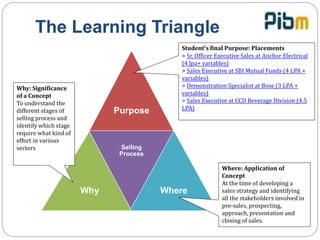
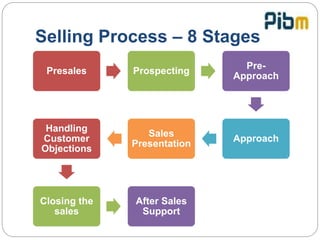
The document outlines the 8 key stages of the selling process: pre-sales, prospecting, pre-approach, approach, sales presentation, handling objections, closing the sale, and follow up/after sales support. It provides details on activities and considerations at each stage, including researching company/product knowledge, qualifying prospects, customizing strategies, focusing presentations on customer benefits, addressing objections, and following up for repeat business. The overall selling process aims to understand customer needs, effectively present products to meet those needs, resolve any concerns, finalize the sale, and ensure post-sale support.