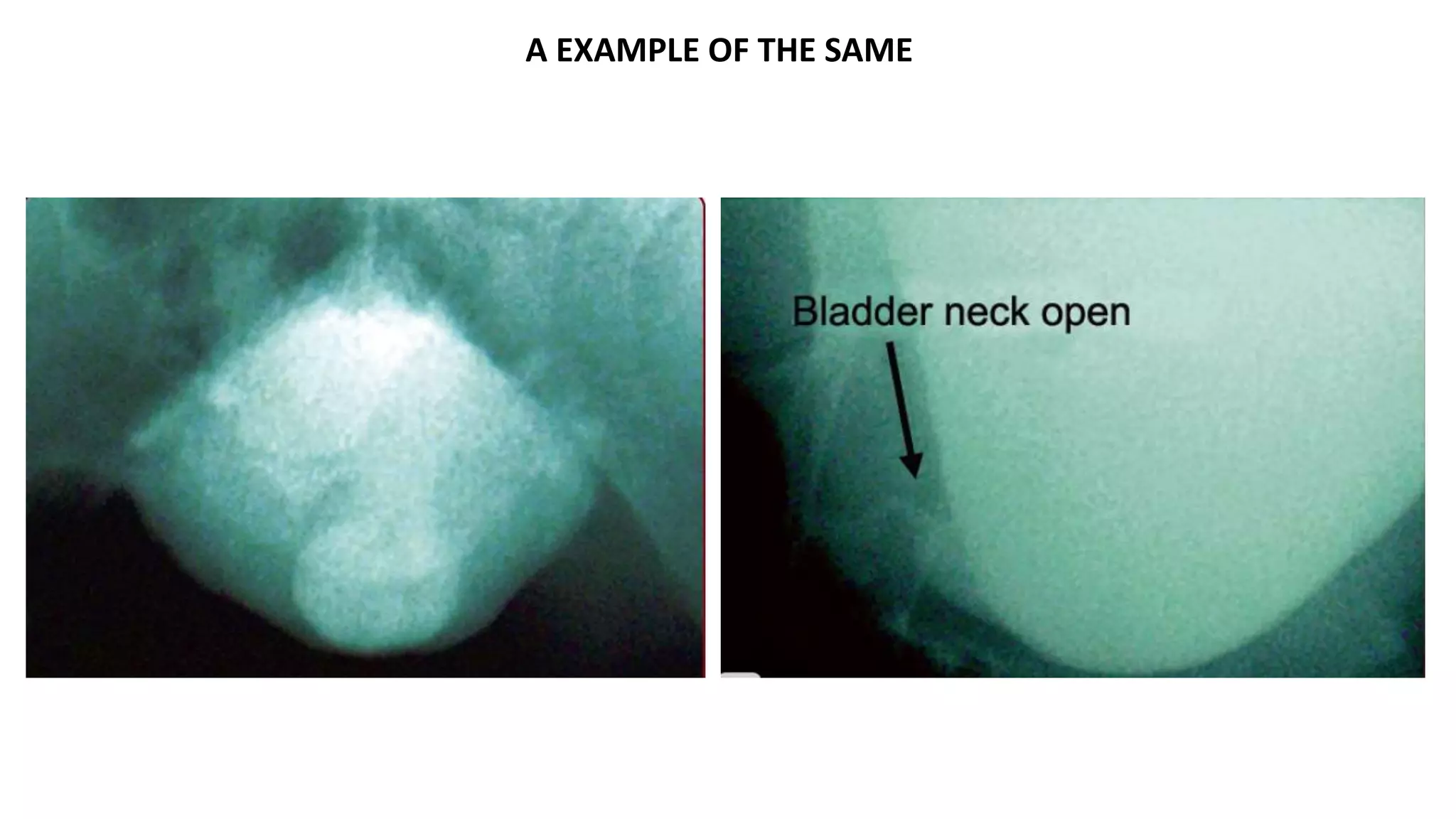
Urodynamic studies require specialized equipment setup to accurately measure pressures and flows in the bladder and urethra. The key components include:
