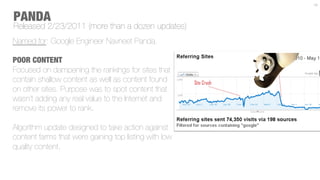
The document discusses the factors influencing Google's organic search algorithm, including off-page, on-page, and technical factors. It highlights the importance of links as a measure of popularity and trust, the role of spiders in indexing content, and the impact of frequent algorithm updates such as Panda and Penguin. It emphasizes creating quality, user-centered content to improve search rankings and maintain relevance in digital strategies.