The document discusses the key concepts of market segmentation, targeting, and positioning. It describes the three main steps as:
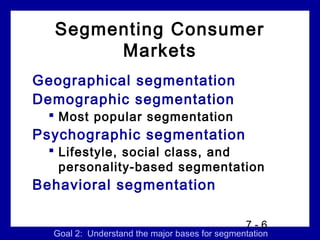
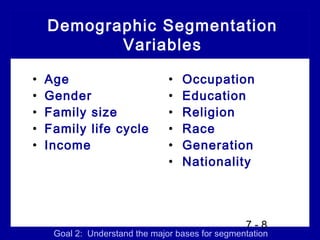
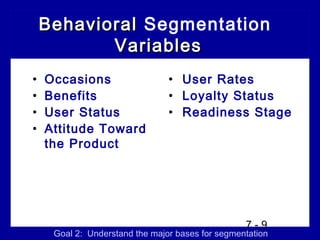
1) Market segmentation which involves dividing the market into distinct groups.
2) Target marketing which is selecting specific market segments to target. Companies evaluate segment attractiveness and select segments.
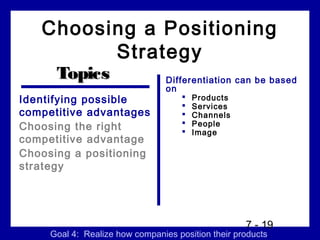
3) Market positioning which is developing a positioning strategy for targeted segments and a marketing mix to communicate the brand's position relative to competitors in customers' minds.