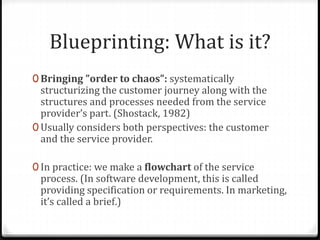
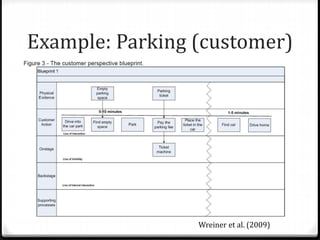
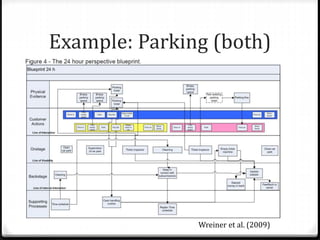
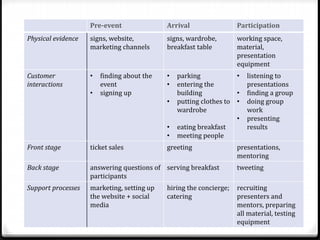
The document outlines the concept of service design, which involves planning and organizing components of a service to enhance quality and user experience. It introduces the blueprinting technique for structuring customer journeys and highlights the importance of physical evidence, customer actions, and support processes in delivering effective services. The document also provides a step-by-step blueprinting process and examples of service design applications across various industries.








![[Help: Customer personas]
0 Customer personas = idealized characterizations of
the intended customers; usually written down as a
profile with demographic and psychographic details.
(E.g., does he/she want quick or thorough service? Is
he pleased with high/low automatization? What
channels for service provision does he/she prefer?)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serviceblueprinting-150228015432-conversion-gate02/85/Service-blueprinting-Service-Jam-2015-13-320.jpg)
![[Help: Touchpoint analysis]
0 Make a SWOT on each individual touchpoint to better
understand its importance
0 Questions
0How important is this touch point relative to others?
0How to make sure expected quality is provided? (Or
surpassed, if that is the strategy.)
0What are the possible WOW moments and why?
0What are the possible fail points and why? (Fail point =
results in harm to the customer or the service provider.)
0When things go wrong, how to manage service recovery?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serviceblueprinting-150228015432-conversion-gate02/85/Service-blueprinting-Service-Jam-2015-14-320.jpg)