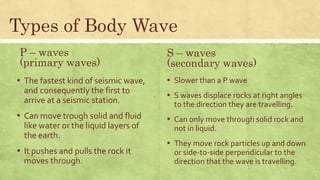
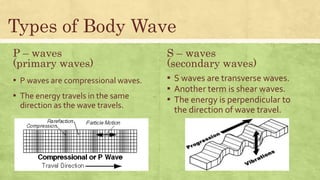
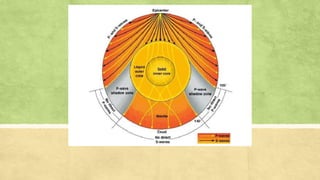
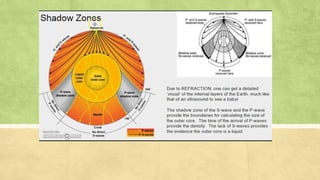
Seismic waves are waves of energy caused by earthquakes or explosions that travel through the earth or along its surface. There are two main types of seismic waves - body waves that travel through the earth's interior and surface waves that travel along the surface. P-waves are the fastest body waves and arrive first, followed by S-waves. Rayleigh waves are the most destructive surface waves and cause most earthquake shaking by rolling along the ground up and down and side to side. Observations of seismic wave speeds through the earth indicate that its interior consists of a solid rocky lithosphere and mantle, with liquid outer core and solid inner core.