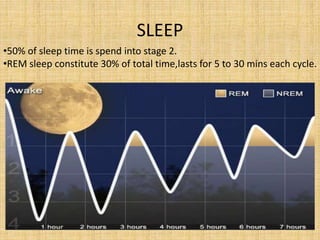
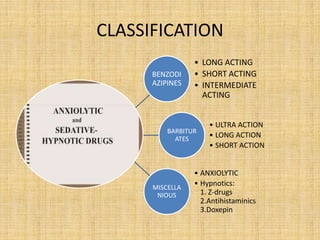
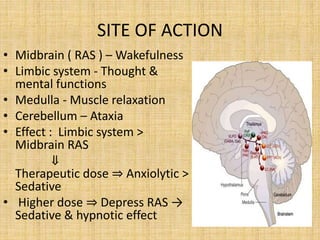
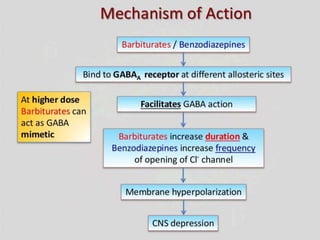
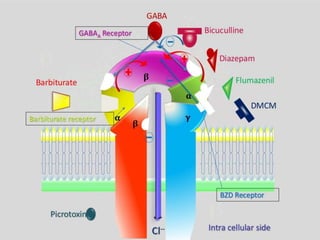
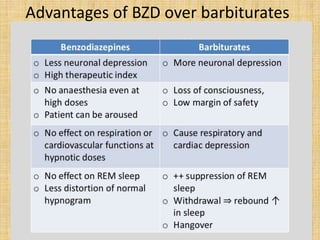
This document discusses sedatives and hypnotics, including their classification, mechanisms of action, and examples of commonly used drugs. It begins with an overview of sedatives, which reduce excitement and calm patients, and hypnotics, which produce sleep. The two main classes covered are barbiturates and benzodiazepines. Barbiturates were historically used but have higher risks, while benzodiazepines like diazepam are now preferred due to stronger safety profiles. Both classes work by enhancing the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA in the brain.