The document discusses security engineering design guidelines and system survivability. It covers:
1) Design guidelines that help make secure design decisions and raise security awareness.
2) Guidelines for avoiding single points of failure, failing securely, balancing security and usability, and more.
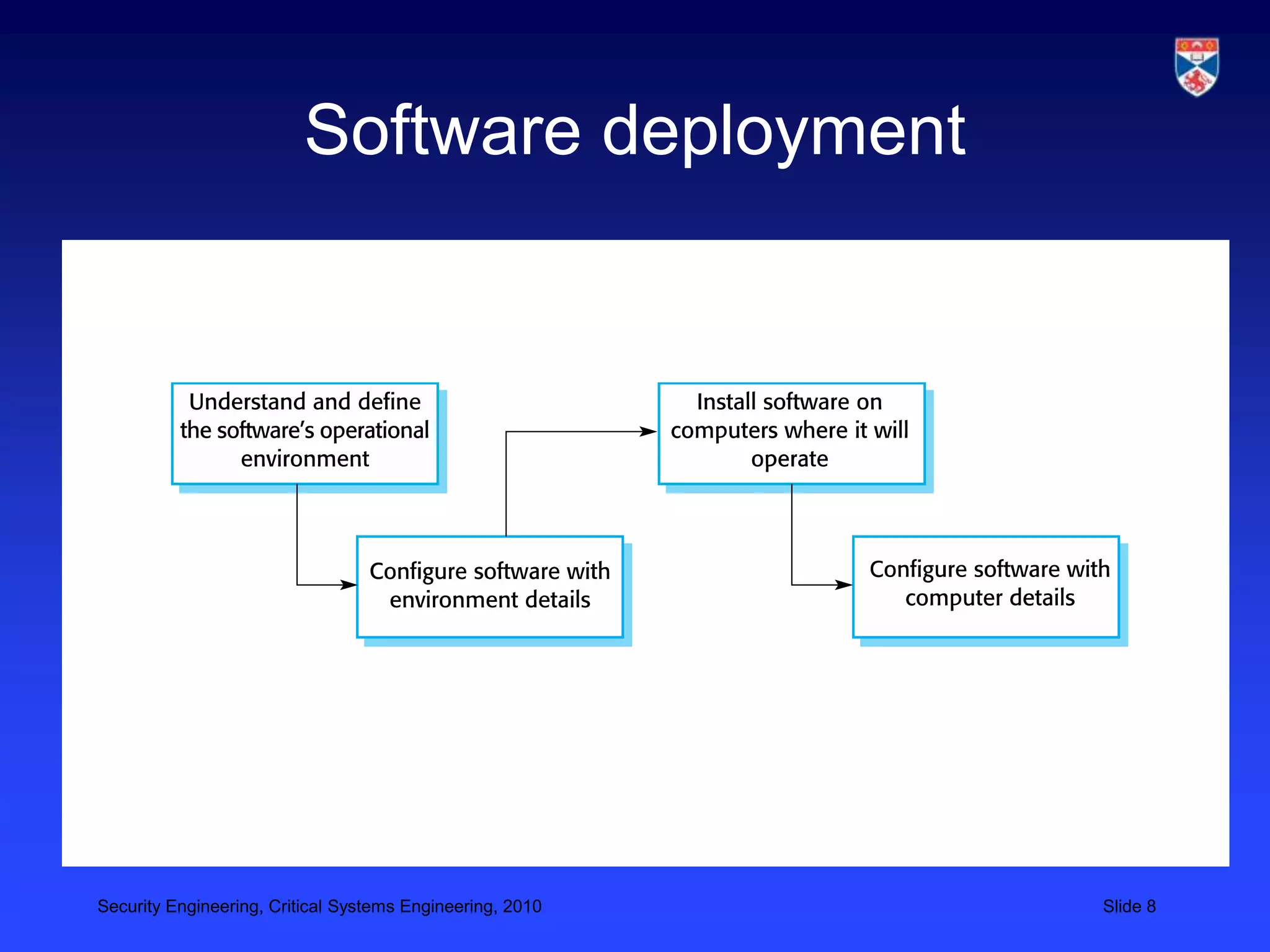
