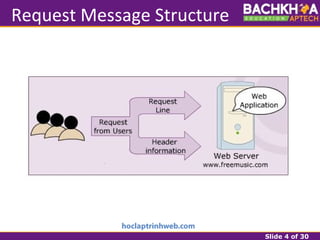
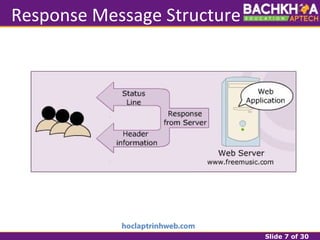
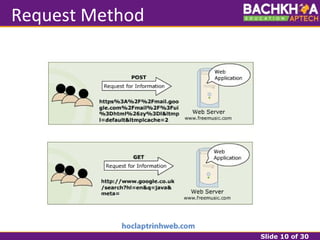
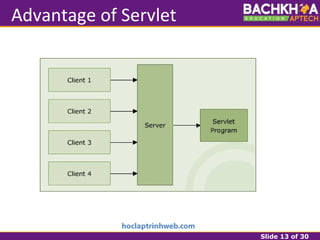
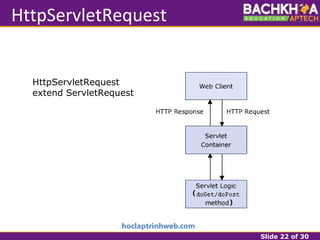
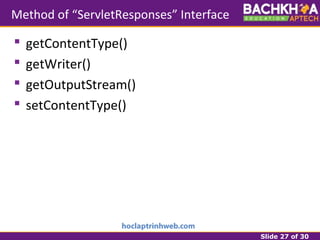
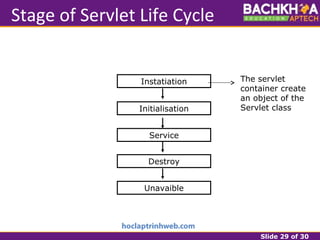
This document provides an overview of web applications and servlet requests and responses. It discusses the client-server model, advantages of web applications, the structure of request and response messages, common request methods, the servlet API, and the lifecycle of servlets. Key topics covered include how servlets are used to add dynamic content to web servers, the roles of GenericServlet, HttpServlet, ServletRequest, ServletResponse, and how servlets handle requests and construct responses.