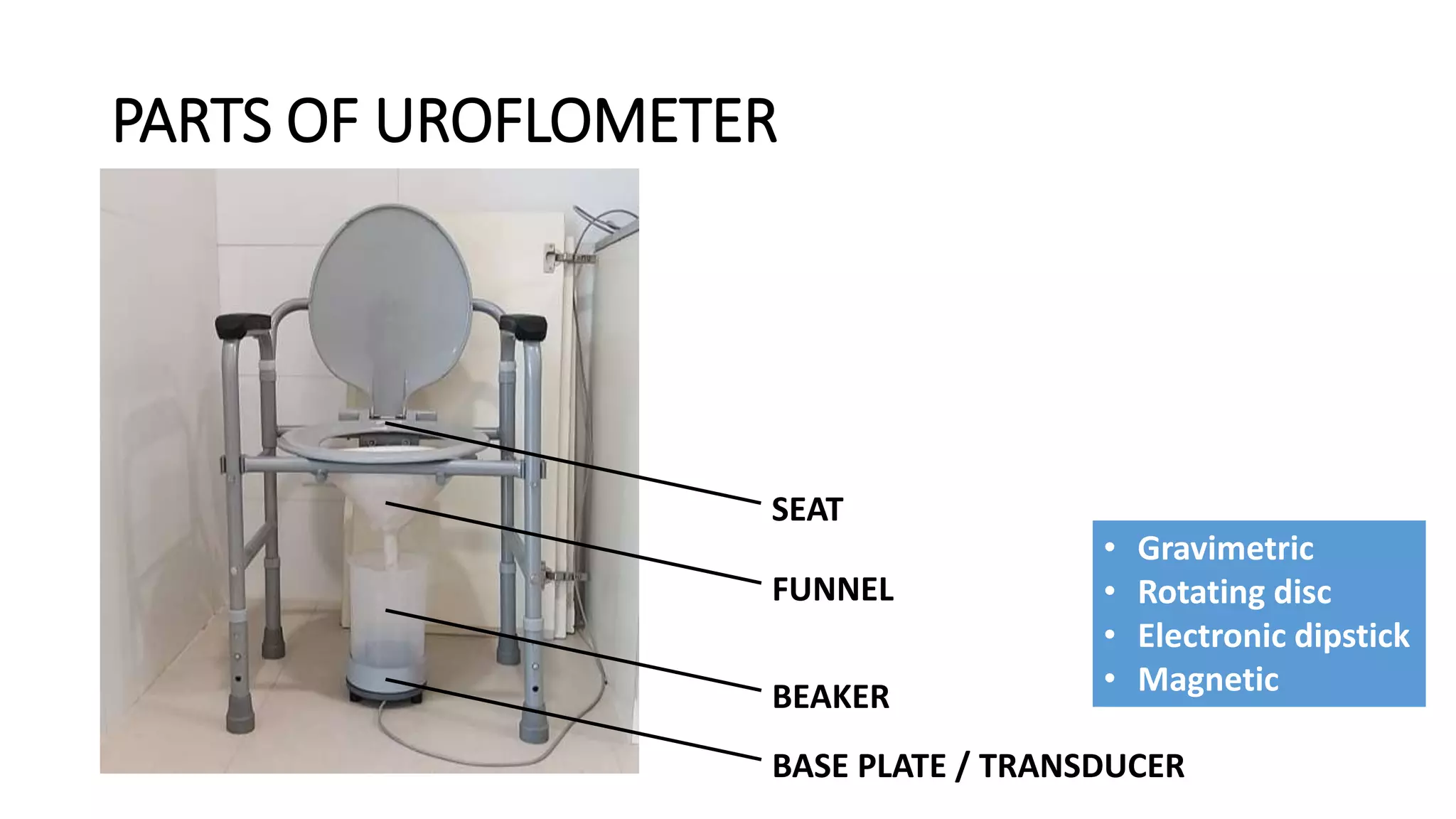
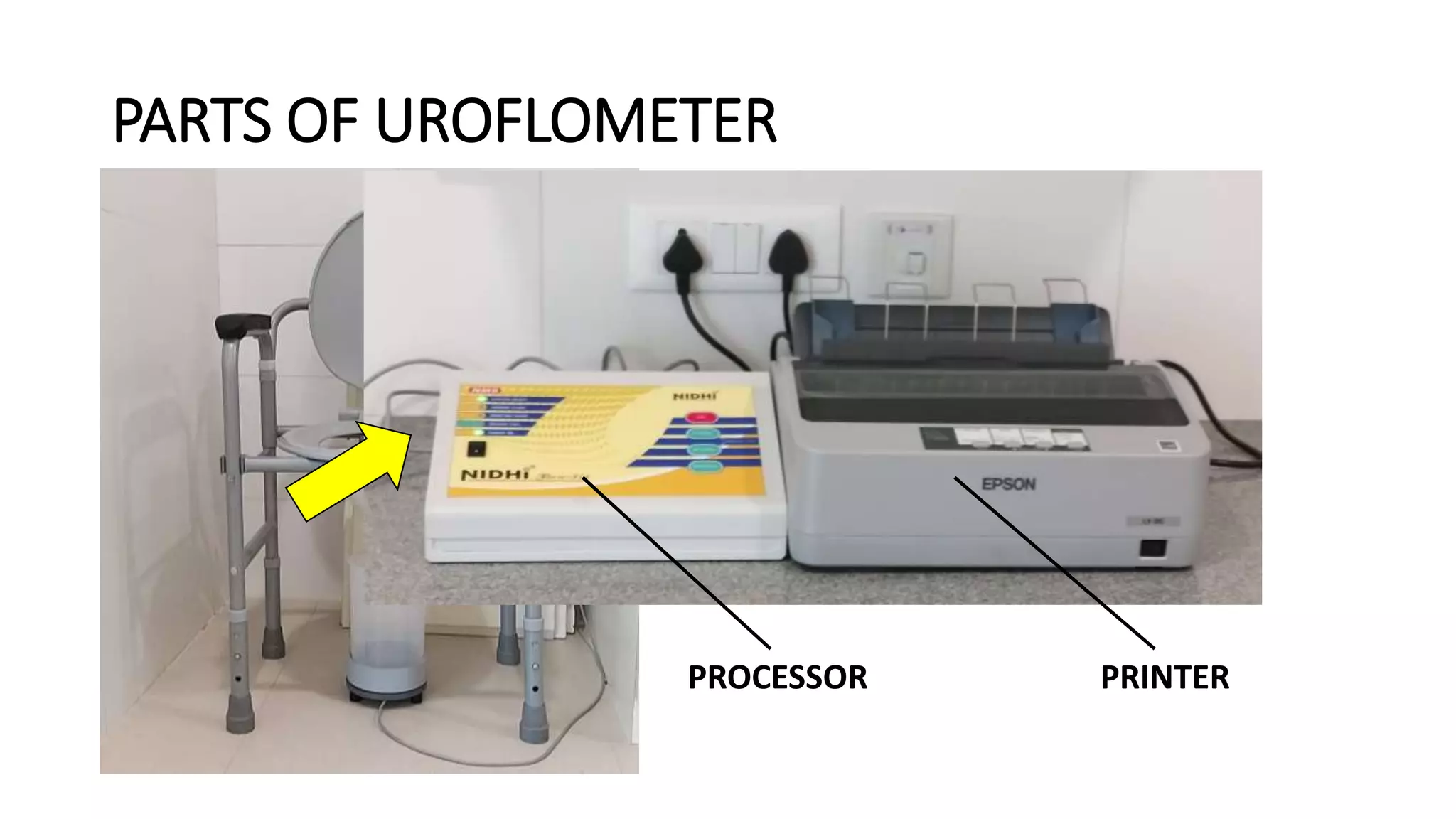
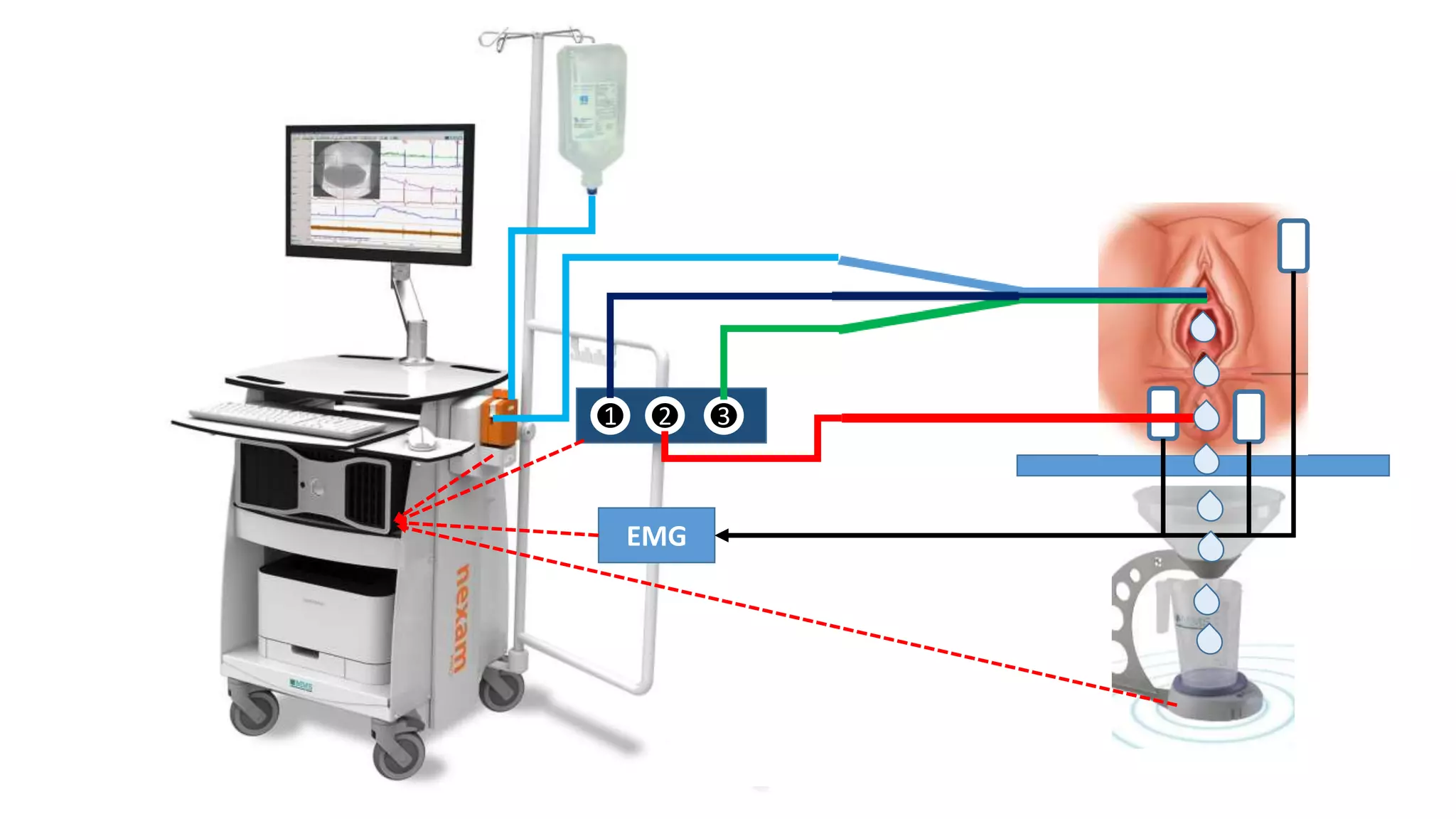
1. A uroflowmeter consisting of a base