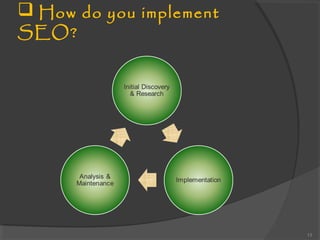
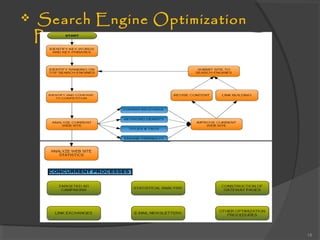
The document provides an overview of search engine optimization (SEO), detailing its definition, functioning, ranking factors, and benefits. It outlines the phases of SEO, such as discovery, implementation, and analysis, and highlights the distinction between organic and paid search engine strategies. Ultimately, it emphasizes that effective SEO increases website visibility and is essential for improving rankings in search engine results.