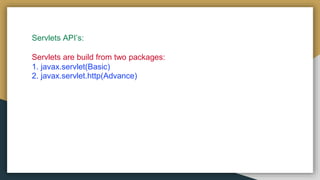
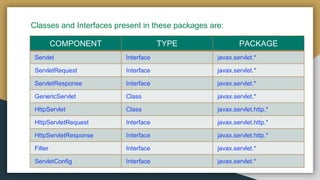
This document provides an introduction to Java servlets, explaining their role in handling web server requests and generating responses. It contrasts servlets with Common Gateway Interface (CGI), highlighting servlets' efficiency, portability, and ability to manage client state without creating new processes for each request. Additionally, it outlines servlet architecture, advantages, and the services provided by servlet containers.