plate, funnel, and processor to measure voiding flow rates.
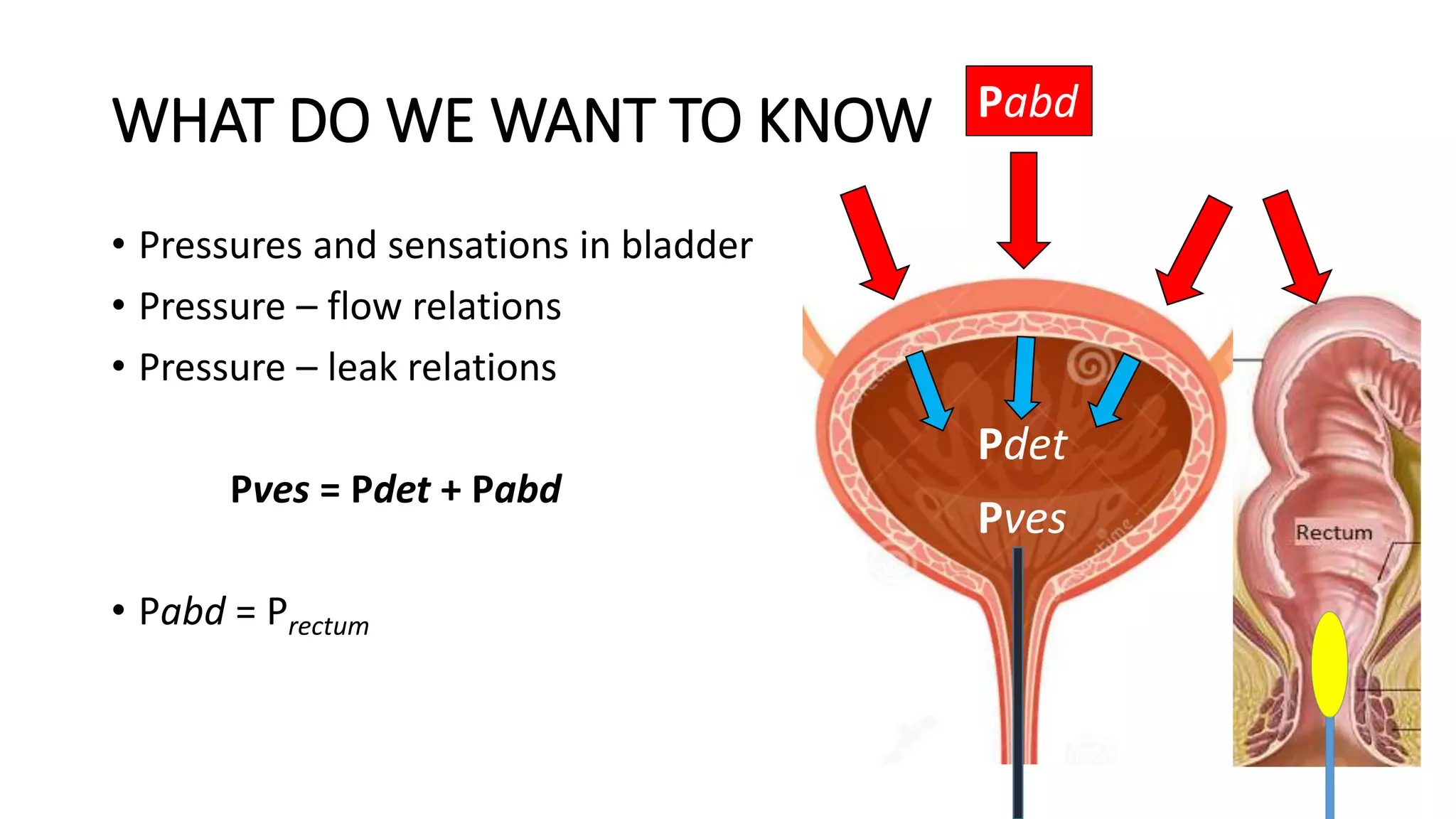
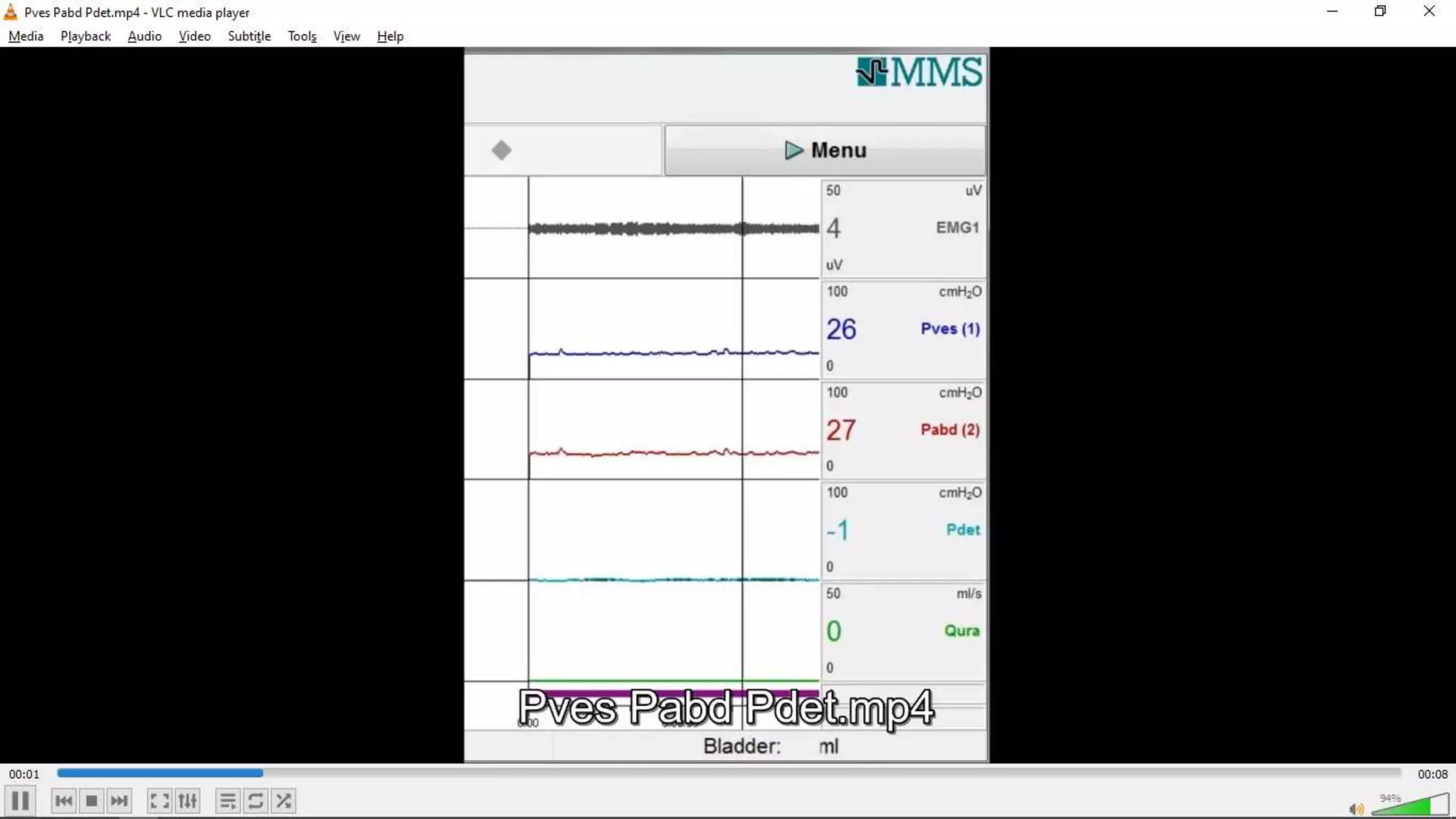
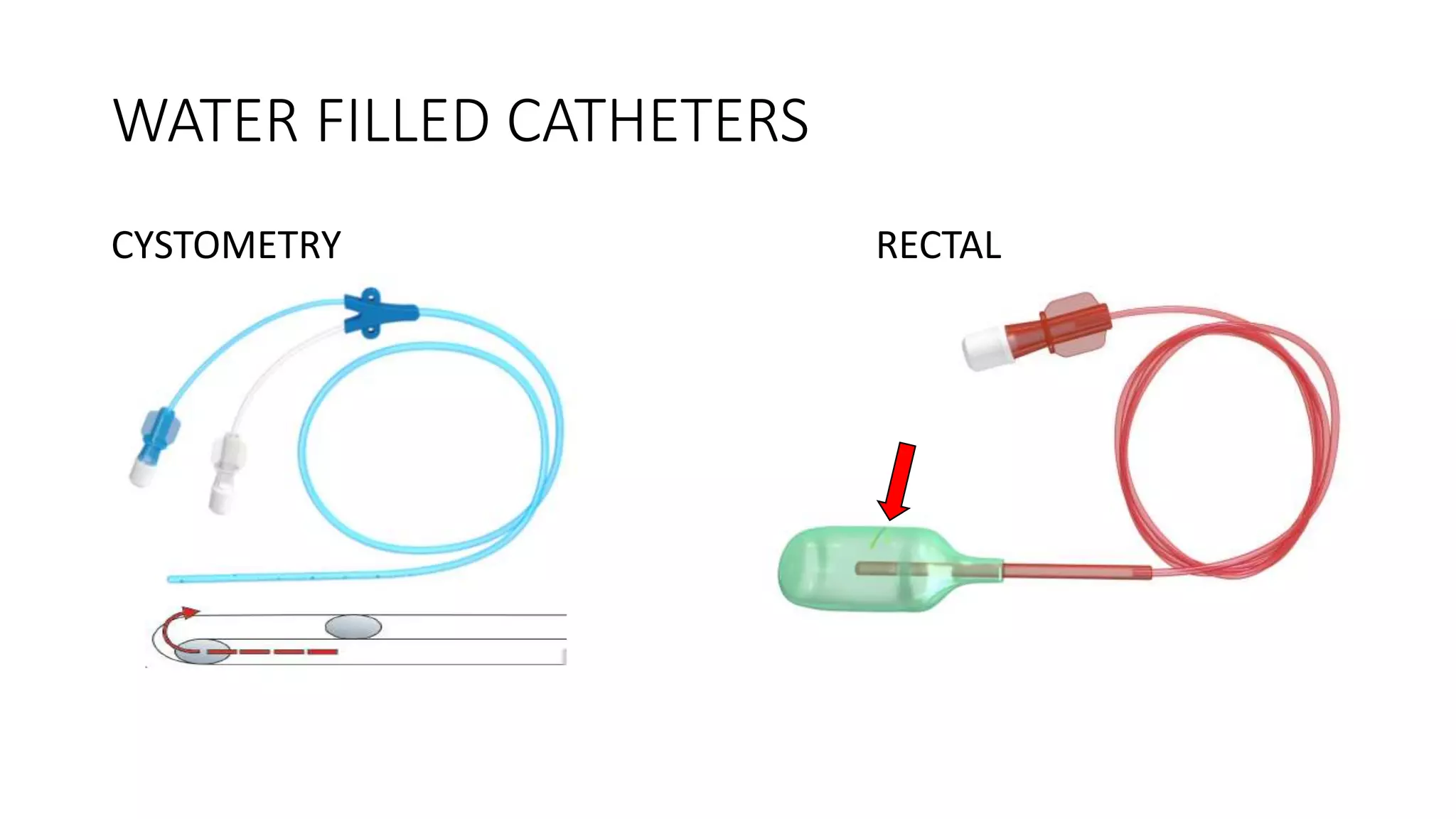
