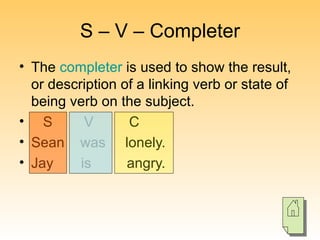
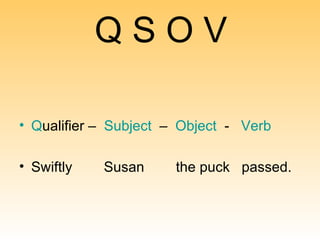
The document outlines the structure of English sentences, specifically focusing on the SVOQ (Subject-Verb-Object-Qualifier) model. It describes the roles of subjects, verbs, objects, and qualifiers, as well as how various combinations can create different sentence forms. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of sentence variety and the writing process, encouraging experimentation and revision.