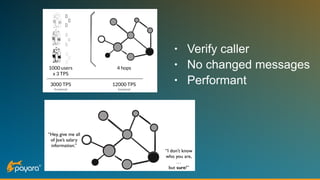
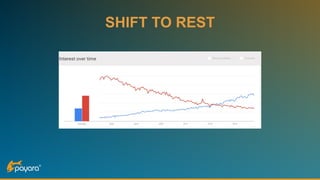
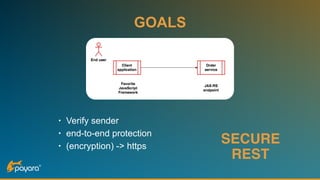
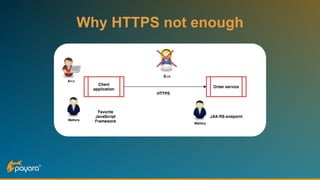
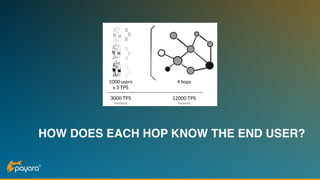
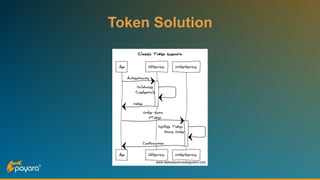
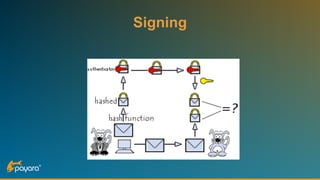
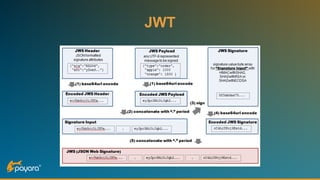
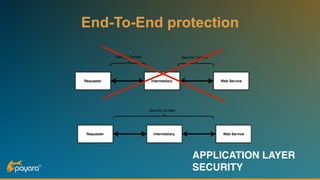
The document discusses security features in JAX-RS for RESTful web services, highlighting that while HTTPS provides confidentiality and integrity, it lacks sender verification and end-to-end protection. It also introduces the use of JWTs for authentication and authorization, and suggests implementing HTTP signatures for content protection. Key takeaways include the need for additional security measures beyond SSL to ensure comprehensive protection in REST architectures.