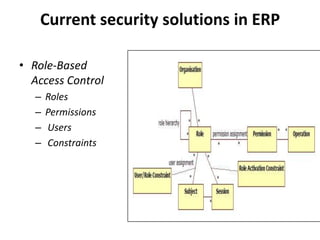
This document discusses security concerns with web-based ERP systems. It outlines several security issues including physical security, transmission security, storage security, access security, and data security. It also describes common security problems like resource protection, data confidentiality, and authentication. The document then provides an overview of ERP architecture and the typical 3-tier architecture before examining current security solutions like role-based access control. It analyzes security in SAP/R3 systems and proposes an open security model for the future.