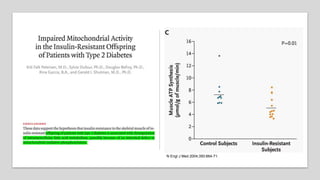
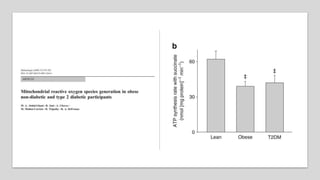
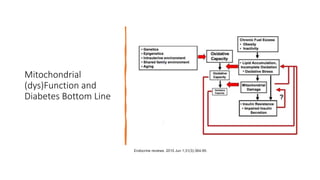
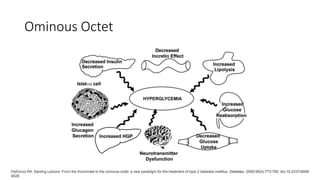
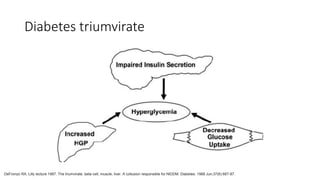
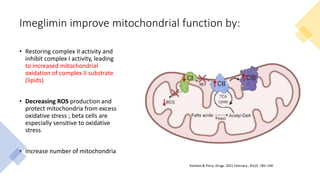
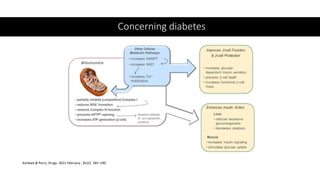
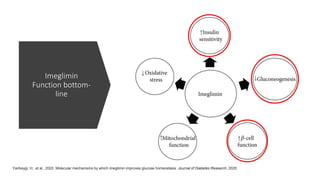
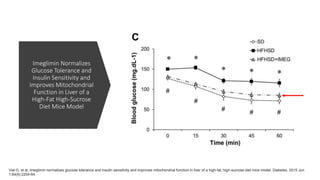
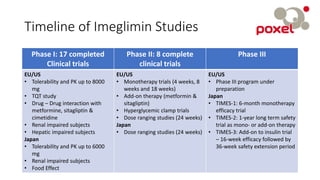
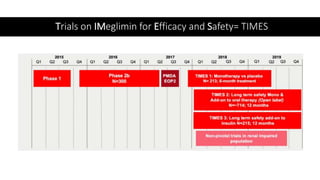
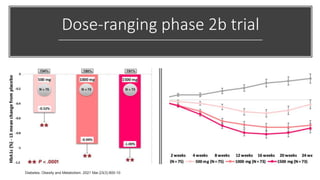
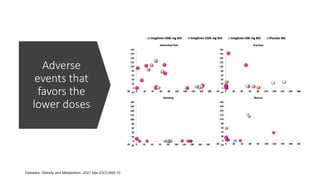
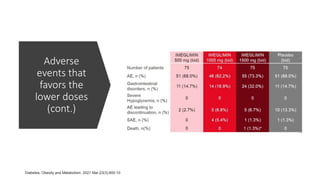
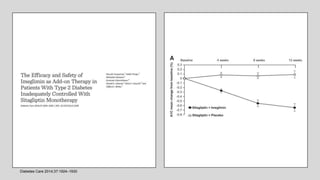
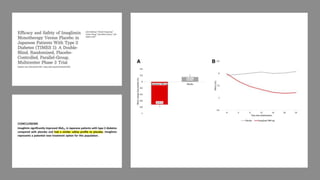
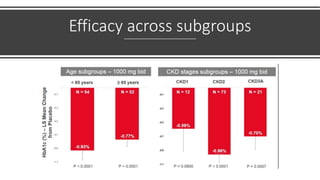
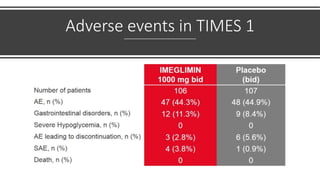
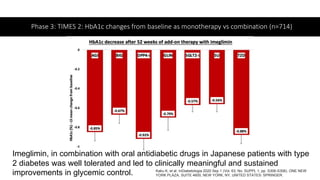
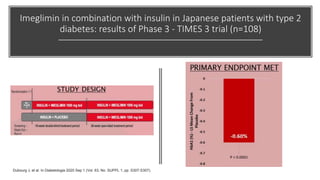
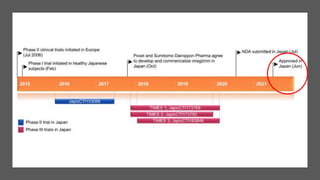
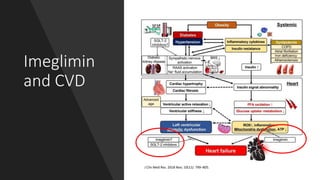
Imeglimin is a novel, first-in-class antidiabetic drug that targets mitochondrial function. It was shown to improve both insulin resistance and insulin secretion based on animal and human studies. Imeglimin received its first approval in Japan in 2021 based on positive results from the Phase III TIMES clinical trials program demonstrating its efficacy in lowering blood glucose levels and its safety both as monotherapy and in combination with other oral antidiabetic drugs or insulin. Imeglimin may also provide cardiovascular benefits given its effects on improving mitochondrial function in multiple tissues beyond just glycemic control.