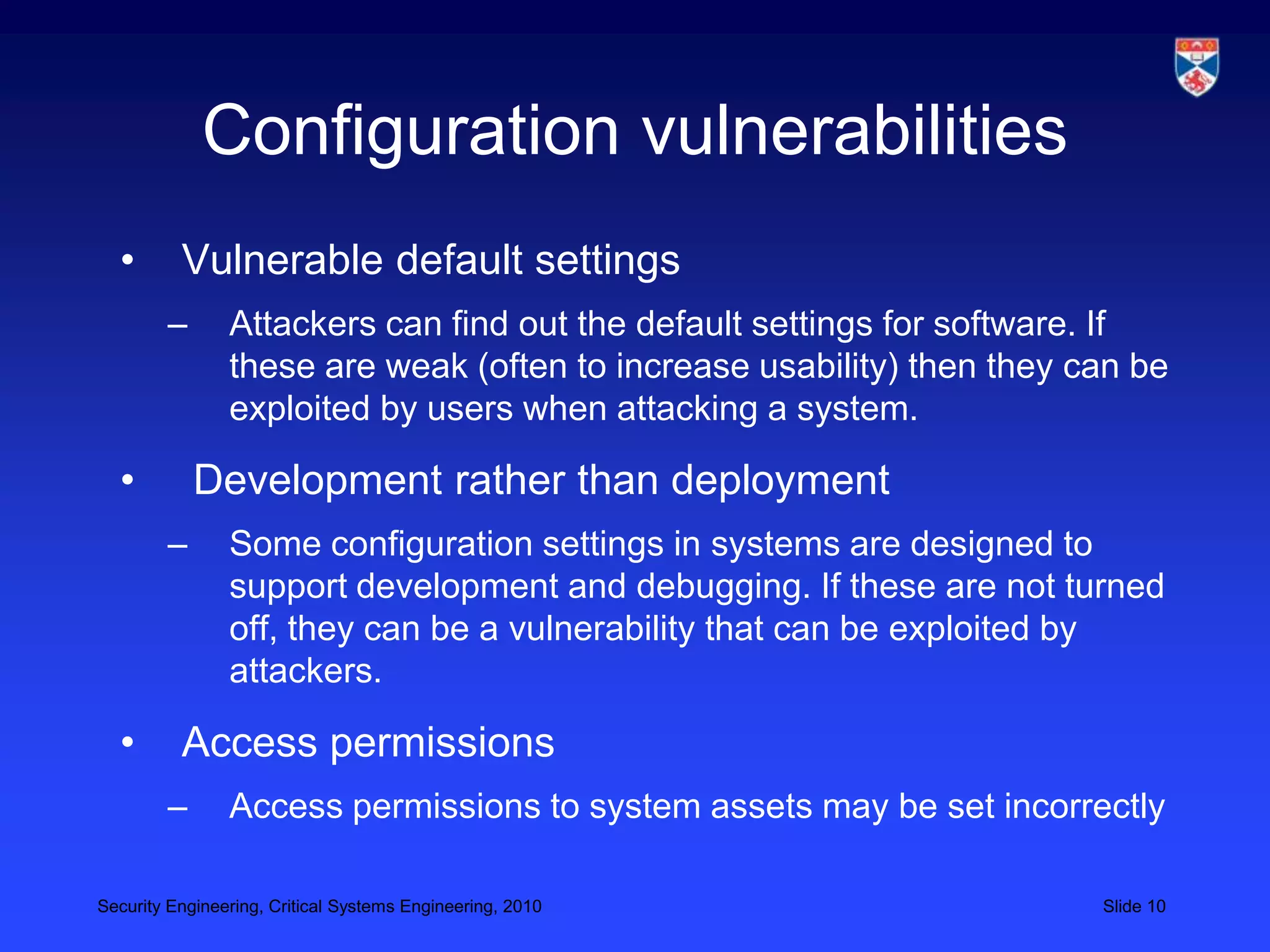
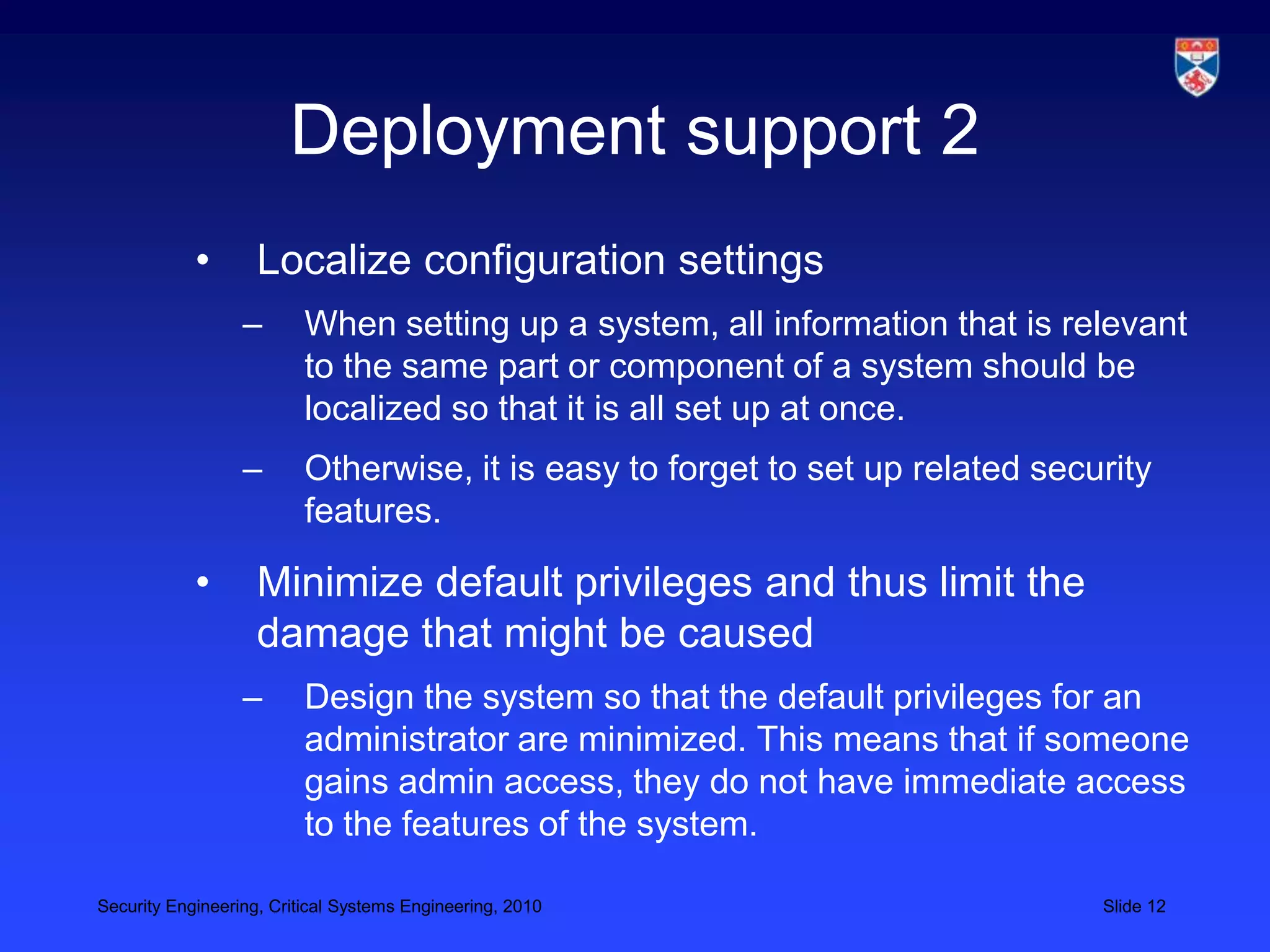
3) Designing for deployment to minimize vulnerabilities introduced during configuration and installation.
