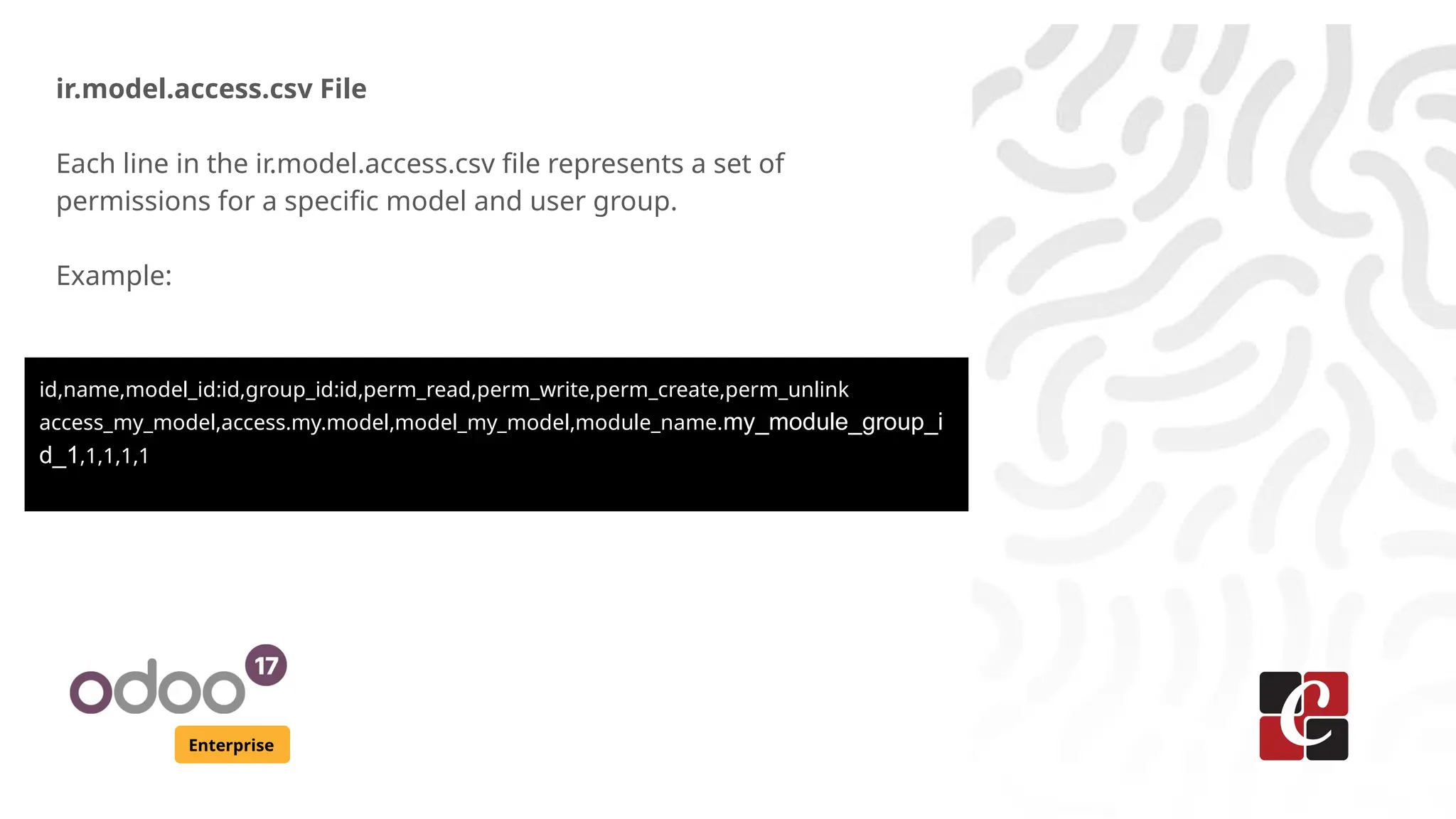
The document outlines the security framework in Odoo 17 Enterprise, focusing on user groups and access rights management. It details how to create user groups, assign access rights to control user actions, and implement security rules for record access based on user roles. Additionally, it provides steps for defining user groups and configuring access permissions using XML and CSV files.











![Enterprise
Let's break down each component of this example:
<record model="ir.rule" id="rule_name">
<field name="name">Rule Name</field>
<field name="model_id" ref="model_my_model_name"/>
<field name="global" eval="False"/>
<field name="domain_force">[('field_name', '=',
user.partner_id.field_name)]</field>
<field name="groups" eval="[(4, ref('module.group_name'))]"/>
</record>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitygroupsandaccessrightsinodoo17-240808090314-eed63692/75/Security-Groups-and-Access-Rights-in-Odoo-17-13-2048.jpg)


![Enterprise
● <field name="domain_force">[('field_name', '=',
user.partner_id.field_name)]</field>
This field defines the condition for the security rule using a
domain. The domain_force field specifies a domain expression
that restricts access to records based on conditions. Here,
('field_name', '=', user.partner_id.field_name) ensures that users
can only see records where field_name matches their
partner_id's field_name.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitygroupsandaccessrightsinodoo17-240808090314-eed63692/75/Security-Groups-and-Access-Rights-in-Odoo-17-16-2048.jpg)
![Enterprise
● <field name="groups" eval="[(4,
ref('module.group_name'))]"/>
This field assigns the security rule to specific user groups. The
groups field uses the eval attribute to evaluate a list of tuples.
The tuple (4, ref('module.group_name')) adds the group with the
external identifier module.group_name to the list of groups that
the rule applies to.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securitygroupsandaccessrightsinodoo17-240808090314-eed63692/75/Security-Groups-and-Access-Rights-in-Odoo-17-17-2048.jpg)

