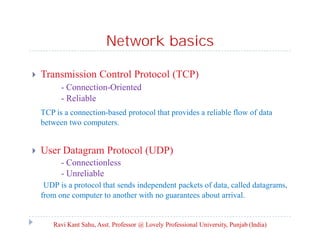
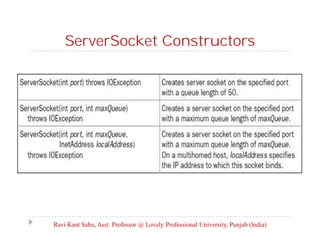
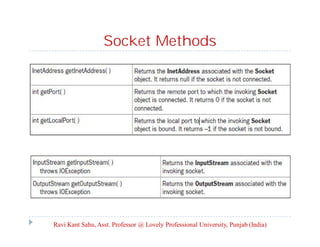
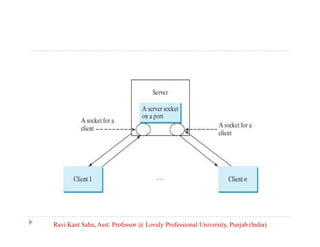
This document discusses advanced Java programming topics related to networking. It covers network basics like TCP, UDP, IP addresses and ports. It then discusses client-server architecture and how sockets are used for communication. It explains how to create server and client sockets and handle multiple clients. It also discusses how to send and receive objects and provides an overview of the Java Mail API for sending emails.





















![Steps to send email using JavaMail API
3. Send the message
The javax.mail.Transport class provides method to send the
message.
public static void send(Message message)
public static void send(Message message, Address [] address)
Ravi Kant Sahu, Asst. Professor @ Lovely Professional University, Punjab (India)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/networking-131130064002-phpapp02/85/Networking-27-320.jpg)
