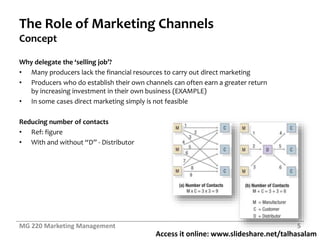
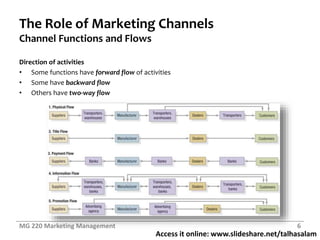
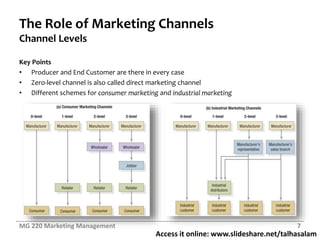
This document contains slides from a marketing management class discussing marketing channels and value networks. It covers topics like the importance of channels, channel functions and flows, channel design decisions, and channel management. Specifically, it discusses how companies develop channel systems as they grow, the concept of hybrid channels, value networks, enterprise resource planning systems, analyzing customer service needs, identifying channel alternatives, and selecting, training and motivating channel members. The overall document provides an overview of key concepts regarding how companies design and manage their marketing channels.