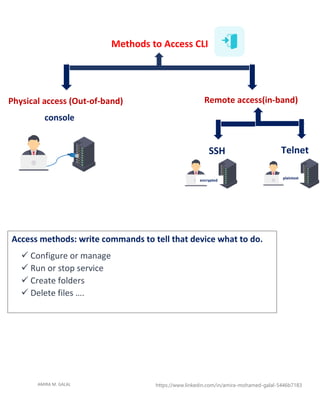
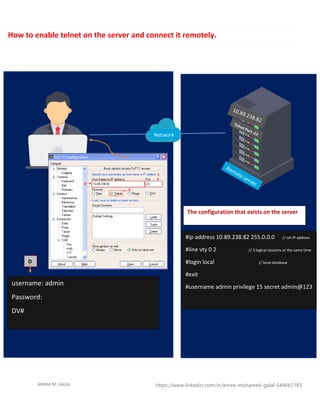
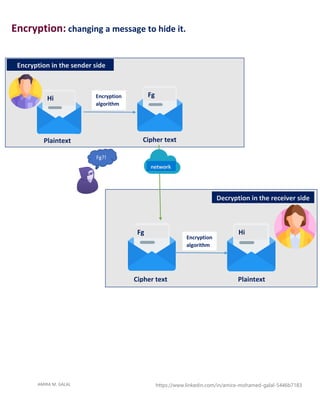
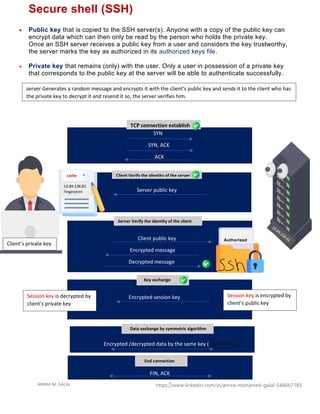
The document discusses secure shell (SSH) and methods for remotely accessing network devices. It explains that SSH uses encryption to securely connect to devices, protecting usernames, passwords, and data from being sent in plaintext like telnet. It provides details on how SSH implements encryption using asymmetric and symmetric encryption algorithms like RSA to encrypt the session key exchange and AES for data transmission. Configuration steps are also provided to set up and enable SSH access on network devices.