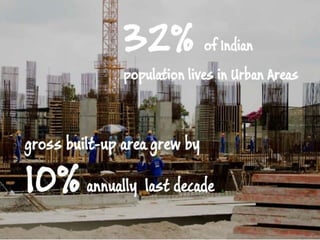
The document discusses the concept of green buildings, which aim to use less water, energy, and resources while generating less waste and providing healthier living spaces. It highlights the significant environmental impact of conventional buildings in India, including high energy consumption and waste generation during construction. Additionally, it outlines the benefits and obstacles of green building practices, as well as the GRIHA rating system for assessing environmental performance.