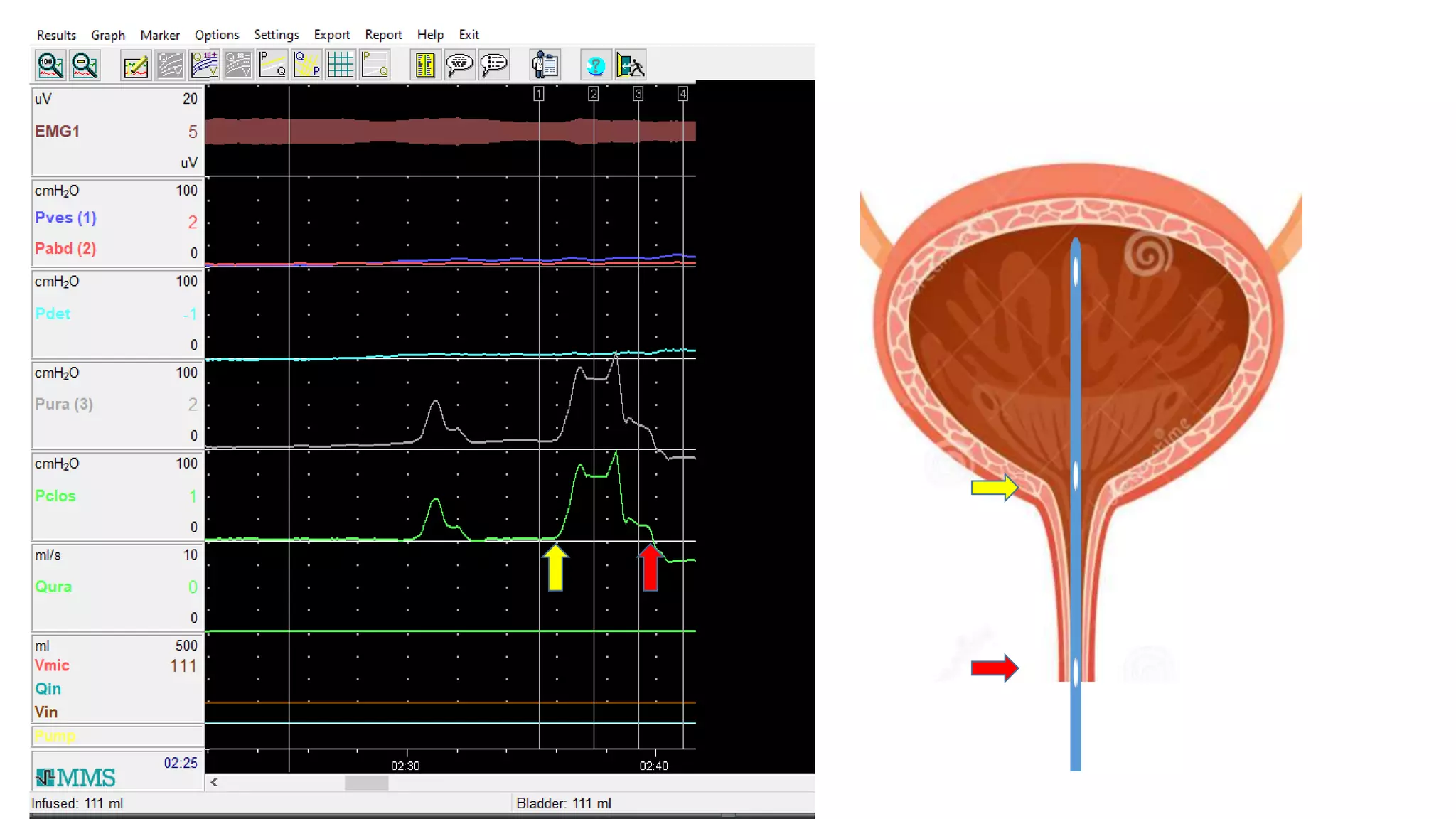
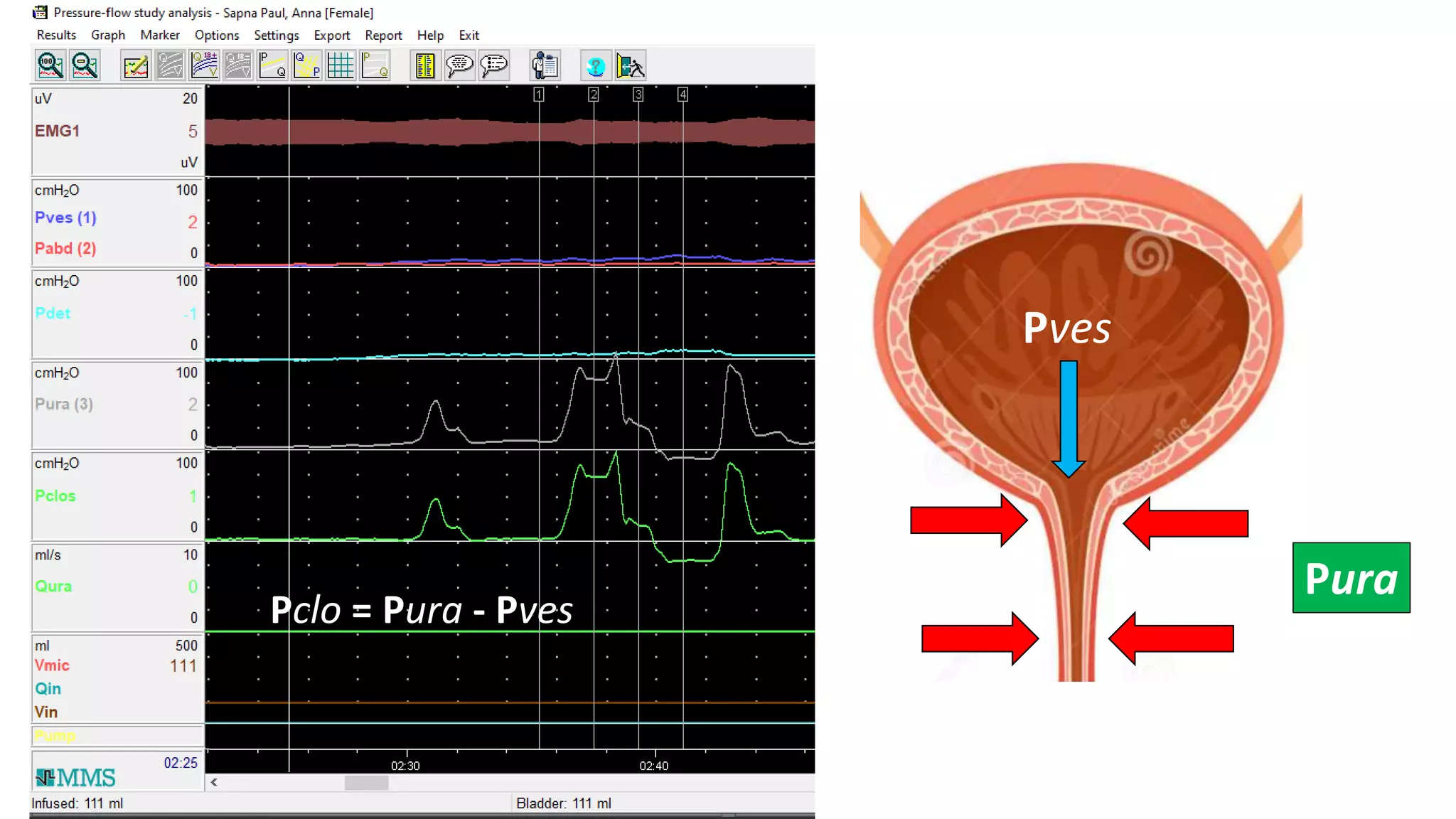
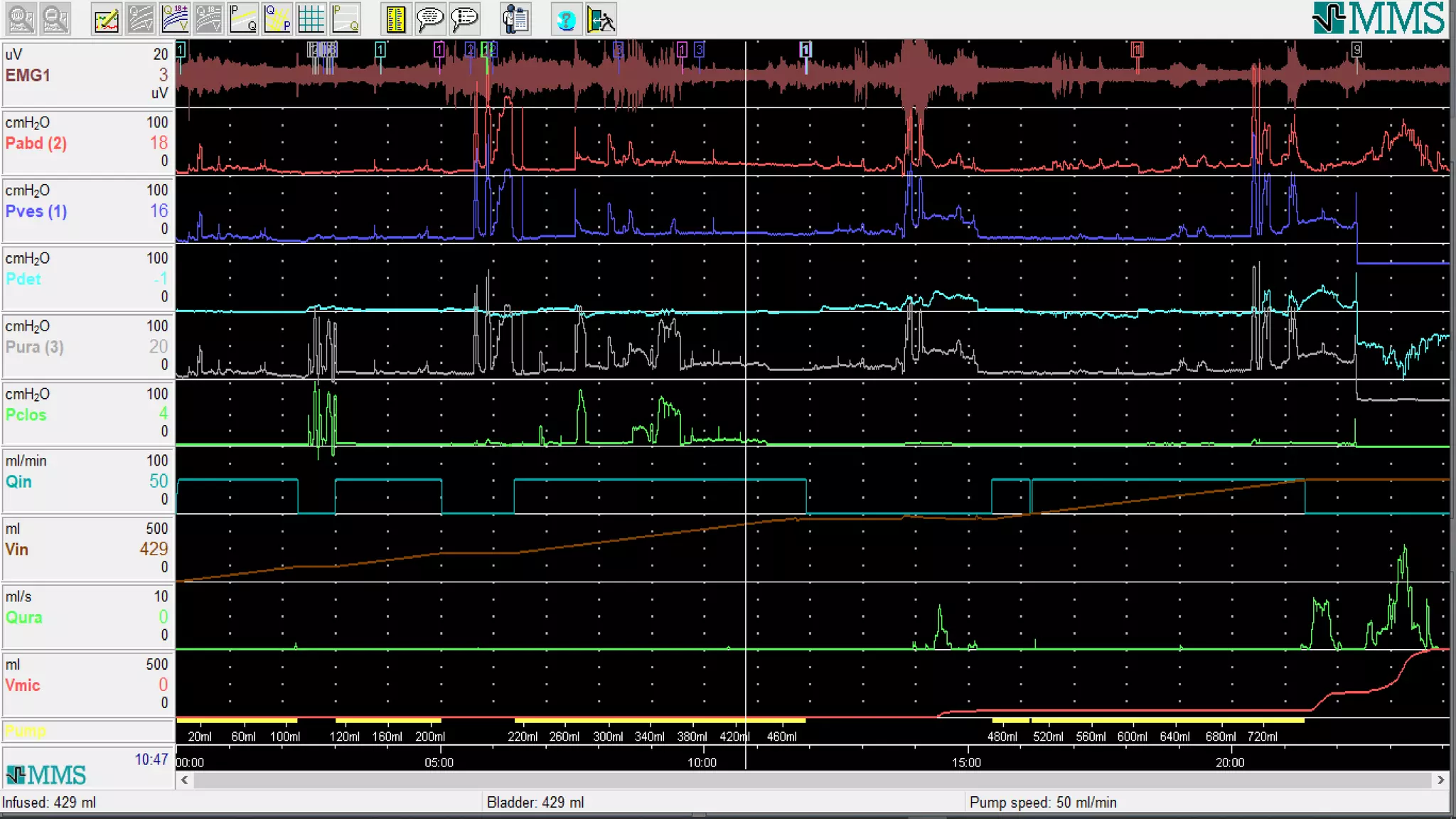
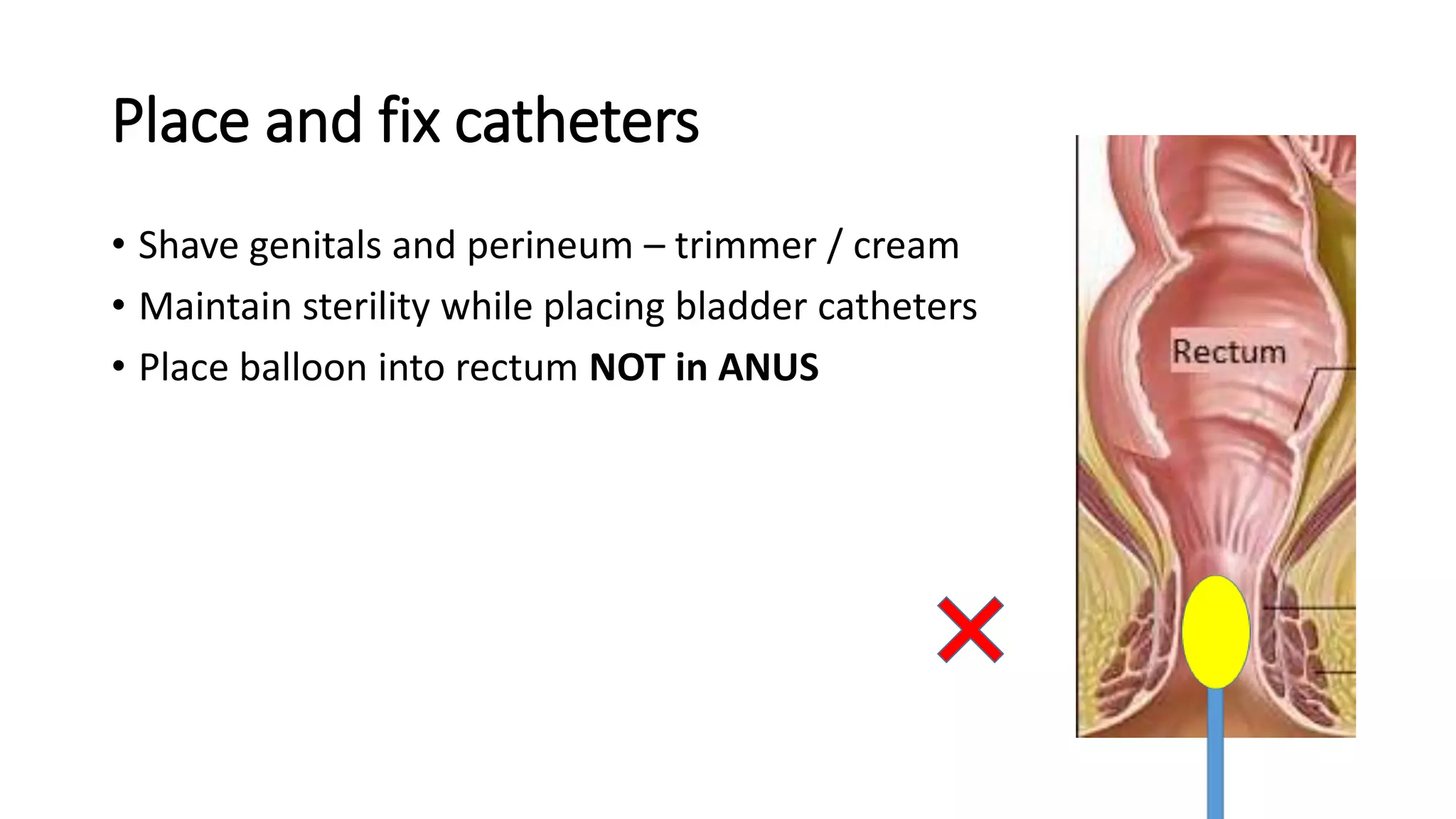
