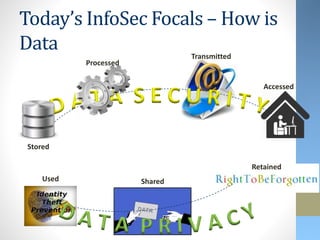
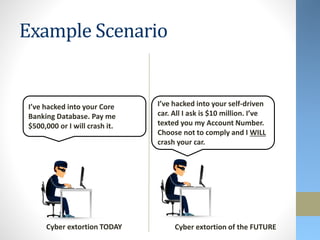
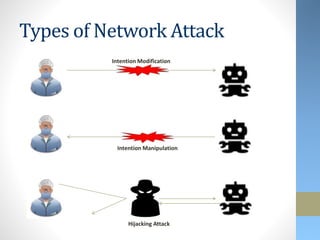
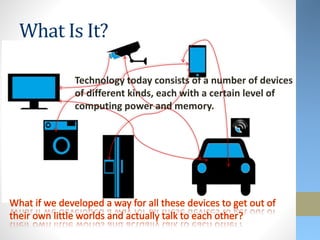
This document discusses emerging security challenges with new technologies. It begins with an overview of how information security has evolved from a focus on confidentiality to also include integrity and availability. Four emerging technologies are then examined: robotics, 3D printing, the Internet of Things, and wearables. Each section identifies applications of the technology and discusses associated security risks. For example, robotic systems could be hacked and manipulated to cause physical harm. The document emphasizes that security needs to be considered from the early design stages of new technologies and provides some approaches to help secure them.