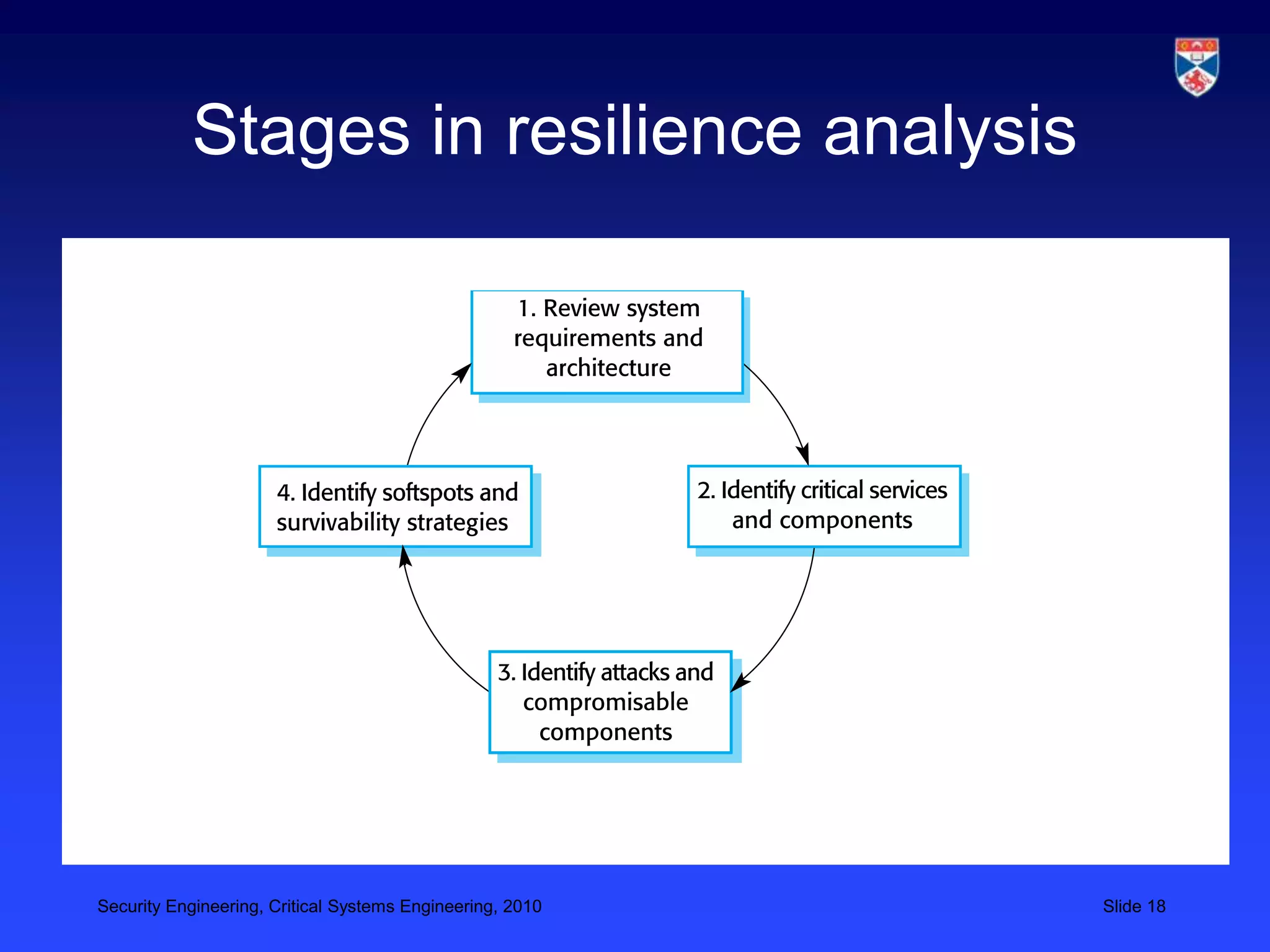
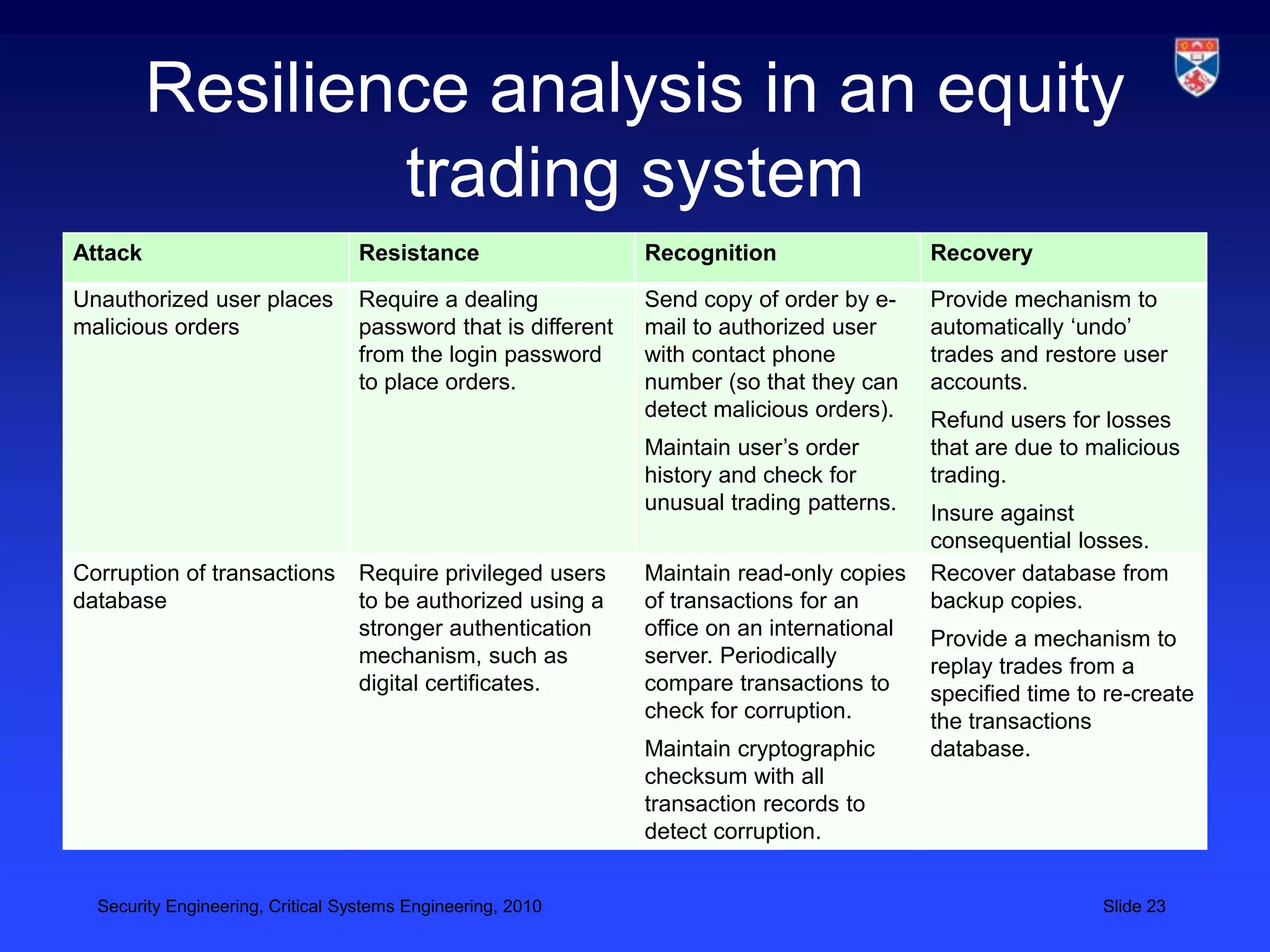
4) Ensuring systems can continue essential services when under attack through resilience and recoverability.