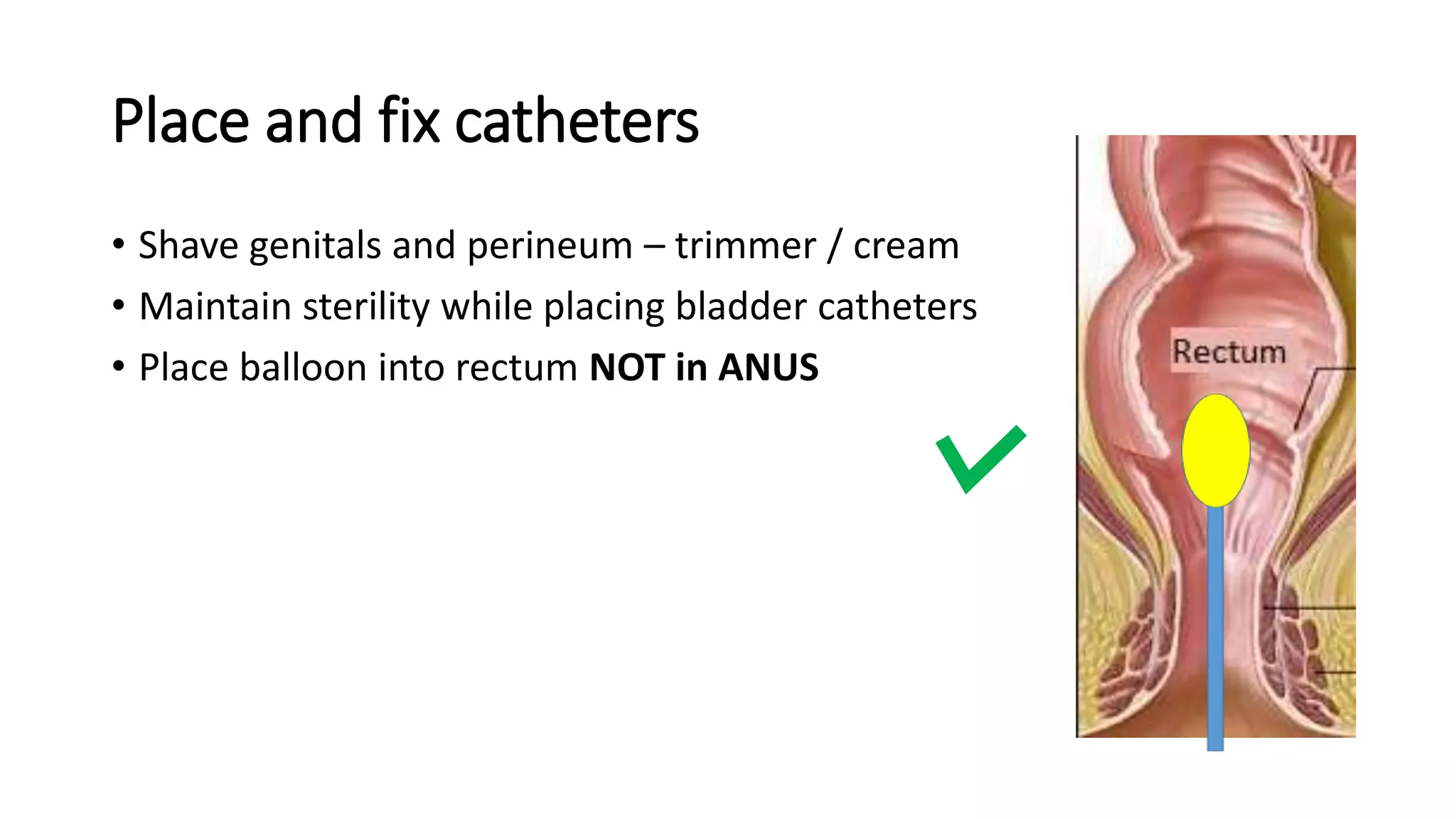
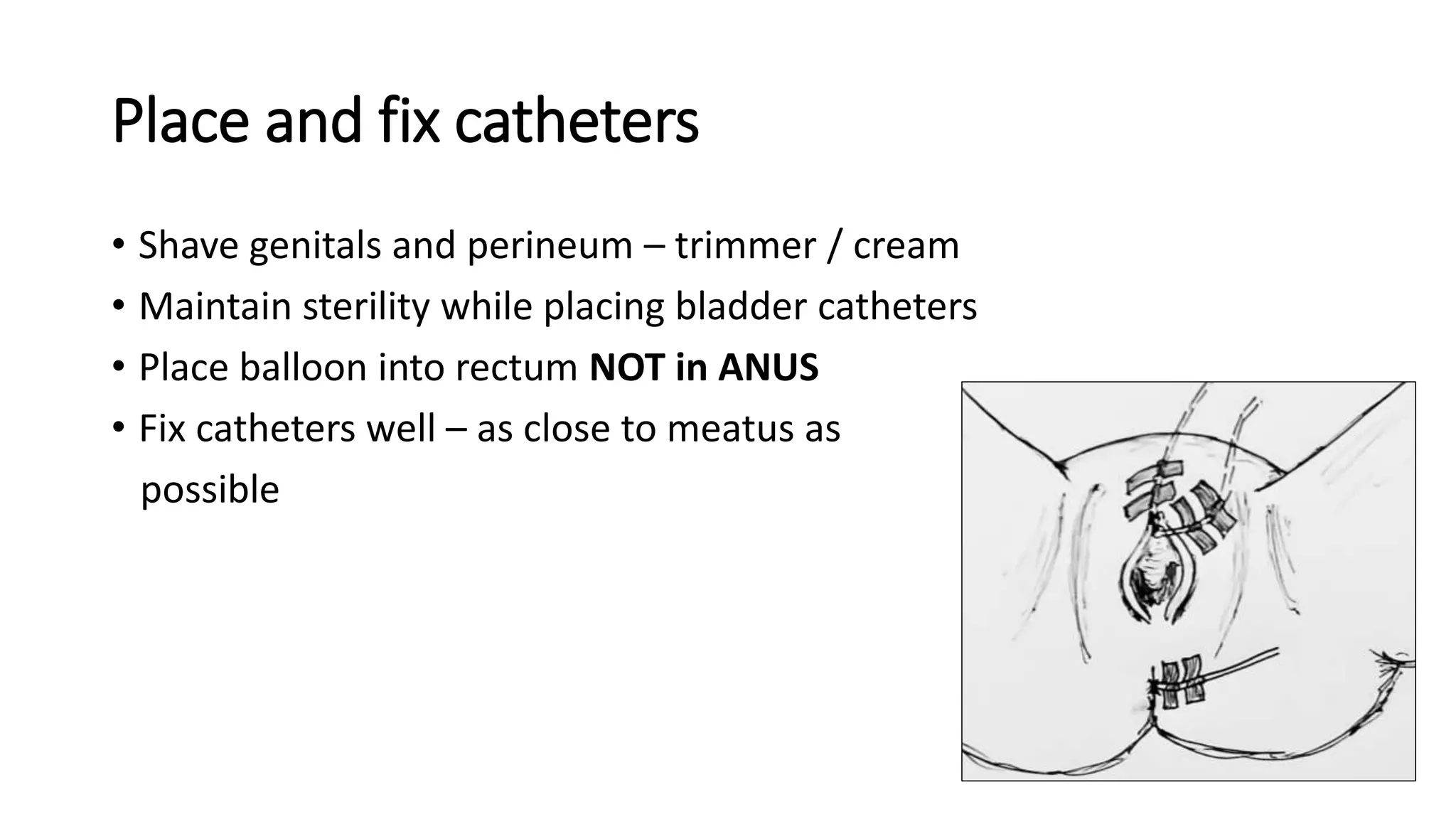
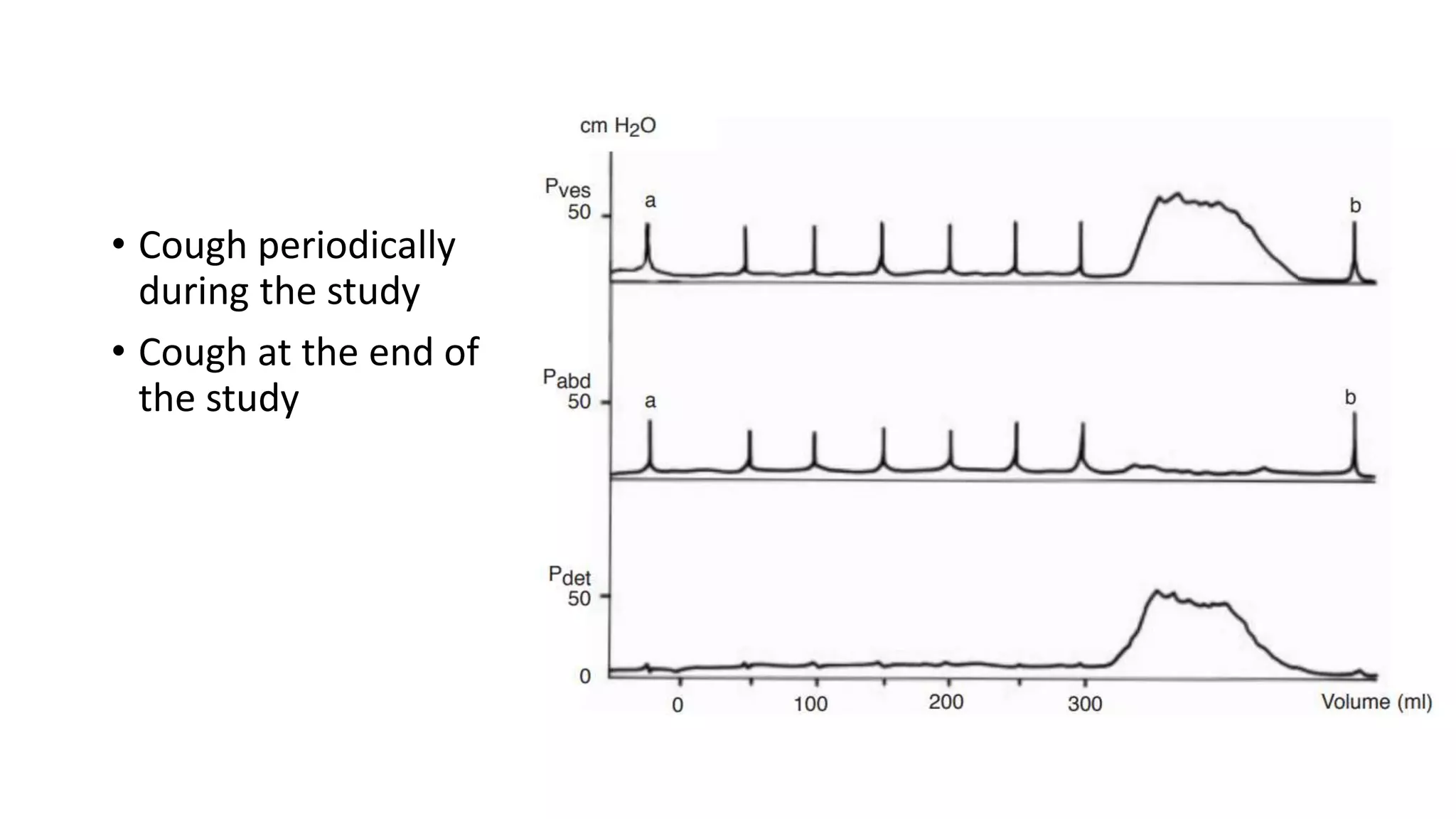
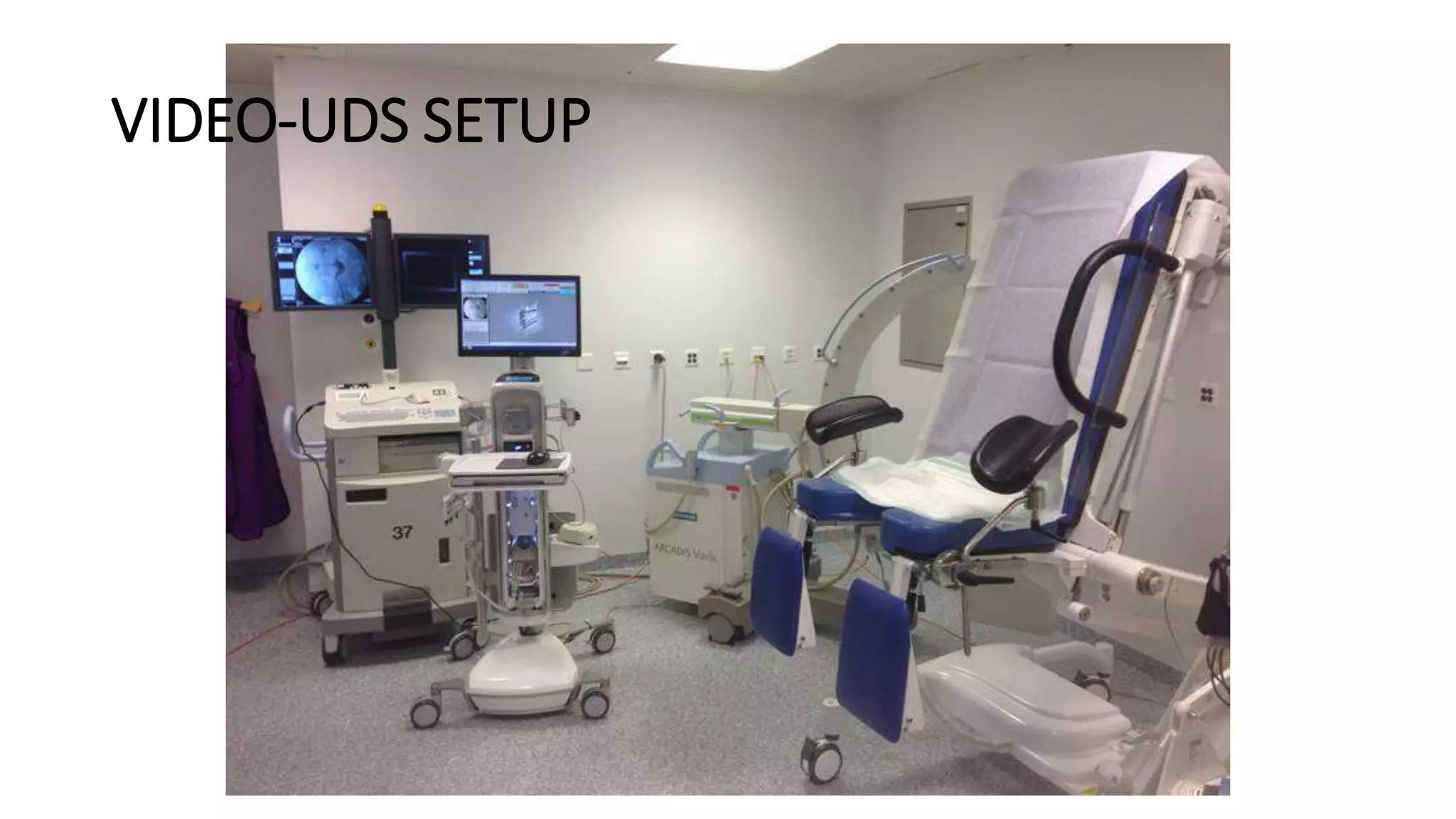
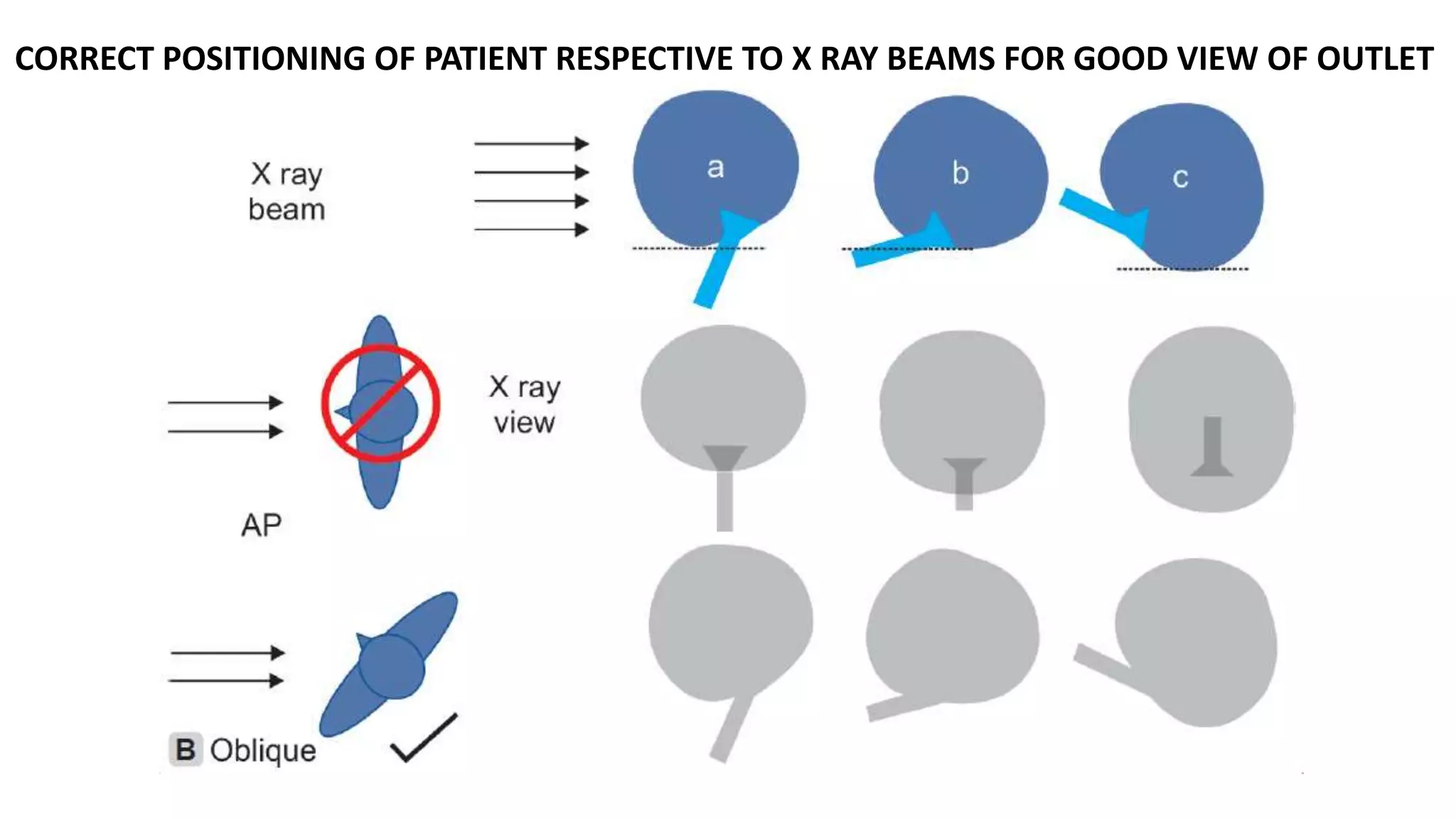
2. A multichannel urodynamics system using fluid or air-filled catheters placed in the bladder, rectum, and urethra to measure pressures during filling and voiding.
