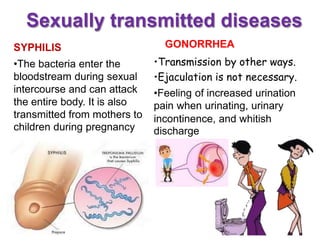
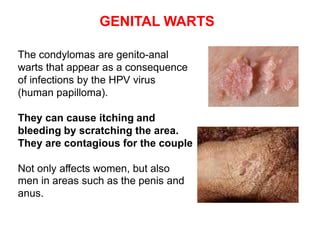
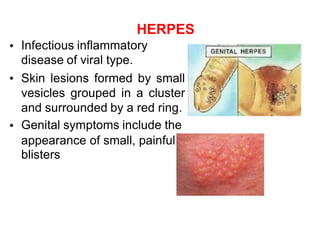
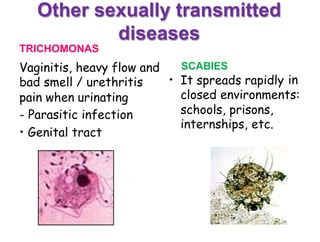
Sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted through sexual contact via mucous membranes or bodily fluids. They include chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes, syphilis, and human papillomavirus. Symptoms vary but can include discharge, sores, rashes, or pain. Prevention requires abstinence or correct and consistent condom use. Anyone experiencing symptoms should see a doctor for testing and treatment to prevent further spread.