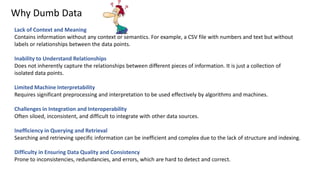
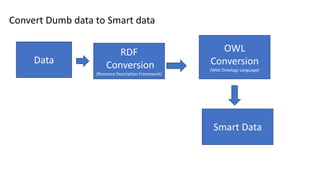
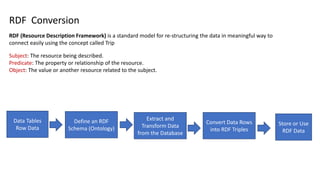
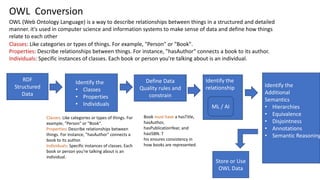
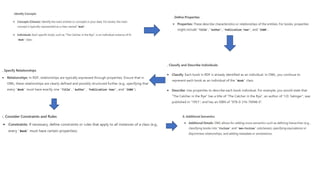
The document discusses the transformation of 'dumb data' into 'smart data' using RDF (Resource Description Framework) and OWL (Web Ontology Language) to enhance data quality, integration, and semantic meaning within organizations. It highlights the limitations of traditional data formats, including inefficiencies in querying, difficulty in ensuring data quality, and challenges in interoperability. By adopting RDF and OWL, organizations can create a unified data representation that improves understanding, reasoning, and knowledge management across different systems.