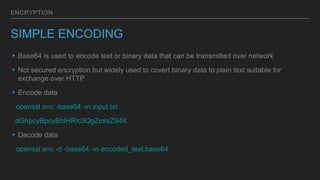
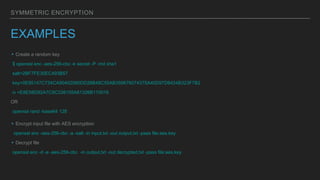
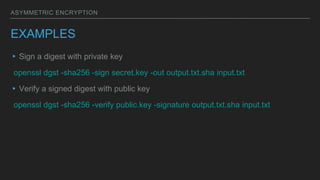
SSL/TLS encryption ensures secure communication between a client and server by encrypting all data transmitted. It works by having the client and server exchange certificates and generate a symmetric key to encrypt their connection, protecting against eavesdropping and impersonation. There are different types of encryption, including symmetric encryption which uses a single shared key, and asymmetric encryption which uses public/private key pairs to securely transmit data over untrusted networks. Cryptographic hashes and digital certificates signed by certificate authorities also help ensure the integrity and identity of data.