3. Electromyography electrodes to measure pelvic floor muscle activity.
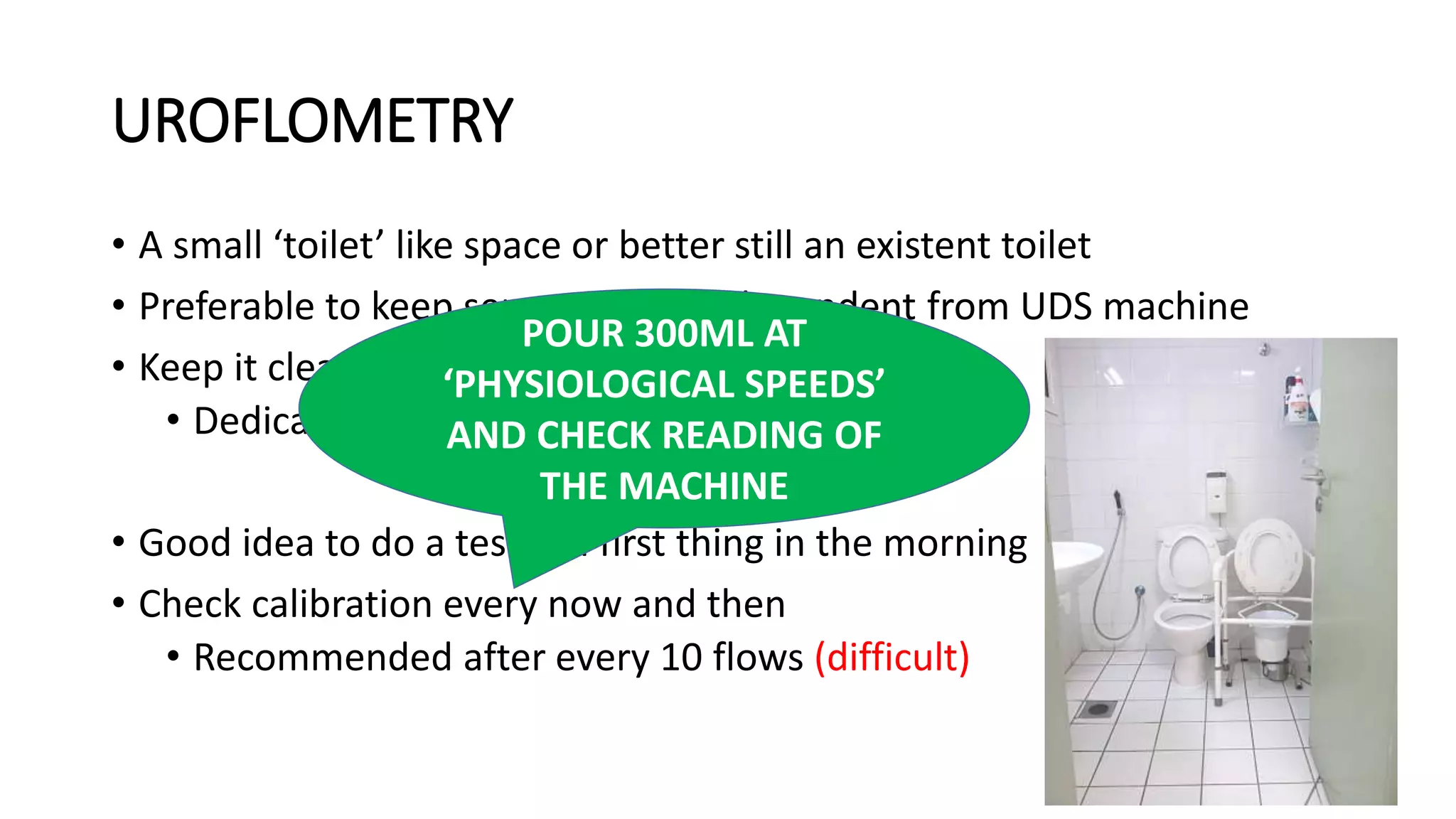
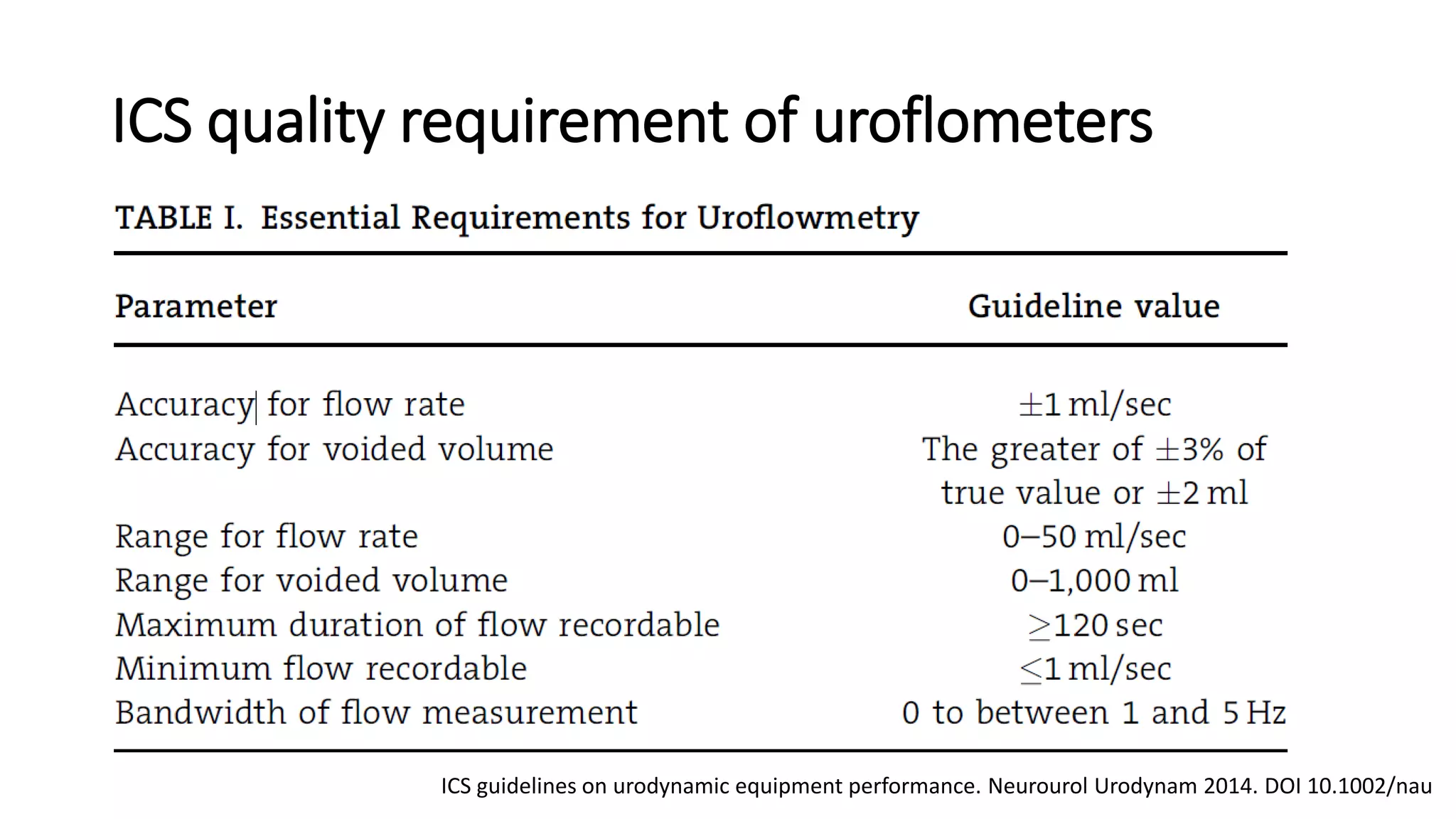
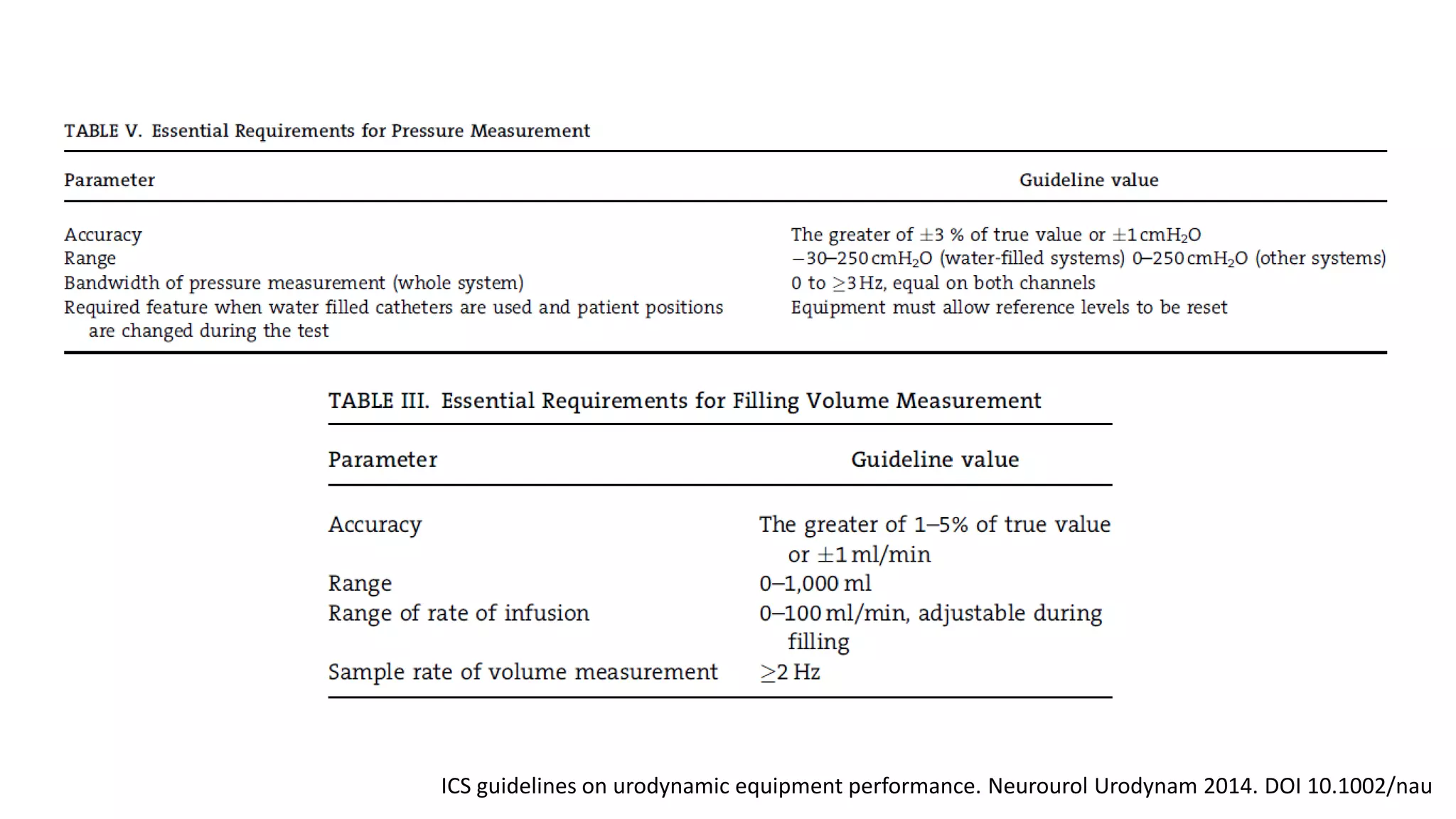
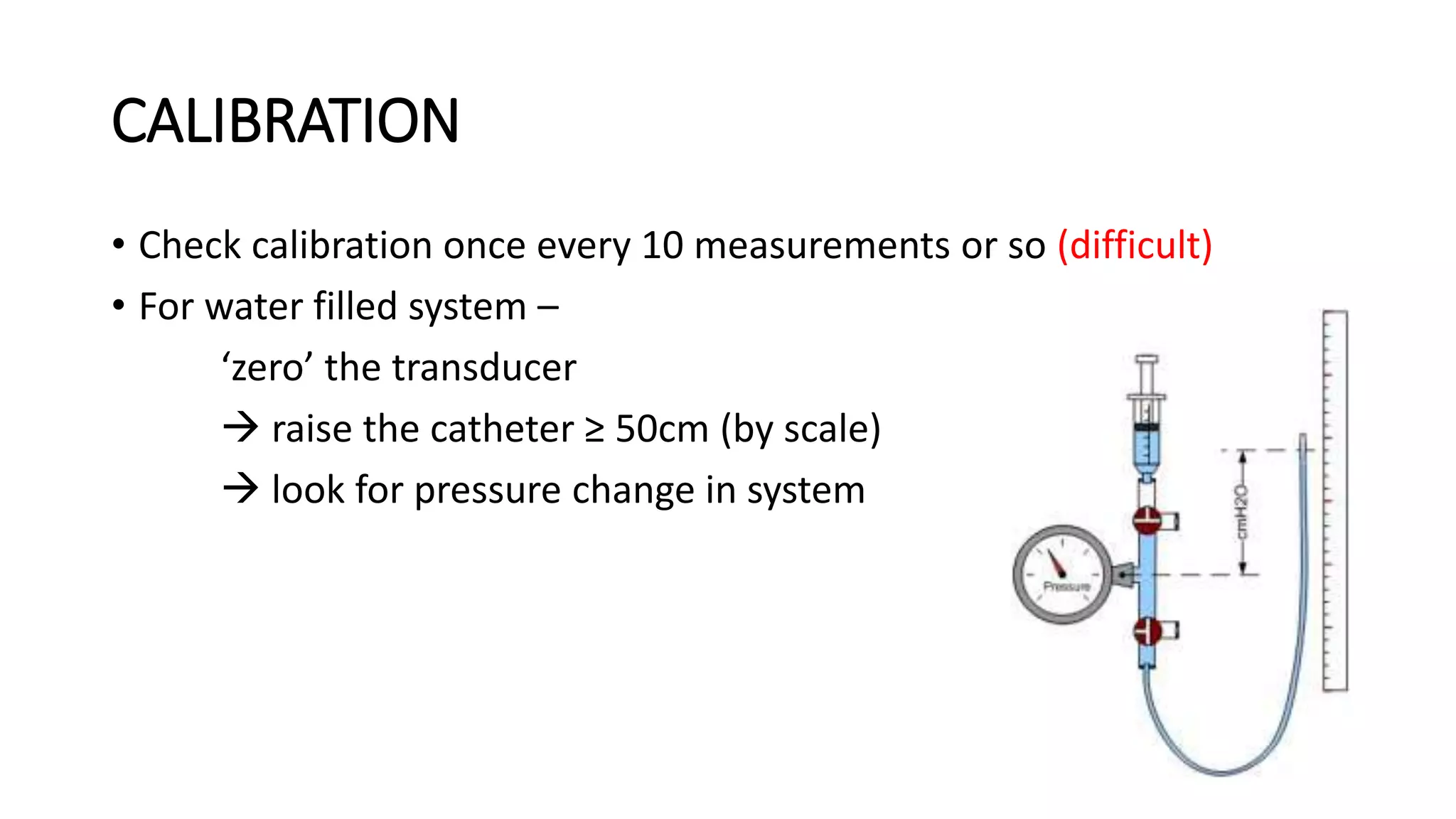
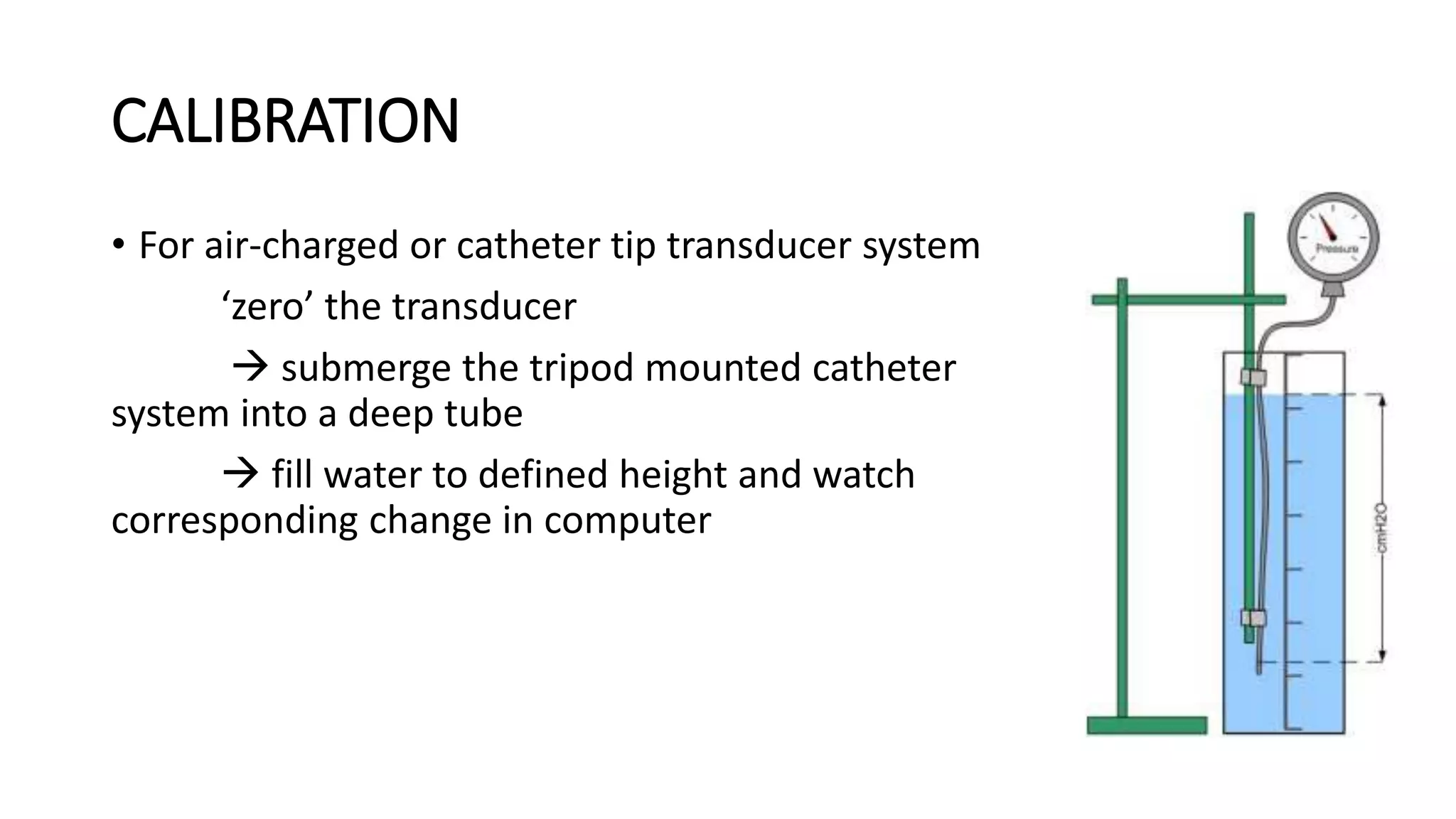
Proper calibration and maintenance of equipment is important for quality results. A private, clean testing environment helps patients relax for representative readings.